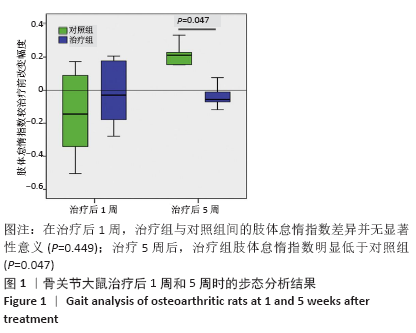
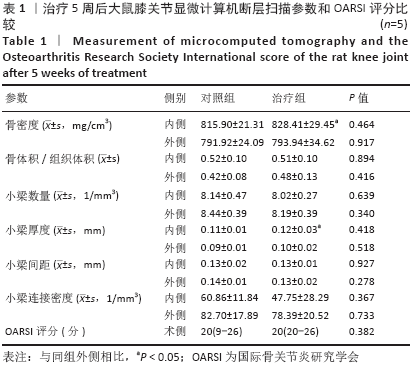
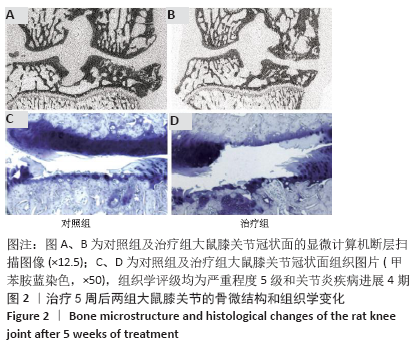
[1] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BARR AJ, CICUTTINI FM, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16072.
[2] VINA ER, KWOH CK. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: literature update. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2018;30(2):160-167.
[3] HUSSAIN SM, NEILLY DW, BALIGA S, et al. Knee osteoarthritis: a review of management options. Scott Med J. 2016;61(1):7-16.
[4] DRAGOS D, GILCA M, GAMAN L, et al. Phytomedicine in joint disorders. Nutrients. 2017;9(1):70.
[5] LI Y, YAO J, HAN C, et al. Quercetin, Inflammation and Immunity. Nutrients. 2016;8(3):167.
[6] BRITTI D, CRUPI R, IMPELLIZZERI D, et al. A novel composite formulation of palmitoylethanolamide and quercetin decreases inflammation and relieves pain in inflammatory and osteoarthritic pain models. BMC Vet Res. 2017;13(1):229.
[7] HART A, COTA A, MAKHDOM A, et al. The Role of Vitamin C in Orthopedic Trauma and Bone Health. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2015;44(7):306-311.
[8] IMAM MU, ZHANG S, MA J, et al. Antioxidants mediate both iron homeostasis and oxidative stress. Nutrients. 2017;9(7):671.
[9] HUANG Z, HE G, HUANG Y. Deferoxamine synergizes with transforming growth factor-beta signaling in chondrogenesis. Genet Mol Biol. 2017; 40(3):698-702.
[10] CHEUK YC, FU SC, MOK SW, et al. Intra-articular injection of an antioxidant formulation did not improve structural degeneration in a rat model of post-traumatic osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. 2017;8: 25-31.
[11] GLYN-JONES S, PALMER AJ, AGRICOLA R, et al. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2015;386(9991):376-387.
[12] LIAO CR, WANG SN, ZHU SY, et al. Advanced oxidation protein products increase TNF-alpha and IL-1beta expression in chondrocytes via NADPH oxidase 4 and accelerate cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis progression. Redox Biol. 2020;28:101306.
[13] DAI WL, ZHOU AG, ZHANG H, et al. Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Arthroscopy. 2017;33(3):659-670.
[14] YANG G, FAN M, ZHU J, et al. A multifunctional anti-inflammatory drug that can specifically target activated macrophages, massively deplete intracellular H2O2, and produce large amounts CO for a highly efficient treatment of osteoarthritis. Biomaterials. 2020;255:120155.
[15] FENG K, CHEN Z, PENGCHENG L, et al. Quercetin attenuates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis via SIRT1/AMPK-mediated inhibition of ER stress in rat chondrocytes and prevents the progression of osteoarthritis in a rat model. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(10):18192-18205.
[16] WEI B, ZHANG Y, TANG L, et al. Protective effects of quercetin against inflammation and oxidative stress in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis. Drug Dev Res. 2019;80(3):360-367.
[17] HU Y, GUI Z, ZHOU Y, et al. Quercetin alleviates rat osteoarthritis by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis of chondrocytes, modulating synovial macrophages polarization to M2 macrophages. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;145:146-160.
[18] ZHANG J, YIN J, ZHAO D, et al. Therapeutic effect and mechanism of action of quercetin in a rat model of osteoarthritis. J Int Med Res. 2019: 1219673013.
[19] PERMATASARI DA, KARLIANA D, ISKANDARSYAH I, et al. Quercetin prevent proteoglycan destruction by inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-9, matrix metalloproteinase-13, a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs-5 expressions on osteoarthritis model rats. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2019;10(1):2-8.
[20] MOK SW, FU SC, CHEUK YC, et al. Intra-articular delivery of quercetin using thermosensitive hydrogel attenuate cartilage degradation in an osteoarthritis rat model. Cartilage. 2020;11(4):490-499.
[21] HOSSEINZADEH A, KAMRAVA SK, JOGHATAEI MT, et al. Apoptosis signaling pathways in osteoarthritis and possible protective role of melatonin. J Pineal Res. 2016;61(4):411-425.
[22] LUBIS A, SIAGIAN C, WONGGOKUSUMA E, et al. Comparison of Glucosamine-Chondroitin Sulfate with and without Methylsulfonylmethane in Grade I-II Knee Osteoarthritis: A Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Acta Med Indones. 2017;49(2):105-111.
[23] GROVER AK, SAMSON SE. Benefits of antioxidant supplements for knee osteoarthritis: rationale and reality. Nutr J. 2016;15:1.
[24] BERLINBERG A, ASHBECK EL, ROEMER FW, et al. Diagnostic performance of knee physical exam and participant-reported symptoms for MRI-detected effusion-synovitis among participants with early or late stage knee osteoarthritis: data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(1):80-89.
[25] FRALLONARDO P, RAMONDA R, PERUZZO L, et al. Basic calcium phosphate and pyrophosphate crystals in early and late osteoarthritis: relationship with clinical indices and inflammation. Clin Rheumatol. 2018;37(10):2847-2853.
[26] CLEMENT ND, BARDGETT M, WEIR D, et al. Three groups of dissatisfied patients exist after total knee arthroplasty: early, persistent, and late. Bone Joint J. 2018;100-B(2):161-169.
[27] KARIKIS I, AHLEN M, SERNERT N, et al. The long-term outcome after early and late anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Arthroscopy. 2018;34(6):1907-1917.
[28] SAKAMOTO T, MIYAZAKI T, WATANABE S, et al. Intraarticular injection of processed lipoaspirate cells has anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects but does not improve degenerative changes in murine monoiodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):335.
|