中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (29): 4710-4716.doi: 10.12307/2024.539
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
骨组织工程支架的制备方法研究进展
皇 磊1,王晓丽1,王思明2,鲍 鑫1,周 鑫1,王犇娣2
- 1江苏海洋大学机械工程学院,江苏省连云港市 222005;2连云港市第二人民医院,江苏省连云港市 222023
-
收稿日期:2023-10-11接受日期:2023-11-22出版日期:2024-10-18发布日期:2024-03-23 -
通讯作者:王晓丽,工学博士,副教授,江苏海洋大学机械工程学院,江苏省连云港市 222005 -
作者简介:皇磊,男,2001年生,江苏省淮安市人,汉族,江苏海洋大学在读硕士,主要从事增材制造方面的研究。 -
基金资助:江苏海洋大学研究生科研与实践创新计划(KYCX2023-77),项目负责人:皇磊
Advance in preparation methods of bone tissue engineering scaffolds
Huang Lei1, Wang Xiaoli1, Wang Siming2, Bao Xin1, Zhou Xin1, Wang Bendi2
- 1College of Mechanical Engineering, Jiangsu Ocean University, Lianyungang 222005, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Second People’s Hospital of Lianyungang, Lianyungang 222023, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2023-10-11Accepted:2023-11-22Online:2024-10-18Published:2024-03-23 -
Contact:Wang Xiaoli, Doctor of Engineering, Associate professor, College of Mechanical Engineering, Jiangsu Ocean University, Lianyungang 222005, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Huang Lei, Master candidate, College of Mechanical Engineering, Jiangsu Ocean University, Lianyungang 222005, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:Graduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Ocean University, No. KYCX2023-77 (to HL)
摘要:
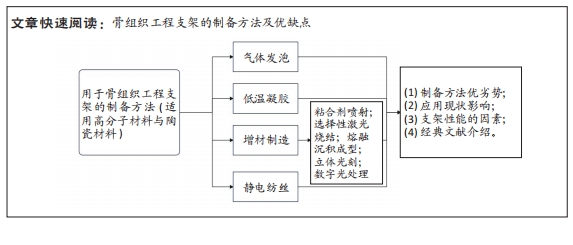
文题释义:
骨组织工程支架:是一种用于促进骨再生和修复的三维结构,它可以提供机械支撑和生物活性,为细胞附着、增殖和分化提供合适的环境。增材制造技术:也称为3D打印,通过逐层加工材料来建立三维实体。与传统的减材制造(如切割、铸造等)不同,增材制造技术通过将材料逐层叠加,直接将数字模型转化为实体产品,具有更高的制造自由度。
背景:由于自体骨源的数量较少,且使用异体骨会产生免疫排斥、疾病扩散等危险,因而人造骨材料在当今的骨移植中起到了不可替代的作用。伴随着功能定制、生物相容性的要求和生物可降解材料的出现,已经出现了多样化的生物材料和多种制备方法。
目的:概述目前应用于骨组织工程支架的制备方法,总结各种制备方法的优缺点、研究现状与进展。方法:使用计算机在中国知网、万方数据、PubMed及ScienceDirect数据库检索2008年1月至2023年8月关于骨组织工程支架方面的文献,以“Tissue engineering,Bone scaffold,Gas foaming,Cryotropic gelation,Additive manufacturing等”为英文检索词,以“组织工程,骨支架,气体发泡,低温凝胶,增材制造等”为中文检索词,排除无关和重复性研究,共保留80篇文献进行了总结归纳。
结果与结论:①相较于传统支架的制备工艺,近年来新兴的增材制造和静电纺丝技术在用于组织工程的复杂结构如骨和软骨的生产中,表现出了巨大的潜力。②增材制造方法除了在速度、精度和使用的材料范围方面更具优势,还提供了制造高度复杂的几何形状和拓扑优化结构的可行性,实现精确调节和构造结构的高重复性。③静电纺丝是生产一系列纤维垫的最具适应性和前景的技术之一。通过静电纺丝产生的纳米纤维支架是与细胞质基质微观结构非常惊人地相似的生物材料。④目前在陶瓷材料上以羟基磷灰石和磷酸三钙应用性能较好,在高分子材料上目前材料种类多样,以生物相容性优良的材料应用较多。⑤因此,在骨组织工程支架材料的选择上应更好地了解它们的特性,避免复杂化,以生产更具增强功能的支架。然而,目前报告的绝大多数文献对临床的适用性都是探索性的,具体适合哪种疾病的治疗还有待检验。未来骨支架的发展需体现在这几个方面:与缺失骨相匹配的力学性能、降解速率可控、促进骨再生力强以及附有特定功能。
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-4211-1318(皇磊);https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3640-1143(王晓丽)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
皇 磊, 王晓丽, 王思明, 鲍 鑫, 周 鑫, 王犇娣. 骨组织工程支架的制备方法研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(29): 4710-4716.
