| [1] Martel-Pelletier J, Barr AJ, Cicuttini FM, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16072 [2] 吕苏梅,张瑞丽. 中老年膝骨关节炎的流行病学研究进展[J].中国老年学, 2016, 36(16):4133-4135.[3] Litwic A, Edwards MH, Dennison EM, et al. Epidemiology and burden of osteoarthritis. Br Med Bull. 2013;105:185-199.[4] 卢宏伟,罗飞,侯天勇,等. 硫酸氨基葡萄糖联合非甾体抗炎药在轻中度膝骨关节炎中的作用[J].中国医药导报, 2016, 13(17):137-139.[5] 张晨,马骏,党晓谦,等. 非甾体抗炎药治疗骨关节炎的研究进展[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2017,11(2):66-69.[6] Wen Y, Li J, Wang L, et al. Udp-glucose dehydrogenase modulates proteoglycan synthesis in articular chondrocytes: Its possible involvement and regulation in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(6):484.[7] 马妮. 针灸治疗膝骨关节炎近十年研究进展及贺氏火针治疗的初步疗效观察[J].北京中医药大学学报, 2014,17(22):485-487.[8] 刘骏达, 吴明霞.从血液流变学探讨瘀血阻滞型膝骨性关节炎的针灸治疗[J].亚太传统医药, 2017, 13(8):59-62.[9] 张婧怡,陈卫东,刘玉蕊,等. 火针疗法的源流及现代应用[J].亚太传统医药, 2016, 12(3):42-44.[10] 黄昌锦,黄应杰,陈楚云.火针疗法的发展源流[J].中国针灸,2013, 33(5):455-458.[11] 曾红文,聂斌, 史琳琳. 刺血合火针点刺治疗膝关节骨性关节炎疗效观察[J].中国针灸, 2008, 28(7):493-495.[12] 王立兴.火针结合电针治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的临床研究[D].广州中医药大学, 2016.[13] 毛雪文,王世广,王桂玲,等. 贺氏火针刺骨法治疗膝骨性关节炎80例疗效观察[J].中医临床研究, 2016, 8(35):20-23.[14] 林国华, 李万瑶, 苏国龙. 火针对实验性小鼠膝骨关节炎关节软骨病理改变的影响[J].广州中医药大学学报, 2005, 22(5):373-376.[15] Lu W, Wang L, Wo C, et al. Ketamine attenuates osteoarthritis of the knee via modulation of inflammatory responses in a rabbit model. Mol Med Rep. 2016; 13(6):5013-5020.[16] Ogura N, Tobe M, Sakamaki H, et al. Interleukin-1 beta induces interleukin-6 mrna expression and protein production in synovial cells from human temporomandibular joint. J Oral Pathol Med. 2002;31(6): 353-360.[17] Krajewska-Wlodarczyk M, Owczarczyk-Saczonek A, Placek W, et al. Articular cartilage aging-potential regenerative capacities of cell manipulation and stem cell therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(2). pii: E623. [18] Yu D, Xu J, Liu F, et al. Subchondral bone changes and the impacts on joint pain and articular cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016;34(5):929-934.[19] 雷鸣,于斐,肖德明.骨关节炎临床表现特点及沉默信息调节因子1在其发病中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017, 21(12):1933-1939.[20] 王昌盛,杨海涛,邓茗中,等. 膝关节骨关节炎软骨下水肿与MRI及临床表现的相关性研究[J].实用放射学杂志, 2017, 33(8): 1236-1240.