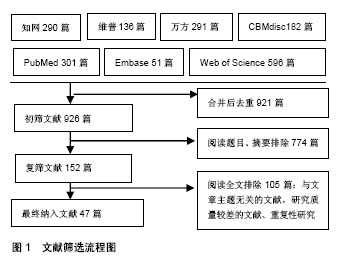
| [1] Schwab P, Lavand Homme P, Yombi JC, et al. Lower blood loss after unicompartmental than total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(12):3494-3500.[2] 石林,刘丙根,庞清江.人工关节置换术后关节周围假体真菌感染研究进展[J].中国感染与化疗杂志,2015,15(2):184-187.[3] Pivec R, Johnson AJ, Mears SC, et al. Hip arthroplasty. Lancet. 2012;380(9855):1768-1777. [4] 王俏杰,张先龙.人工髋关节置换术的现状与热点[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2015,9(6):718-724.[5] 李涛,翁习生.抗生素骨水泥在人工关节置换术后感染中应用研究的系统性综述[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2014,22(20):1868-1874.[6] Esposito S, Leone S, Bassetti M, et al. Italian guidelines for the diagnosis and infectious disease management of osteomyelitis and prosthetic joint infections in adults. Infection. 2009;37(6):478-496. [7] 张晓岗,曹力.人工全髋关节置换术后假体周围感染的处理[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2014,8(1):101-104.[8] 王常德,康鹏德,裴福兴,等.全关节置换术后假体周围感染诊断的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(10):907-910.[9] Corvec S, Portillo ME, Pasticci BM, et al. Epidemiology and new developments in the diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection. Int J Artif Organs. 2018;35(10):923-934. [10] Trampuz A, Perka C, Borens O. Gelenkprotheseninfektion: Neue Entwicklungen in der Diagnostik und Therapie. DMW. 2013; 138(31/32):1571-1573. [11] Parvizi J, Gehrke T, Chen AF. Proceedings of the international consensus on periprosthetic joint infection. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(11):1450-1452. [12] Osmon DR, Berbari EF, Berendt AR, et al. Executive summary: diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56(1):1-10. [13] 赵建宁,曾晓峰,王与荣,等.全髋关节置换术后感染的处理[J].医学研究生学报,2002,15(3):250-251.[14] Chang WH, Wang CH, Yang SY, et al. Rapid isolation and diagnosis of live bacteria from human joint fluids by using an integrated microfluidic system. Lab Chip. 2014;14(17):3376-3384. [15] Trampuz A, Zimmerli W. Prosthetic joint infections: update in diagnosis and treatment Swiss Med Wkly. 2005;135(17-18): 243-251. [16] Maradit KH, Schleck CD, Lewallen EA, et al. Diabetes mellitus and hyperglycemia and the risk of aseptic loosening in total joint arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(9S):S251-S253. [17] Nielen JT, Emans PJ, Dagnelie PC, et al. Severity of diabetes mellitus and total hip or knee replacement: a population-based case-control study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(20):e3739. [18] Meding JB, Reddleman K, Keating ME, et al. Total knee replacement in patients with diabetes mellitus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;(416):208-216. [19] Burnett RS, Kelly MA, Hanssen AD, et al. Technique and timing of two-stage exchange for infection in TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;464:164-178. [20] 张宁,赵翔,周鑫叠,等.关节液与组织培养在髋膝关节置换术后感染诊断价值的Meta分析[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2014,8(1): 72-76.[21] Hindle P, Davidson E, Biant LC. Septic arthritis of the knee: the use and effect of antibiotics prior to diagnostic aspiration. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2012;94(5):351-355. [22] Chaudhary G, Lee JD. Neurologic complications of infective endocarditis. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2013;13(10):380. [23] 王东伟,郑大伟,翟晓慧,等.人工关节置换术后感染病原菌分布与耐药性分析[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2015,25(19):4415-4417.[24] 高川渤,袁绍辉.人工关节置换术后感染病原菌谱的临床意义[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2015,4(4):319-323.[25] Tsai J, Sheng W, Lo W, et al. Clinical characteristics, microbiology, and outcomes of prosthetic joint infection in Taiwan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2015;48(2):198-204. [26] Sendi P, Zimmerli W. Challenges in periprosthetic knee-joint infection. Int J Artif Organs. 