| [1] 倪国华,张璟,郑风田. 中国肥胖流行的现状与趋势[J]. 中国食物与营养, 2013,19(10): 70-74.[2] Bray GA, Kim KK, Wilding JPH; World Obesity Federation. Obesity: a chronic relapsing progressive disease process. A position statement of the World Obesity Federation. Obes Rev.2017;18(7): 715-723. [3] Ashish KK, Neha D. Drug treatment of obesity: Current status and future prospects. Eur J Intern Med. 2015;26(2):89-94.[4] Mitchell NS, Catenacci VA, Wyatt HR, et al. Obesity: overview of an epidemic. Psychiatr Clin North Am.2011; 34(4): 717-732.[5] Whaley-Connell A, Sowers JR. Obesity and kidney disease: from population to basic science and the search for new therapeutic targets. Kidney Int.2017;92(2): 313-323.[6] Kilov D, Kilov G. Philosophical determinants of obesity as a disease. Obes Rev.2018;19(1): 41-48.[7] Guglielmo D, Hootman JM, Murphy LB, et al. Health Care Provider Counseling for Weight Loss Among Adults with Arthritis and Overweight or Obesity - United States, 2002-2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep.2018;67(17): 485-490. [8] Wolfe BM, Kvach E, Eckel RH. Treatment of Obesity: Weight Loss and Bariatric Surgery. Circ Res.2016;118(11): 1844-1855. [9] Chin SH, Kahathuduwa CN, Binks M. Physical activity and obesity: what we know and what we need to know. Obes Rev.2016;17(12): 1226-1244. [10] Bae JY, Woo J, Roh HT, et al. The effects of detraining and training on adipose tissue lipid droplet in obese mice after chronic high-fat diet. Lipids Health Dis.2017;16(1):13.[11] Chiu CH, Ko MC, Wu LS, et al. Benefits of different intensity of aerobic exercise in modulating body composition among obese young adults: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Health Qual Life Outcomes.2017;15(1):168.[12] Marques CM, Motta VF, Torres TS, et al. Beneficial effects of exercise training (treadmill) on insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in high-fat fed C57BL/6 mice. Braz J Med Biol Res.2010;43(5):467-475.[13] Strasser B. Physical activity in obesity and metabolic syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci.2013;1281:141-159.[14] Lefterova MI, Haakonsson AK,Lazar MA, et al. PPARγ and the global map of adipogenesis and beyond. Trends Endocrinol. Metab.2014;25(6): 293-302.[15] Zhang Y, Li H. Three important transcription factors related to lipogenesis and adipogenesis in mam mal. J Northeast Agric Univ.2010;17(3):62-75.[16] Issemann I, Green S. Activation of a number of steroid receptor superfamily by peroxisome proliferators. Nature.1990;347 (6294): 645-650.[17] Ahmadian M, Suh Jm, Han N, et al. PPARγ Signaling and Metabolism: The Good, the Bad and Future. Nat Med. 2013;19(5): 557-566.[18] Picard F, A uwerx J. PPARγ AND GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS. Annu Rev Nutr.2002;22:167- 97.