Huang Lei, Wang Xiaoli, Wang Siming, Bao Xin, Zhou Xin, Wang Bendi. Advance in preparation methods of bone tissue engineering scaffolds[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(29): 4710-4716.
2.1 气体发泡 是一种在材料内部产生气体或使气体通过材料从而产生多孔结构的制备方法。目前常用的发泡技术有物理发泡法和化学发泡法。物理发泡是从外部将惰性气体(如N2和CO2)通过基质以产生所需的内部多孔结构。化学发泡首先将基质、发泡剂与粘合剂混合,然后将混合物制成所需求的形状并固化,之后将材料浸入含有发泡剂的溶液中,由于化学反应会产生气体作为副产物,因此支架内部逸出的气泡会形成所需的多孔状。POURSAMAR等[9]提出以碳酸氢钠为发泡剂,通过气体发泡的方法,成功制备了多孔明胶支架,经实验发现交联支架的微观结构具有理想的互连孔隙率。
与增材制造技术相比,气体发泡的主要优点是成本更低,加工时间更快。不过气体发泡的方法不适合制造复杂形状的支架,并且在单独使用气体发泡技术制备多孔支架时,孔间的连通率通常较低。目前可以通过与其他制备方法联合使用或添加其他材料来进行改善。MANAVITEHRANI等[10]对聚碳酸亚丙酯、淀粉和生物玻璃颗粒共混物使用气体发泡的方法,开发出一种具有良性降解副产物的多孔支架,经过观察,气体发泡技术有效地产生了具有高孔隙互连性的多孔结构。PETRIE ARONIN等[11]提出了一种新型支架制造方法,使用聚合物共混挤出和气体发泡技术来控制孔径分布。在对聚合物单独挤出和共挤出后分别进行发泡处理,发现单独使用挤出方法的支架产生的孔面积较大,但是孔隙率较低,孔间的连通性也较差;而在气体压力和退火时间保持恒定的条件下,在两种聚合物的共挤出之后进行气体发泡促进了更大范围的孔径分布,且对总孔隙率几乎没有影响。
气体发泡技术常通过控制材料与发泡剂的混合比来调控孔径,一般在该过程产生的气体越多,孔隙度水平就越高。聚乳酸、聚己内酯等具有适合于气体发泡的流变特性,已广泛用于该技术[12]。不过只是通过聚合物材料制备很难满足人工骨支架的需求,可以通过添加陶瓷填料以形成聚合物-陶瓷复合支架来改善聚合物支架的骨传导性能。另外由于常用的发泡剂一般都不利于细胞繁殖和生长,且在制备过程中不能很好地控制孔的尺寸和分布,用化学发泡制备组织工程多孔支架需要优化过程。MOON等[13]在制备了醋酸纤维素膜后,通过气体发泡与相关的化学反应同时进行,使银纳米粒子覆盖到三维纤维素上,制备了三维纤维素-银纳米粒子支架。对其研究后发现,这样的支架易于制造,具有良好的生物活性、抗菌效果和生物相容性。此外,也有学者通过应力-应变曲线的线性区域研究了气体发泡结构的力学性能[10]。
2.2 低温凝胶 其制备方法也被称为冷冻凝胶法,该方法先通过搅拌或超声等方法将凝胶剂(如高分子聚合物)均匀分散到溶剂中;然后将聚合物溶液冷冻至低于冰点的温度,使凝胶剂在溶剂中发生相分离产生微孔结构[14];接着将凝胶样品保持在低温条件下,直至凝胶完全形成和固化。凝胶形成后,通过洗涤、干燥后获得所需样品。
低温凝胶的制备由于在较低温度下进行,制备凝胶的过程可以更好地控制,避免材料的热降解,可以用于制备高度互连的多孔结构和高机械稳定性支架。另外预制的大孔冷冻凝胶支架可以种植细胞,细胞/支架结构可以通过小口径针输送,在细胞输送后几乎完全恢复几何形状,这可以保持高的细胞活力[15],但凝胶及其衍生物形成的支架通常力学性能较差。此外当低温凝胶法用作于制造组织再生的支架时,缺乏能够充分支持细胞黏附和增殖的特定细胞信号传导基序[16]。为了解决这一限制,一种策略是将凝胶或其衍生物与其他材料整合,以形成杂化或复合水凝胶,从而具有结合多种组分的优点。KAI等[17]研究发现纳米纤维(聚己内酯/明胶)增强的水凝胶与纯明胶水凝胶相比,复合水凝胶的杨氏模量显著增加,进行体外培养时细胞在支架上的增殖数量也有明显的提升。
低温凝胶技术适用一系列的生物相容性材料且几乎不改变材料原有的性能,这使得该工艺成为流行的选择。SALGADO等[18]将胶原蛋白溶液与纳米羟基磷灰石聚集体溶液以特定比例混合,在低温条件下加上交联剂制备了胶原及胶原-羟基磷灰石凝胶,结果发现羟基磷灰石纳米颗粒的添加可以改善材料的力学性能和生物降解能力,通过体外实验证实了冷冻凝胶提高了细胞活力,并且细胞能够进行增殖和成骨分化。KIM等[19]采用低温凝胶法来表征成骨蛋白、生物玻璃添加剂和药物的联合作用,通过体外细胞培养,发现了细胞能够进行持续的增殖分化。
已经有研究发现,低温凝胶在交联阶段所允许的时间用量对支架的形态有着直接的影响。一般情况下,允许交联时间越长,支架孔隙率水平越高,相邻孔间距越小[20]。 此外,在材料的选择上,相较从聚合物中获得的冷冻凝胶,明胶基冷冻凝胶展现出明显的优越性[21]。
