中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (11): 1669-1673.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0950
• 口腔组织构建 oral tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
牙周炎大鼠正畸牙移动过程中基质金属蛋白酶7在牙周组织中的表达
刘 红,王 毅,张 勤
- (新疆医科大学附属中医医院口腔科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830000)
Expression of matrix metalloproteinase 7 in the periodontium during orthodontic tooth movement in rats with periodontitis
Liu Hong, Wang Yi, Zhang Qin
- (Department of Stomatology, the Affiliated Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
基质金属蛋白酶7:在基质金属蛋白酶家族中虽然分子质量最小,但却属于蛋白水解酶活性最强的成员,在体内分布广泛,主要作用是降解Ⅳ型胶原、促进炎症细胞迁移和降解基底酶。研究发现,基质金属蛋白酶7 在牙周炎患者的龈沟液中表达量较高,但其能否作为反映牙周炎的指标还需进一步研究。
正畸:简单的说,矫正牙齿、解除错牙合畸形的科学就是正畸。正畸主要研究错牙合 畸形是什么表现,分哪些类型,这些错牙合 都是什么原因导致的,如何确诊,如何更有效地矫治。口腔正畸学的英文名称来源于三个希腊词根的组合,它们的意思分别是“牙齿”“矫正”“学科”,即大家所说的“矫正牙齿”。但随着这门学科的发展,已不仅仅局限于排齐牙齿,还涉及解决颌骨、颅面的不协调,从而达到面部整体的和谐美。
文题释义:
基质金属蛋白酶7:在基质金属蛋白酶家族中虽然分子质量最小,但却属于蛋白水解酶活性最强的成员,在体内分布广泛,主要作用是降解Ⅳ型胶原、促进炎症细胞迁移和降解基底酶。研究发现,基质金属蛋白酶7 在牙周炎患者的龈沟液中表达量较高,但其能否作为反映牙周炎的指标还需进一步研究。
正畸:简单的说,矫正牙齿、解除错牙合畸形的科学就是正畸。正畸主要研究错牙合 畸形是什么表现,分哪些类型,这些错牙合 都是什么原因导致的,如何确诊,如何更有效地矫治。口腔正畸学的英文名称来源于三个希腊词根的组合,它们的意思分别是“牙齿”“矫正”“学科”,即大家所说的“矫正牙齿”。但随着这门学科的发展,已不仅仅局限于排齐牙齿,还涉及解决颌骨、颅面的不协调,从而达到面部整体的和谐美。
.jpg) 文题释义:
基质金属蛋白酶7:在基质金属蛋白酶家族中虽然分子质量最小,但却属于蛋白水解酶活性最强的成员,在体内分布广泛,主要作用是降解Ⅳ型胶原、促进炎症细胞迁移和降解基底酶。研究发现,基质金属蛋白酶7 在牙周炎患者的龈沟液中表达量较高,但其能否作为反映牙周炎的指标还需进一步研究。
正畸:简单的说,矫正牙齿、解除错牙合畸形的科学就是正畸。正畸主要研究错牙合 畸形是什么表现,分哪些类型,这些错牙合 都是什么原因导致的,如何确诊,如何更有效地矫治。口腔正畸学的英文名称来源于三个希腊词根的组合,它们的意思分别是“牙齿”“矫正”“学科”,即大家所说的“矫正牙齿”。但随着这门学科的发展,已不仅仅局限于排齐牙齿,还涉及解决颌骨、颅面的不协调,从而达到面部整体的和谐美。
文题释义:
基质金属蛋白酶7:在基质金属蛋白酶家族中虽然分子质量最小,但却属于蛋白水解酶活性最强的成员,在体内分布广泛,主要作用是降解Ⅳ型胶原、促进炎症细胞迁移和降解基底酶。研究发现,基质金属蛋白酶7 在牙周炎患者的龈沟液中表达量较高,但其能否作为反映牙周炎的指标还需进一步研究。