[19] de la Rosa Rodriguez MA, Kersten S. Regulation of lipid droplet-associated proteins by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids.2017;1862(10 Pt B): 1212-1220.[20] Huang B, Yuan HD, Kim DY, et al. Cinnamaldehyde prevents adipocyte differentiation and adipogenesis via regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) and AMP-activated proteinkinase (AMPK) pathways. J Agric Food Chem.2011;59(8): 3666-3673.[21] Lefterova MI, Haakonsson AK, Lazar MA, et al. PPARγ and the global map of adipogenesis and beyond. Trends Endocrinol Metab.2014;25(6): 293-302.[22] Rosen ED, Spiegelman BM. PPARγ: a Nuclear Regulator of Metabolism, Differentiation, and Cell Growth. J Biol Chem.2001; 276(41):37731-37734.[23] Lee JE, Ge K. Transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of PPARγ expression during adipogenesis. Cell Biosci. 2014;4:29.[24] Li P, Song Y, Zan W, et al. Lack of CUL4B in Adipocytes Promotes PPARγ-Mediated Adipose Tissue Expansion and Insulin Sensitivity. Diabetes.2017;66(2): 300-313. [25] Gross B, Pawlak M, Lefebvre P, et al. PPARs in obesity-induced T2DM, dyslipidaemia and NAFLD. Nat Rev Endocrinol.2017;13(1): 36-49.[26] Barak Y, Nelson MC, Ong ES, et al. PPARγ is required for placental, cardiac, and adipose tissue development. Mol Cell.1999;4(4): 585-595.[27] Wang F, Mullican SE, DiSpirito JR, et al. Lipoatrophy and severe metabolic disturbance in mice with fat-specific deletion of PPARγ. Proc Natl Acad Sci.2013;110(46): 18656-18661.[28] Akyürek N, Aycan Z, Çetinkaya S, et al. Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor (PPAR)-gamma concentrations in childhood obesity. Scand J Clin Lab Invest.2013;73(4): 355-360. [29] Ruschke K, Fishbein L, Dietrich A, et al. Gene expression of PPARgamma and PGC-1alpha in human omental and subcutaneous adiposetissues is related to insulin resistance markers and mediates beneficial effects of physical training. Eur J Endocrinol.2010;162(3): 515-23.[30] 夏书宇.不同强度跑台运动对高脂饮食大鼠脂肪组织PPARγ/脂联素/ TNF-αmRNA的影响[J]. 成都体育学院学报, 2015, 41(3): 98-102.[31] Chandler PC, Viana JB, Oswald KD, et al.Feeding response to melanocortin agonist predicts preference for and obesity from a high-fat diet.Physiol Behav.2005;85(02): 221-230.[32] Bedford, Toby G, Charles M, et al. Maximum oxygen consumption of rats and its changes with various experimental procedures[J]. J Appl Physiol, 1979, 47(6): 1278-1283.[33] Kus V, Prazak T, Brauner P, et al. Induction of muscle thermogenesis by high-fat diet in mice: association with obesity-resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.2008; 295(2): E356-E367.[34] Gollisch KS, Brandauer J, Jessen N, et al. Effects of exercise training on subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue in normal-and high-fat diet-fed rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.2009;297: E495-E504.