2.3 增材制造 也被称为3D打印技术,是一种通过逐层添加材料来加工组织结构的先进制造方法,通过计算机控制设备逐层制造,将一层层的材料堆积成实体来创建复杂的三维结构。目前可以通过对打印参数的优化设计实现对支架外形、孔隙率等的精确调控[22]。由于增材制造技术在生物医用材料上精密、智能以及快捷的特性,目前在制造医用材料上已成为主流的方法[23]。同时增材制造技术在与患者相关的护理方面显示出惊人的潜力,可以依据需求为临床提供个性化设计,并匹配专门的定制部件。目前从解剖模型到定制骨支架,再到临床的挑战性转变,均体现出了增材制造技术的灵活性和多功能性[24]。增材制造技术的方法种类很多,其中粘合剂喷射、选择性激光烧结、熔融沉积成型、立体光刻和数字光处理是广泛用于组织支架的制造方法。
2.3.1 粘合剂喷射 也称为基于粉末的3D打印。通过使用粘合剂,发生化学或其他相互作用,将粉末状材料结合,在该过程中,打印头将有机粘合剂溶液逐滴施加到粉末床表面的选定区域上,以这种方式构建第一层,然后将构建平台降低限定的高度,重新散布新的粉末层,以相同的方式重复这些步骤,直到完成整个部件。再通过后处理(如固化、脱脂和烧结等)进行进一步的固结,以达到最终产品的最大可能密度[25]。
作为一种3D打印方式,粘合剂喷射可以制备出具有复杂结构的、与患者高度匹配的植入体。与其他使用液体材料的制造技术相比,粘合剂喷射的方式不受工作材料分散、稳定性不高等相关问题的影响,在构建过程中也不需要支撑结构[26];另外,在材料的选择上只要是粉末态基本上均可以使用,也可以进行彩色打印。不过粘合剂喷射技术制备的支架在强度和精度上较其他的增材制造技术会差一些[27]。此外,为了提升治疗效果,有时会添加一些药物和生物因子。粘合剂喷射技术是会将药物和生物因子直接掺入基质,由于高温条件下药物和生物因子会热解,使用粘合剂喷射的方法可能达不到预期的效果。
粘合剂喷射技术主要使用金属和陶瓷材料,陶瓷材料的种类又以生物陶瓷和结构陶瓷为主。其中,多孔陶瓷由于优异的热绝缘性和物理性能而应用广泛,然而在常规的制造环境中,需要额外的工艺用于人工孔隙控制。此外,由于成形工艺的限制,这些方法在制造产品的几何设计方面较差[28],但可以通过添加不同类型的氧化物流动剂以及对温度等参数控制,来克服传统制造工艺的局限性。有学者通过使用氧化铝粉末作为氧化物流动剂,较好地实现了多孔陶瓷的制备[25]。
在使用粘合剂喷射技术时,打印支架的精度和强度与粉末、粘结剂、印刷参数、热处理、设备及后处理等密切相关,其中以粉末和粘结剂的选择最为重要。就陶瓷粉末而言,其流动性和堆积密度会受到几何性能(如形状和粒度分布等)的影响。球形颗粒的流动性更加优异,而不规则形状的颗粒会具有更高的堆积密度。有研究者使用羟基磷灰石进行了实验,在烧结后发现尽管使用不规则粉末打印的零件相较球形打印的零件孔隙率略低,但零件的机械性能高出近一倍[29]。粘合剂性能是影响支架质量的另一项关键因素,但生物相容性、生物降解性、毒性和机械强度等要求限制了可用于骨支架制造的粘合剂数量。WEI等[30]对此采用分子动力学模拟和实验的方法,研究了3种聚合物粘结剂(聚乙烯吡咯烷酮,聚丙烯酰胺,聚乙烯醇)在羟基磷灰石骨三维制作中的内聚能密度、力学性能、粘结行为和表面形态,通过揭示3种聚合物粘合剂的粘合机制,为粘合剂的选择提供了理论依据。此外,有学者针对羟基磷灰石粉末与标准水基油墨之间难以混合的问题,通过将羟基磷灰石粉末与聚乙烯醇作为粘合喷射制剂,来改善羟基磷灰石粉末基支架的结构、机械和生物性能[31]。其他因素如热处理也会影响打印陶瓷的高功能性。CHAVEZ等[32]分析了烧结条件对介电和压电能力的影响,发现垂直于印刷层测试的压电响应比平行测试的压电响应高35%以上。
2.3.2 选择性激光烧结 此工艺出现在20世纪80年代,是通过使用高功率激光器(如二氧化碳激光器)熔融或烧结粉末材料的连续层来生产聚合物部件的制造技术。在该过程中,高功率激光束由控制系统按CAD数据进行轨迹的精确控制,利用激光束扫描,对可熔粉末进行烧结,被照射的粉末材料在激光束的瞬间高温下熔融,并与相邻的材料颗粒结合,形成固态的物体层。在完成当前层的烧结之后,工作台会降低相应的层厚度,再次加装一层粉末材料,重复上述过程,直到整个物体构建完成。在冷却后用高压空气砂磨或用加压空气清洁[33]。
选择性激光烧结技术具有多个优点,如无须支撑结构制造复杂几何形状的能力,允许使用多种材料混合以及产品表面粗糙等[34]。由于加工过程涉及的温度相对较低,因此适合加工低熔点聚合物,但是设备的成本较高[35]。在加工陶瓷材料时,选择性激光烧结技术可用于制备无裂纹的致密陶瓷部件,研究发现制备的陶瓷部件具有极高的熔点、低塑性和较低的抗热震性[36]。虽然选择性激光烧结方法制备的陶瓷部件分辨率低,表面光洁度差,但在构建多孔骨支架方面的应用仍然广泛[37]。
