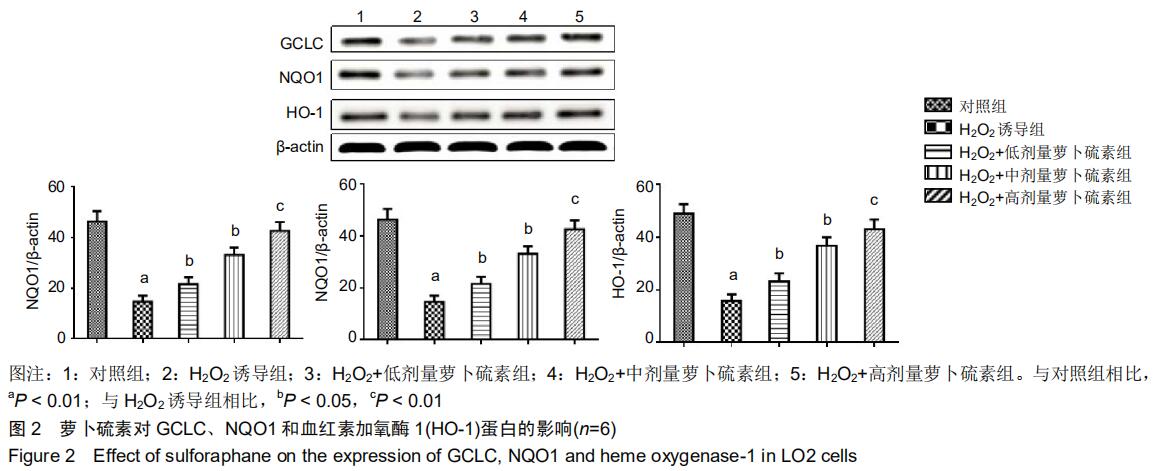
|
[1] HEIDARI R, NIKNAHAD H, SADEGHI A, et al. Betaine treatment protects liver through regulating mitochondrial function and counteracting oxidative stress in acute and chronic animal models of hepatic injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;103:75-86.
[2] SHINTO S, MATSUOKA Y, YAMATO M, et al. Antioxidant nitroxides protect hepatic cells from oxidative stress-induced cell death. J Clin Biochem Nutr.2018;62(2):132-138.
[3] HU J, CHENG P, HUANG GY, et al. Effects of Xin-Ji-Er-Kang on heart failure induced by myocardial infarction: Role of inflammation, oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction. Phytomedicine.2018;42:245-257.
[4] ZHUANG Y, LI Y, LI X, et al. Atg7 knockdown augments concanavalin a-induced acute hepatitis through an ROS-mediated p38/MAPK pathway. PLoS One.2016;11(3): e0149754.
[5] CHEN XQ, WU SH, ZHOU Y, et al. Lipoxin A4-induced heme oxygenase-1 protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/ reoxygenation injury via p38 MAPK activation and Nrf2/ARE complex. PLoS One.2013;8(6):e67120.
[6] ZHANG Z, WANG S, ZHOU S, et al. Sulforaphane prevents the development of cardiomyopathy in type 2 diabetic mice probably by reversing oxidative stress-induced inhibition of LKB1/AMPK pathway.J Mol Cell Cardiol.2014; 77:42-52.
[7] SHEN B, WANG W, MA L, et al. RETRACTED: Sulforaphane restores oxidative stress induced by di-N-butylphthalate in testicular Leydig cells with low basal reactive oxygen species levels. Urology.2014; 84(4):850-856.
[8] ROBERTS RA, SMITH RA, SAFE S, et al. Toxicological and pathophysiological roles of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Toxicology.2010;276(2):85-94.
[9] KLAUNIG JE, KAMENDULIS LM, HOCEVAR BA. Oxidative stress and oxidative damage in carcinogenesis.Toxicol Pathol. 2010;38(1):96-109.
[10] SIES H. Role of metabolic H2O2 generation: redox signaling and oxidative stress.J Biol Chem.2014; 289(13):8735-8741.
[11] 覃正碧,毛卫林.萝卜硫素对肾小管上皮细胞氧化应激及Nrf2/ HO -1信号通路的影响[J].中国药师,2017,20(5):809-812.
[12] VANDUCHOVA A, TOMANKOVA V, ANZENBACHER P, et al. Influence of sulforaphane metabolites on activities of human drug-metabolizing cytochrome P450 and determination of sulforaphane in human liver cells. J Med Food. 2016;19(12): 1141-1146.
[13] AXELSSON AS, TUBBS E, MECHAM B, et al. Sulforaphane reduces hepatic glucose production and improves glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Sci Transl Med.2017; 9(394): 116-124.
[14] WANG W, HE Y, YU G, et al. Sulforaphane Protects the liver against cdSe quantum dot-induced cytotoxicity. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0138771.
[15] SUN B, ZHANG X,YIN Y, et al. Effects of sulforaphane and vitamin E on cognitive disorder and oxidative damage in lead-exposed mice hippocampus at lactation. J Trace Elem Med Biol.2017;44(3):88-92.
[16] CHI X, ZHANG R, SHEN N, et al. Sulforaphane reduces apoptosis and oncosis along with protecting liver injury-induced ischemic reperfusion by activating the Nrf2/ARE pathway.Hepatol Int.2015; 9(2):321-329.
[17] LEONARDUZZI G, SOTTERO B, POLI G. Targeting tissue oxidative damage by means of eell signaling modulators:the an-tioxidant concept revisited. Pharmaeol Ther.2010;128: 336-374.
[18] ABED DA, GOLDSTEIN M, ALBANYAN H, et al. Discovery of direct inhibitors of Keap1-Nrf2 protein-protein interaction as potential therapeutic and preventive agents. Acta Pharm Sin B.2015;5(4):285-299.
[19] GREANEY AJ,MAIER NK,LEPPLA SH,et al.Sulforaphane inhibits multiple inflammasomes through an Nrf2-independent mechanism. J Leukoc Biol.2016; 99(1): 189-199.
[20] RUSSO M, SPAGNUOLO C, RUSSO GL, et al. Nrf2 targeting by sulforaphane: A potential therapy for cancer treatment. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr.2018; 58(8):1391-1405.
[21] BELLEZZA I,GIAMBANCO I,MINELLI A, et al. Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res.2018;1865(5):721-733.
[22] MURAKAMI S, MOTOHASHI H. Roles of Nrf2 in cell proliferation and differentiation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015; 88(Pt B):168-178.
[23] DONG W, YANG B, WANG L, et al. Curcumin plays neuroprotective roles against traumatic brain injury partly via Nrf2 signaling. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.2018;3346:28-36.
[24] ZHANG Z,QU J,ZHENG C,et al.Nrf2 antioxidant pathway suppresses Numb-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition during pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Death Dis.2018; 9(2):83-91.
[25] LOBODA A, DAMULEWICZ M, PYZA E, et al. Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative stress response and diseases: an evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci.2016;73(17):3221-3247.
[26] KUBO E, CHHUNCHHA B, SINGH P, et al. Sulforaphane reactivates cellular antioxidant defense by inducing Nrf2/ARE/Prdx6 activity during aging and oxidative stress. Sci Rep.2017;7(1):141-150.
|