[35] Chen N, Lei T, Xin L, et al. Depot-specific effects of treadmill running and rutin on white adipose tissue fuction in diet-induced obese mice. J Physiol Biochem.2016;72(3): 453-467.[36] Kawamura T, Yoshida K, Sugawara A, et al. Regulation of skeletal muscle peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma expression by exercise and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in fructose-fed hypertensive rats. Hypertens Res.2004;27(1):61-70.[37] 杨星雅,李鹏飞,房国梁,等.有氧和抗阻运动对大鼠白色脂肪棕色化的作用[J].体育科学, 2017, 37(6): 69-74.[38] 李萌,柏友萍,崔建飞,等.不同强度运动处方对青春期肥胖大鼠PPARγ及相关指标的影响[J].卫生研究,2014,43(5):732-737.[39] 刘长金,刘磊,柯大智,等.高果糖引起的脂肪肝大鼠肾脏脂质合成相关基因和蛋白的表达[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2014,36(4): 446-454.[40] 罗祖纯,戴霞,张泰辉,等.有氧、抗阻运动对糖尿病前期人群血清胰高血糖素样肽1、血糖水平的影响[J].山东医药,2017,57(2): 18-21.[41] Hasan AU, Ohmori K, Hashimoto T, et al. PPARγ activation mitigates glucocorticoid receptor-induced excessive lipolysis in adipocytes via homeostatic crosstalk. J Cell Biochem.2018; 119(6): 4627-4635.[42] Engin A. Fat Cell and Fatty Acid Turnover in Obesity[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol.2017;960:135-160. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ(peroxisome proliferators-activated receptors,PPARγ):是重要的指标分子。PPARγ于1990年被发现,属于核内激素受体超家族,其表达范围较广,在脂肪细胞、巨噬细胞、心肌细胞和内皮细胞均有表达,PPARγ在脂肪细胞的生成分化、糖脂代谢等方面发挥着重要的生理作用,并且研究发现PPARγ是脂肪分化调控的关键因子,其他转录调控因子必须在PPARγ存在的条件下才能进行脂肪细胞的分化过程。
白色脂肪(white adipose):是人体内脂肪组织的一种,和褐色脂肪相对应,主要功能就是把多余的脂肪存储在体内,最新研究表明受基因控制,可以抑制白色脂肪的形成,从而治疗肥胖症。
文题释义:
过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ(peroxisome proliferators-activated receptors,PPARγ):是重要的指标分子。PPARγ于1990年被发现,属于核内激素受体超家族,其表达范围较广,在脂肪细胞、巨噬细胞、心肌细胞和内皮细胞均有表达,PPARγ在脂肪细胞的生成分化、糖脂代谢等方面发挥着重要的生理作用,并且研究发现PPARγ是脂肪分化调控的关键因子,其他转录调控因子必须在PPARγ存在的条件下才能进行脂肪细胞的分化过程。
白色脂肪(white adipose):是人体内脂肪组织的一种,和褐色脂肪相对应,主要功能就是把多余的脂肪存储在体内,最新研究表明受基因控制,可以抑制白色脂肪的形成,从而治疗肥胖症。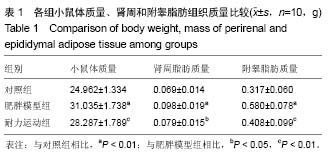
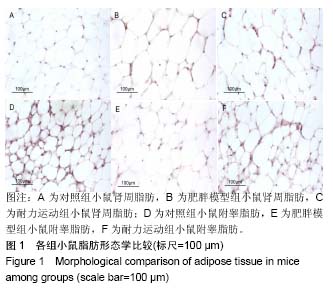
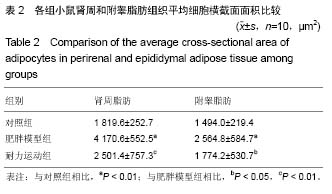
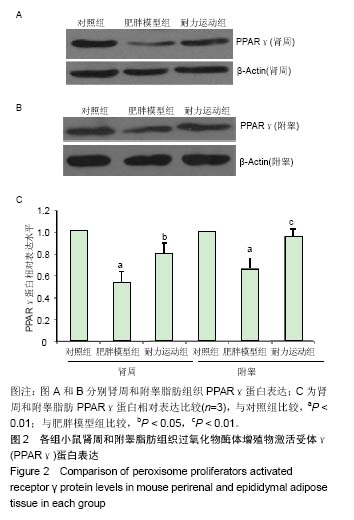
.jpg) 文题释义:
过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ(peroxisome proliferators-activated receptors,PPARγ):是重要的指标分子。PPARγ于1990年被发现,属于核内激素受体超家族,其表达范围较广,在脂肪细胞、巨噬细胞、心肌细胞和内皮细胞均有表达,PPARγ在脂肪细胞的生成分化、糖脂代谢等方面发挥着重要的生理作用,并且研究发现PPARγ是脂肪分化调控的关键因子,其他转录调控因子必须在PPARγ存在的条件下才能进行脂肪细胞的分化过程。
白色脂肪(white adipose):是人体内脂肪组织的一种,和褐色脂肪相对应,主要功能就是把多余的脂肪存储在体内,最新研究表明受基因控制,可以抑制白色脂肪的形成,从而治疗肥胖症。
文题释义:
过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ(peroxisome proliferators-activated receptors,PPARγ):是重要的指标分子。PPARγ于1990年被发现,属于核内激素受体超家族,其表达范围较广,在脂肪细胞、巨噬细胞、心肌细胞和内皮细胞均有表达,PPARγ在脂肪细胞的生成分化、糖脂代谢等方面发挥着重要的生理作用,并且研究发现PPARγ是脂肪分化调控的关键因子,其他转录调控因子必须在PPARγ存在的条件下才能进行脂肪细胞的分化过程。
白色脂肪(white adipose):是人体内脂肪组织的一种,和褐色脂肪相对应,主要功能就是把多余的脂肪存储在体内,最新研究表明受基因控制,可以抑制白色脂肪的形成,从而治疗肥胖症。