近年来,已有许多通过选择性激光烧结工艺制备出生物相容性能良好的骨支架。LIN等[38]通过选择性激光烧结的方法,使用纳米羟基磷灰石和聚丙交酯复合微球制备了骨支架,该支架具有较好的细胞黏附性。此外,在利用选择性激光烧结技术时,可以向粉末混合物中添加陶瓷改性剂,来增强支架的骨诱导和骨传导性能;也可以通过添加生长因子使支架能进一步增强骨的生成。为了减弱热降解的风险,生长因子通常稍晚些通过浸泡加入。SASKA等[39]通过在聚羟基丁酸酯支架上加入成骨生长肽,使支架具有了一定的促进成骨和造血功能。另外也有学者通过添加纳米氧化钛等材料,使打印的支架具有良好的抑菌性能[40]。
此外,不同的研究人员探索使用选择性激光烧结技术来调控支架的表面质量和孔隙率。PAXTON等[41]通过比较新型激光烧结多孔高密度聚乙烯支架、传统模制的高密度聚乙烯支架和临床金标准植入物支架的孔隙率变化,来研究表面化学性质和孔隙率对组织向内生长的影响,与其他方法制备的支架相比,激光烧结支架显示出更高的“组织向内生长”和血管形成的能力。同样,对于骨科应用,MUMITH等[42]通过激光烧结制备了具有不同孔径的复合材料支架,这表明择性激光烧结技术具有制造不同孔径支架的潜力。
另外,也有学者研究材料以及工艺参数的选择对支架性能的影响。HAN等[43]采用选择性激光烧结法,制备了多个生物活性玻璃/聚己内酯复合支架,支架的硼酸盐生物活性玻璃含量各不相同,经检测发现这些支架结构的机械强度足以支撑在修复期间的稳定性。IMANIAN等[44]采用聚乙烯醇和炭黑复合材料,通过选择性激光烧结技术,制备了支架样件,分析了主要工艺参数及其交互作用对表面粗糙度和尺寸精度的影响,发现激光速度、扫描间距、激光功率、和层间厚度均显著影响表面粗糙度和尺寸精度。因此在具体的材料和设备条件下,需要对工艺参数进行优化,以获得良好的性能。
2.3.3 熔融沉积成型 该方法是将热塑性材料在螺杆挤出机的工作下挤出成丝,然后在机械作用下,将热塑丝条送进液化器流道,通过喷嘴将材料按预定的路径挤出,在打印平台上冷却凝固。一层结束后,平台高度下降一个层厚,重复过程一直到样件成型。此外,在制造一些结构复杂的样件(如空腔、悬突等)结构时,需要添加支撑材料,在后续处理时再去除支撑。
相较于其他的增材制造技术,熔融沉积成型方法涉及到的设备较为简单,成本较低,只需要液化器加热及运动机构就可以实现;打印过程清洁无污染,也不涉及高温高压,安全性高;对于需要有支撑结构的部件进行机械剥离或化学溶解即可[45],后处理简单。CALì等[46]通过聚乳酸以及农业废弃物的有机副产物作为原料,以评估熔融沉积成型打印的适用性,结果发现在轻量化、强度和粗糙度方面的性能均适合于生物医学的应用。此外,这种创新的生物复合材料允许降低环境影响的成本以及生产管理成本。不过熔融沉积成型制备的支架往往表面粗糙、精度较差,同时对材料要求熔点不能过高[47]。
熔融沉积成型技术可用于制备特定孔径和孔隙率的骨支架,并具有互连的孔结构[48-49]。DHANDAPANI等[50]采用熔融沉积技术制造了互连多孔、可生物降解的皮质骨螺钉,而传统螺钉成型技术无法制造这种螺钉。另外,由于大多数熔融沉积成型技术使用的长丝材料是石油基,在印刷过程中可能会释放有毒物质,因此熔融沉积成型技术可使用的材料较为有限。目前开发用于熔融沉积成型的生物基长丝越来越受欢迎,已有许多研究在熔融沉积成型技术中使用来自可再生资源(如玉米、玉米糖蜜和甜菜糖含量)的合成聚合物来作为支架材料[46,51-52]。
在用熔融沉积成型方法制造骨支架时,需要重点考虑设计结构、材料和工艺参数3个因素。微结构设计是骨支架制备的重要环节。骨支架结构分为两种,第一种是基于单位单元设计,第二种是基于整个设计。诸如八隅结构晶格和螺旋晶格的结构设计可以具有与骨支架一样优异的压缩性能。工艺参数的设置(层厚度、光栅角度、构建方向、填充密度、打印速度、填充图案、挤出温度、光栅宽度、喷嘴直径、轮廓宽度、轮廓到轮廓气隙、轮廓数和气隙)对结构部件的特征及其生产效率同样具有重大影响[51]。有学者对连续纤维增强复合材料进行实验,总结了打印温度、层厚、纤维体积分数及打印速度等熔融沉积成型常见的参数对复合材料产品的力学性能影响[53]。
2.3.4 立体光刻 该方法使用光学能量源来扫描光聚合物液体的容器,从而固化液体表面上的特定区域。通常定位支撑板(打印床)在液面正下方,打印一层后,将该板从表面移开一个距离,其尺寸等于下一层的厚度。重复这个过程,逐渐堆叠每一层的固态材料,形成完整的打印物体。打印完成后,需要进行后处理以去除未固化的树脂和支撑结构[54]。