[21] Huang H, Zheng J, Shen N, et al. Identification of pathways and genes associated with synovitis in osteoarthritis using bioinformatics analyses. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):10050.[22] Mathiessen A, Conaghan PG. Synovitis in osteoarthritis: Current understanding with therapeutic implications. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):18. [23] Ma CH, Lv Q, Cao Y, et al. Genes relevant with osteoarthritis by comparison gene expression profiles of synovial membrane of osteoarthritis patients at different stages. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18(3):431-439.[24] 葛伟韬,高云,刘珍珠,等. 膝骨关节炎中医病名辨识[J].中医杂志, 2016,57(23):1989-1992.[25] 吴玖斌,李蒙,谢雁鸣,等. 膝关节骨性关节炎当代中医学术团队研究[J].北京中医药大学学报, 2016, 39(6):516-519.[26] 刘源,郭艳幸,郭珈宜,等. 膝骨关节炎的中医诊疗进展[J].亚太传统医药, 2017, 13(1):56-59.[27] 刘保延.火针[M]. 北京:中医古籍出版社, 1994.[28] 李彬,谢新才,王麟鹏.火针治疗膝骨关节炎临床观察[J].北京中医药, 2011,30(12):923-925.[29] Blazek AD, Nam J, Gupta R, et al. Exercise-driven metabolic pathways in healthy cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(7):1210-1222.[30] Huang G, Chubinskaya S, Liao W, et al. Wnt5a induces catabolic signaling and matrix metalloproteinase production in human articular chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(9):1505-1515.[31] Sun MM, Beier F, Pest MA. Recent developments in emerging therapeutic targets of osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2017;29(1):96-102. [32] 高宁阳,曹月龙,刘婷,等. Wnt信号通路与骨关节炎[J].中国骨伤, 2010, 23(4):320-323.[33] 徐伟丽,牛玲玲,王文侠,等. 经典Wnt信号通路对骨代谢的调节作用[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2016, 22(3):376-380.[34] Bejsovec A. Wingless signaling: A genetic journey from morphogenesis to metastasis. Genetics. 2018,208(4):1311-1336.[35] Hui T, Zhou Y, Wang T, et al. Activation of beta-catenin signaling in aggrecan-expressing cells in temporomandibular joint causes osteoarthritis-like defects. Int J Oral Sci. 2018;10(2):13.[36] Kremer R, Gilsanz V. Fat and bone: An odd couple. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2016;6:190.[37] Zhou X, Li W, Jiang L, et al. Tetrandrine inhibits the wnt/ beta -catenin signalling pathway and alleviates osteoarthritis: An in vitro and in vivo study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:809579..