2011;34(9):947-956. [27] Zimmerli W, Trampuz A, Ochsner PE. Prosthetic-joint infections. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(16):1645-1654. [28] Mahmoud SS, Sukeik M, Alazzawi S, et al. Salvage procedures for management of prosthetic joint infection after hip and knee replacements. Open Orthop J. 2016;10:600-614. [29] 万永鲜,张忠杰,陈歌,等.关节置换术后假体周围感染早期诊断与治疗的临床研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015,30(10):1117-1118.[30] Wang KH, Yu SW, Iorio R, et al. Long term treatment results for deep infections of total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2015; 30(9):1623-1628. [31] Kim JH, Chun SK, Yoon YC, et al. Efficacy of debridement for early periprosthetic joint infection after hip arthroplasty. Hip Pelvis. 2014;26(4):227-234. [32] Sia IG, Berbari EF, Karchmer AW. Prosthetic joint infections. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2005;19(4):885-914. [33] Vlahakis NE, Temesgen Z, Berbari EF, et al. Osteoarticular infection complicating enterococcal endocarditis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2003;78(5):623-628. [34] Marculescu CE, Berbari EF, Hanssen AD, et al. Outcome of prosthetic joint infections treated with debridement and retention of components. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42(4):471-478. [35] Zimmerli W, Trampuz A, Ochsner PE. Prosthetic-joint infections. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(16):1645-1654. [36] Zeller V, Lhotellier L, Marmor S, et al. One-stage exchange arthroplasty for chronic periprosthetic hip infection: results of a large prospective cohort study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014; 96(1):e1. [37] Zheng H, Barnett AG, Merollini K, et al. Control strategies to prevent total hip replacement-related infections: a systematic review and mixed treatment comparison. BMJ Open. 2014; 4(3):e3978. [38] Saginur R, Stdenis M, Ferris W, et al. Multiple combination bactericidal testing of staphylococcal biofilms from implant-associated infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50(1):55-61. [39] Jacqueline C, Caillon J. Impact of bacterial biofilm on the treatment of prosthetic joint infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014;69 Suppl 1:i37-i40. [40] Tornero E, Morata L, Martinez-Pastor JC, et al. Importance of selection and duration of antibiotic regimen in prosthetic joint infections treated with debridement and implant retention. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016;71(5):1395-1401. [41] Bejon P, Berendt A, Atkins BL, et al. Two-stage revision for prosthetic joint infection: predictors of outcome and the role of reimplantation microbiology. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010; 65(3):569-575. [42] Lockhart PB, Garvin KL, Osmon DR, et al. The antibiotic prophylaxis guideline for prosthetic joints: trying to do the right thing. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2013;21(3):193-194. [43] Berbari EF, Marculescu C, Sia I, et al. Culture-negative prosthetic joint infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45(9):1113-1119. [44] Bernard L, Legout L, Zurcher-Pfund L, et al. Six weeks of antibiotic treatment is sufficient following surgery for septic arthroplasty. J Infect. 2010;61(2):125-132. [45] 唐淼,汤瑞新,周烨,等.利福平联合用药结合保留假体清创术治疗人工关节初期感染[J].实用骨科杂志,2017,23(7):593-596.[46] Keller SC, Cosgrove SE, Higgins Y, et al. Role of suppressive oral antibiotics in orthopedic hardware infections for those not undergoing two-stage replacement surgery. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2016;3(4):w176. [47] Matthews PC, Berendt AR, Mcnally MA, et al. Diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection. BMJ. 2009;338:b1773. |
.jpg)

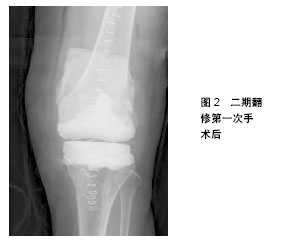
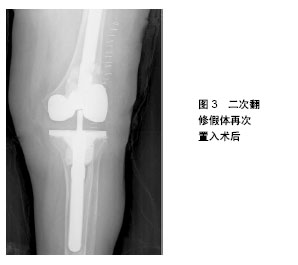
.jpg)