除了易于操作、有光滑的表面光洁度以及制造复杂结构的能力外,立体光刻技术的一个突出特点是具有良好的分辨率,因此在组织工程中实用性较好。不过立体光刻技术制备成型件主要面临树脂的黏度大、收缩率高、生物相容性光聚合物的可用性限制等问题。对此有学者通过使用硅烷偶联剂制备了超支化聚硅氧烷,研究了不同含量聚硅氧烷对试件的体积收缩率和线收缩率的影响,并得出了最优值[55]。此外由于用于立体光刻的大多数聚合物未被FDA批准,在使用时可能会引起未知的反应问题,导致产生毒性,立体光刻打印物的安全性问题值得关注[56]。
作为被首个发现的增材制造方法[57],立体光刻技术已广泛用于制造各种骨科应用的支架。ALEXANDER等[58]使用立体光刻技术,利用氧化铝陶瓷浆料制备了4种不同的大孔陶瓷骨植入物。THAVORNYUTIKARN等[59]证明立体光刻技术可以制备各种相互连接的多孔有序支架,通过改变支架的孔径可以调控支架的机械强度。CHEN等[60]通过立体光刻技术制备了聚乙二醇二丙烯酸酯/纳米羟基磷灰石生物材料,实验发现印刷样品的压缩强度满足骨组织的抗压强度要求。
在工艺参数的选择上,有学者通过建立高精度的仿真模型研究了激光功率和扫描速度对双应力植入式三维打印机形成过程的影响,揭示了其机制[61],结果表明立体光刻技术打印的残余应力随扫描速度的增加而减小,随激光功率的增加而增大。另外,立体光刻方法中的打印分辨率主要取决于工艺中使用的激光直径和层厚度参数[62]。此外,也有学者研究了孔几何形状对立体光刻制造的钙硅酸盐生物陶瓷支架结构强度的影响[63]。
2.3.5 数字光处理 该技术与立体光刻技术的基本原理相同,即通过紫外光的选择性照射来控制陶瓷浆料的局部固化,不同的是,数字光处理技术通过使用对象横截面图像的紫外线光或蓝光投影代替激光,固化液体光聚合物。另外,连续数字光处理技术通过利用连续层图像的连续数字投影来创建从一个层到下一个层的平滑过渡,从而使数字光处理技术有着高分辨率和更光滑表面光洁度的结构[64]。
相较立体光刻技术,数字光处理技术具有更好的分辨率和更快的处理速度[65]。同样,由于光聚合在光和光引发剂的存在下发生,有毒的光聚合物、光引发剂、染料引发剂和溶剂造成严重的细胞毒性风险,缩小了可行材料的部署范围。
数字光处理技术在结构陶瓷领域应用广泛,但受限于光源和投影设备,数字光处理技术通常用于制造尺寸不大的陶瓷零件。
PREOBRAZHENSKIY等[66]使用数字光处理方法制备基于填充磷酸钙的水凝胶生物复合材料,有望作为用于骨组织恢复的弹性生物植入物。WU等[67]通过数字光处理技术为打印磷酸钙陶瓷提供一种高精度和低缺陷的闭环解决方案,获得了高性能磷酸钙陶瓷。也有学者使用含氮化硅的陶瓷聚合物与光敏树脂浆料,通过数字光处理制备了复杂结构的陶瓷基复合材料[68]。研究发现,陶瓷填料的引入不仅防止了材料在热解过程中的坍塌,而且有效地降低了材料的线收缩率和质量损失。此外,作为增强相,显著提高了最终复合材料的机械性能。
不过,通过数字光处理打印制备高精度羟基磷灰石增强复合材料以有效促进骨再生仍然是一个挑战。为此,SONG等[69]以明胶甲基丙烯酰胺和羟基磷灰石复合油墨,通过数字光处理技术制备了高精度的骨修复支架,经测量,多孔复合支架的实际打印分辨率达到了100 μm。在体外实验中,多孔复合支架显著促进了成骨细胞的黏附和增殖,并促进了成骨分化。
在数字光处理制造工艺参数的选择上,增加暴露于UV光的时间在改善材料的弹性性质和强度方面起相关作用。在暴露时间较长时,设定小的层厚度有助于改善拉伸性能;由于其有限的透明度而在材料中发生有限的聚合,使用太大的层厚度会降低机械拉伸性能;此外,承重聚合物部件的工艺设置和印刷布局需要特别注意,因为它们对最终的机械特性影响很大[70]。
2.4 静电纺丝 是一种制备纳米纤维的技术,利用静电力将聚合物溶液或熔融聚合物从尖端喷出,形成纤维纳米级别的结构。液体聚合物在所施加压力的作用下,液体材料以液滴的形式被挤出针尖,并且暴露于喷丝头和收集器之间的静电场中,静电场作用在该液滴外层上的带电材料颗粒上,将它们拉向更靠近集电板的单个点(通常称为泰勒锥),随着朝向收集器尖端方向积累增长,材料进一步伸长最终导致材料从喷丝头侧加速转移到收集器而不破坏链节。同时在材料朝向收集器加速转移过程中,观察到直径进一步减小,使得该过程能够制造具有纳米/微米尺度直径的纤维[71]。
相较其他的制备技术,静电纺丝技术的突出特点是可以生产具有大表面积的微米至纳米级纤维[72]。有学者制备了聚己内酯/羧甲基壳聚糖/海藻酸钠复合微米纤维,研究发现复合微米纤维具有优良的拉伸强度,同时复合支架无明显的细胞毒性,可促进成骨细胞的黏附[73]。静电纺丝纤维膜通过动态压缩应变和分层影响成骨细胞的增殖和分化,这往往有利于细胞的附着和生长[74]。不过由于静电纺丝支架固有的弱机械性能,限制了其在骨再生和骨修复方面的临床应用。
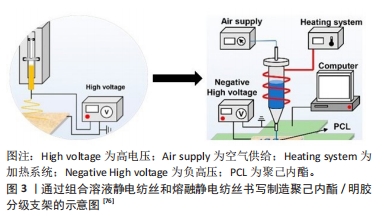