[38] 史纪元,易智,刘宗智,等.不同程度骨关节炎中Wnt/β-catenin信号通路、OPN和MMP-13的相关性的研究[J].现代生物医学进展, 2017, 17(24):4639-4644.[39] Nguyen LT, Sharma AR, Chakraborty C, et al. Review of prospects of biological fluid biomarkers in osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(3). pii: E601. [40] Rose BJ, Kooyman DL. A tale of two joints: The role of matrix metalloproteases in cartilage biology. Dis Markers. 2016;2016: 4895050.[41] Murakami K, Maeda S, Yonezawa T, et al. Synovial fluid matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 activities in dogs suffering from joint disorders. J Vet Med Sci. 2016;78(6):1051-1054. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
Wnt信号通路:1982年在小鼠乳腺癌发现了Wnt基因,由于此基因激活依赖小鼠乳腺癌相关病毒基因的插入,因此,当时被命名为Int1基因,之后的研究表明,Int1基因在小鼠正常胚胎发育中起重要作用,相当于果蝇的无翅(Wingless)基因,可控制胚胎的轴向发育。此后大量研究提示了Int1基因在神经系统胚胎发育中的重要性,因此将Wingless与Int1结合,称为Wnt基因。人Wnt基因定位于12q13.在胚胎发育中,Wnt基因调控的重要信号传导系统即为Wnt通路。
火针:较为常见的一种针刺方法,该疗法汇集了毫针激发经气、火气温阳散寒的功效,可以直接刺激病灶的反应点,迅速消除或改善局部组织水肿、充血、渗出、粘连、钙化、挛缩、缺血等病理变化,从而加快循环、促进代谢,使受损组织和神经重新修复,治疗效果明显。
文题释义:
Wnt信号通路:1982年在小鼠乳腺癌发现了Wnt基因,由于此基因激活依赖小鼠乳腺癌相关病毒基因的插入,因此,当时被命名为Int1基因,之后的研究表明,Int1基因在小鼠正常胚胎发育中起重要作用,相当于果蝇的无翅(Wingless)基因,可控制胚胎的轴向发育。此后大量研究提示了Int1基因在神经系统胚胎发育中的重要性,因此将Wingless与Int1结合,称为Wnt基因。人Wnt基因定位于12q13.在胚胎发育中,Wnt基因调控的重要信号传导系统即为Wnt通路。
火针:较为常见的一种针刺方法,该疗法汇集了毫针激发经气、火气温阳散寒的功效,可以直接刺激病灶的反应点,迅速消除或改善局部组织水肿、充血、渗出、粘连、钙化、挛缩、缺血等病理变化,从而加快循环、促进代谢,使受损组织和神经重新修复,治疗效果明显。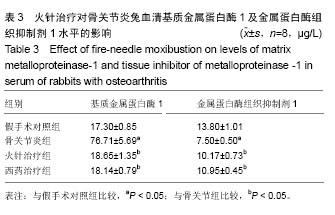
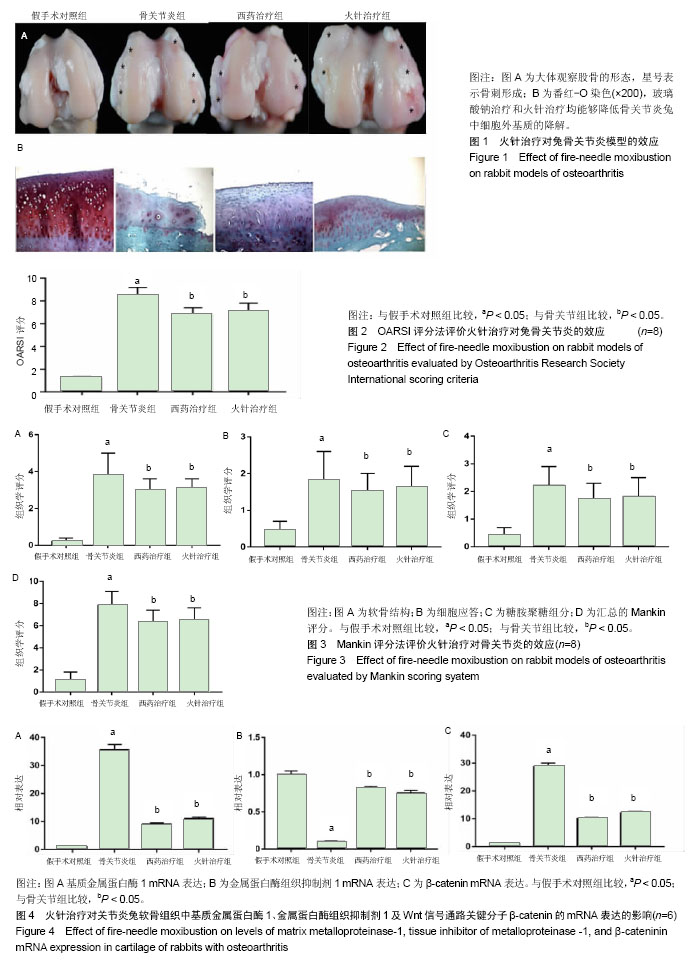
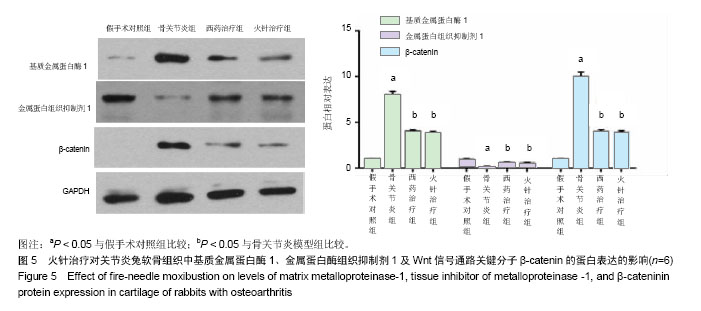
.jpg) 文题释义:
Wnt信号通路:1982年在小鼠乳腺癌发现了Wnt基因,由于此基因激活依赖小鼠乳腺癌相关病毒基因的插入,因此,当时被命名为Int1基因,之后的研究表明,Int1基因在小鼠正常胚胎发育中起重要作用,相当于果蝇的无翅(Wingless)基因,可控制胚胎的轴向发育。此后大量研究提示了Int1基因在神经系统胚胎发育中的重要性,因此将Wingless与Int1结合,称为Wnt基因。人Wnt基因定位于12q13.在胚胎发育中,Wnt基因调控的重要信号传导系统即为Wnt通路。
火针:较为常见的一种针刺方法,该疗法汇集了毫针激发经气、火气温阳散寒的功效,可以直接刺激病灶的反应点,迅速消除或改善局部组织水肿、充血、渗出、粘连、钙化、挛缩、缺血等病理变化,从而加快循环、促进代谢,使受损组织和神经重新修复,治疗效果明显。
文题释义:
Wnt信号通路:1982年在小鼠乳腺癌发现了Wnt基因,由于此基因激活依赖小鼠乳腺癌相关病毒基因的插入,因此,当时被命名为Int1基因,之后的研究表明,Int1基因在小鼠正常胚胎发育中起重要作用,相当于果蝇的无翅(Wingless)基因,可控制胚胎的轴向发育。此后大量研究提示了Int1基因在神经系统胚胎发育中的重要性,因此将Wingless与Int1结合,称为Wnt基因。人Wnt基因定位于12q13.在胚胎发育中,Wnt基因调控的重要信号传导系统即为Wnt通路。
火针:较为常见的一种针刺方法,该疗法汇集了毫针激发经气、火气温阳散寒的功效,可以直接刺激病灶的反应点,迅速消除或改善局部组织水肿、充血、渗出、粘连、钙化、挛缩、缺血等病理变化,从而加快循环、促进代谢,使受损组织和神经重新修复,治疗效果明显。