正畸:简单的说,矫正牙齿、解除错牙合畸形的科学就是正畸。正畸主要研究错牙合 畸形是什么表现,分哪些类型,这些错牙合 都是什么原因导致的,如何确诊,如何更有效地矫治。口腔正畸学的英文名称来源于三个希腊词根的组合,它们的意思分别是“牙齿”“矫正”“学科”,即大家所说的“矫正牙齿”。但随着这门学科的发展,已不仅仅局限于排齐牙齿,还涉及解决颌骨、颅面的不协调,从而达到面部整体的和谐美。摘要
背景:基质金属蛋白酶7主要功能是降解Ⅳ型胶原、弹力蛋白、蛋白聚糖以及纤维粘连蛋白,研究提示其可能参与了牙周炎的组织破坏过程。
目的:观察牙周炎大鼠在正畸力刺激下基质金属蛋白酶7在牙周组织中的表达。
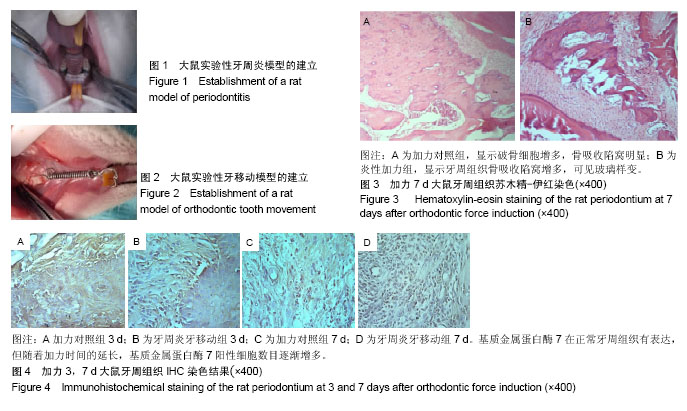
方法:实验选用60只8周龄左右的健康雄性SD大鼠,随机分为加力对照组和牙周炎牙移动组,建立牙周炎牙移动动物模型,分别在加力0,1,3,7,14,21 d处死大鼠,采用苏木精-伊红染色和免疫组织化学法研究牙周炎大鼠牙齿受力的不同阶段牙周组织中基质金属蛋白酶7表达和分布变化。
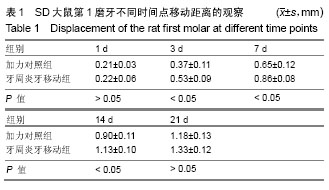
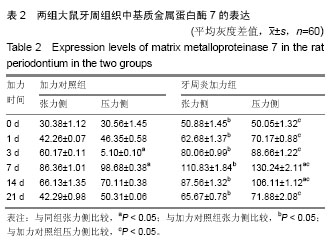
结果与结论:①基质金属蛋白酶7阳性表达主要定位于上皮细胞和巨噬细胞的胞浆中,呈棕黄色。基质金属蛋白酶7在正常组织有表达,随着加力时间的延长,基质金属蛋白酶7阳性细胞数目逐渐增多,加力对照组和牙周炎加力组大鼠牙周组织内基质金属蛋白酶7的表达均在受力后7 d达到高峰,之后开始下降;②0-14 d牙周炎加力组大鼠张力侧、压力侧牙周组织中基质金属蛋白酶7的表达均显著高于加力对照组(P < 0.05);3,7 d加力对照组张力侧基质金属蛋白酶7的表达显著高于压力侧(P < 0.05);3,7 d牙周炎加力组张力侧基质金属蛋白酶7的表达显著高于压力侧(P < 0.05);③结果表明,基质金属蛋白酶7作为牙周组织中的局部调控因子参与了正畸牙周组织的改建过程,正畸力和牙周炎均可导致基质金属蛋白酶7的表达增高。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-7831-5892(刘红)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
基质金属蛋白酶7:在基质金属蛋白酶家族中虽然分子质量最小,但却属于蛋白水解酶活性最强的成员,在体内分布广泛,主要作用是降解Ⅳ型胶原、促进炎症细胞迁移和降解基底酶。研究发现,基质金属蛋白酶7 在牙周炎患者的龈沟液中表达量较高,但其能否作为反映牙周炎的指标还需进一步研究。
正畸:简单的说,矫正牙齿、解除错牙合畸形的科学就是正畸。正畸主要研究错牙合 畸形是什么表现,分哪些类型,这些错牙合 都是什么原因导致的,如何确诊,如何更有效地矫治。口腔正畸学的英文名称来源于三个希腊词根的组合,它们的意思分别是“牙齿”“矫正”“学科”,即大家所说的“矫正牙齿”。但随着这门学科的发展,已不仅仅局限于排齐牙齿,还涉及解决颌骨、颅面的不协调,从而达到面部整体的和谐美。
文题释义:
基质金属蛋白酶7:在基质金属蛋白酶家族中虽然分子质量最小,但却属于蛋白水解酶活性最强的成员,在体内分布广泛,主要作用是降解Ⅳ型胶原、促进炎症细胞迁移和降解基底酶。研究发现,基质金属蛋白酶7 在牙周炎患者的龈沟液中表达量较高,但其能否作为反映牙周炎的指标还需进一步研究。
正畸:简单的说,矫正牙齿、解除错牙合畸形的科学就是正畸。正畸主要研究错牙合 畸形是什么表现,分哪些类型,这些错牙合 都是什么原因导致的,如何确诊,如何更有效地矫治。口腔正畸学的英文名称来源于三个希腊词根的组合,它们的意思分别是“牙齿”“矫正”“学科”,即大家所说的“矫正牙齿”。但随着这门学科的发展,已不仅仅局限于排齐牙齿,还涉及解决颌骨、颅面的不协调,从而达到面部整体的和谐美。