目前根据溶液状态分为传统的溶液静电纺丝和熔体静电纺丝。相较传统静电纺丝,熔体静电纺丝的纳米纤维有着高比表面积、高孔隙率等特点,纤维射流的路径更稳定,也没有有机溶剂残留[75]。不过,也有学者提出了将熔融静电纺丝书写(熔融静电纺丝书写技术是熔体静电纺丝与3D打印相结合的一种新兴技术,与传统3D打印技术相比,该方法可以实现亚微米纤维的精确定位,比3D打印技术小约2个数量级)和溶液静电纺丝相结合来制备微纳米分级骨组织工程支架。有学者使用聚己内酯和明胶材料,通过交替堆叠熔融静电纺丝书写层和溶液静电纺丝层来制备多层复合支架[76],结果表明,两种技术相结合的复合支架比单熔融静电纺丝书写具有更高的细胞黏附效率、细胞增殖能力和成骨能力。该在研究中,通过交替堆叠溶液静电纺丝制备的纳米明胶纤维和熔融静电纺丝制备的聚己内酯微米纤维来制造复合支架。首先将明胶纳米纤维通过常规溶液静电纺丝制备,然后将覆盖有明胶纳米纤维的导电玻璃放置在移动平台上,进行熔融静电纺丝制备聚己内酯网格,此过程重复5次。图3为通过组合溶液静电纺丝和熔融静电纺丝书写制造聚己内酯/明胶分级支架的示意图。
静电纺丝的加工可塑性有利于生产各种聚合物纤维。通过将合成聚合物(作为骨架材料)与天然聚合物(在表面上用于改善细胞黏附)组合,可以生产具有最佳机械和相容性的复合纤维支架用于生物医学应用。另外针对静电纺丝支架的弱机械性能,有学者提出一种通过增材制造来打印网状增强的电纺支架方法[77],以提高其机械刚度和强度。将明胶与聚己内酯按一定的比例制成静电纺丝支架,由聚乳酸组成的网状物打印在支架上,结果发现通过3D打印网状材料增强的电纺支架改善了力学性能,并在大鼠颅骨缺损中表现出可接受的生物相容性。此外,也有学者将明胶和聚左旋乳酸组合,使用静电纺丝和熔融沉积技术制备了具有多种功能的新型层状支架,可用于软骨下骨和鼻软骨修复[78]。多材料复合以及与其他制备技术的一同使用,也许有助于解决静电纺丝支架性能的一些局限性。
静电纺丝纳米纤维的直径和形态取决于几个参数,这些参数分为3个主要类别:溶液的固有性质、工艺参数和环境因素[79]。溶液的固有性质(如浓度、黏度、分子质量、电导率、弹性以及溶剂的极性和表面张力)对静电纺丝纳米纤维的形态和最终直径具有显著影响[80]。表1列举了一些静电纺丝工艺参数对纤维形态的具体影响。另外环境因素数如环境的湿度和温度也是非常重要,高的湿度会阻碍纺丝过程和带电喷射,而在低温下会形成珠粒,高温下形成凝聚和扁平纤维。
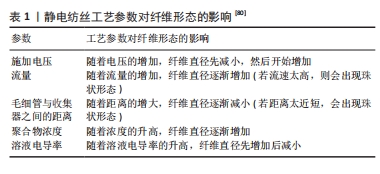
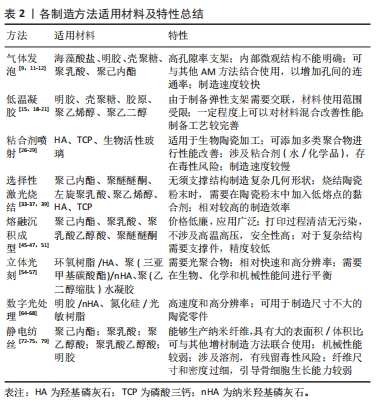
表2总结了上述制造方法适用的材料及其特性,此外,还有一些增加复杂大孔类骨结构的制造方法,如盐浸法及冷冻干燥等[78],其中使用盐浸出技术制备的支架孔径容易控制。致孔剂(如蜡、盐和糖)用于在盐浸出过程中构建支架的孔,将所需尺寸的小盐颗粒倒入模具中,然后用致孔剂填充,最后将聚合物溶液添加到填充有盐和致孔剂的模具中。当盐晶体随着溶剂蒸发浸出时,支架的孔就构建出来,通过盐浸法制备的支架结构特征是具有高孔隙率。冷冻干燥技术使用溶剂的升华过程来设计支架,将聚合物以所需浓度溶解在溶剂中,然后将所需浓度的溶液冷冻并冷冻干燥。支架的孔隙率可以通过冷冻速率来控制,冻干支架的特征是具有高孔隙率和互连性。
| [1] SHI W, ZHANG X, BIAN L, et al. Alendronate crosslinked chitosan/polycaprolactone scaffold for bone defects repairing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;204:441-456. [2] CHEN Z, KLEIN T, MURRAY RZ, et al. Osteoimmunomodulation for the development of advanced bone biomaterials. Mater Today. 2016;19(6):304-321. [3] WANG P, LI X, LUO S, et al. Additively manufactured heterogeneously porous metallic bone with biostructural functions and bone-like mechanical properties. J Mater Sci Technol. 2021;62:173-179. [4] DOROZHKIN SV. A detailed history of calcium orthophosphates from 1770s till 1950. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013;33(6):3085-3110. [5] KOONS GL, DIBA M, MIKOS AG. Materials design for bone-tissue engineering. Nat Rev Mater. 2020;5(8):584-603. [6] 罗卓荆, 毕龙. 我国骨缺损修复的成就与展望[J].空军军医大学学报,2022, 43(4):263-267. [7] WANG Z, WANG Y, YAN J, et al. Pharmaceutical electrospinning and 3D printing scaffold design for bone regeneration. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;174:504-534. [8] 王阮彬,程丽乾,陈凯.高分子材料在3D打印生物骨骼及支架中的应用与价值[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(4):610-616. [9] POURSAMAR SA, HATAMI J, LEHNER AN, et al. Gelatin porous scaffolds fabricated using a modified gas foaming technique: characterisation and cytotoxicity assessment. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;48:63-70. [10] MANAVITEHRANI I, LE TYL, DALY S, et al. Formation of porous biodegradable scaffolds based on poly (propylene carbonate) using gas foaming technology. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;96:824-830. [11] PETRIE ARONIN CE, COOPER JA JR, SEFCIK LS, et al. Osteogenic differentiation of dura mater stem cells cultured in vitro on three-dimensional porous scaffolds of poly (epsilon-caprolactone) fabricated via co-extrusion and gas foaming. Acta Biomater. 2008;4(5):1187-1197. [12] COSTANTINI M, COLOSI C, MOZETIC P, et al. Correlation between porous texture and cell seeding efficiency of gas foaming and microfluidic foaming scaffolds. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;62:668-677. [13] MOON JY, LEE J, HWANG TI, et al. A multifunctional, one-step gas foaming strategy for antimicrobial silver nanoparticle-decorated 3D cellulose nanofiber scaffolds. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;273:118603. [14] CARVALHO BMA, DA SILVA SL, DA SILVA LHM, et al. Cryogel poly (acrylamide): synthesis, structure and applications. Sep Purif Rev. 2013;43(3):241-262. [15] HUANG YH, CHEN HA, CHEN CH, et al. Injectable gelatin/glucosamine cryogel microbeads as scaffolds for chondrocyte delivery in cartilage tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;253(Pt 1):126528. [16] DI MUZIO L, SERGI C, CARRIERO VC, et al. Gelatin-based spongy and compressive resistant cryogels with shape recovery ability as ideal scaffolds to support cell adhesion for tissue regeneration. React Funct Polym. 2023;189:105607. [17] KAI D, PRABHAKARAN MP, STAHL B, et al. Mechanical properties and in vitro behavior of nanofiber-hydrogel composites for tissue engineering applications. Nanotechnology. 2012;23(9):095705. [18] SALGADO CL, GRENHO L, FERNANDES MH, et al. Biodegradation, biocompatibility, and osteoconduction evaluation of collagen-nanohydroxyapatite cryogels for bone tissue regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(1):57-70. [19] KIM HD, AMIRTHALINGAM S, KIM SL, et al. Biomimetic materials and fabrication approaches for bone tissue engineering. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017. doi:10.1002/adhm.201700612. [20] KUMAR A, MISHRA R, REINWALD Y, et al. Cryogels: freezing unveiled by thawing. Mater Today. 2010;13(11):42-44. [21] HE Y, WANG C, WANG C, et al. An overview on collagen and gelatin-based cryogels: fabrication, classification, properties and biomedical applications. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(14):2299. [22] 史耕田.PLGA/PCL复合材料人工骨支架高温挤出3D打印制造方法和性能研究[D]. 宁波:宁波大学,2020. [23] 张光曦,刘世锋,杨鑫,等.增材制造技术制备生物植入材料的研究进展[J].粉末冶金技术,2019,37(4):312-318. [24] CHARBONNIER B, HADIDA M, MARCHAT D. Additive manufacturing pertaining to bone:Hopes, reality and future challenges for clinical applications. Acta Biomater. 2021;121:1-28. [25] KWON M, CHOI JH, KIM JH, et al. Optimization of inorganic powder properties for manufacturing ceramic filter using binder jetting process. Addit Manuf. 2023; 70:103564. [26] LV X, YE F, CHENG L, et al. Binder jetting of ceramics: powders, binders, printing parameters, equipment, and post-treatment. Ceram Int. 2019;45(10):12609-12624. [27] 陈现伦,杨建明,黄大志,等.3DP法三维打印技术制备骨科植入物的发展现状[J].热加工工艺,2018,47(4):35-39. [28] HAMMEL EC, IGHODARO OLR, OKOLI OI. Processing and properties of advanced porous ceramics: an application based review. Ceram Int. 2014;40(10):15351-15370. [29] SUWANPRATEEB J, SANNGAM R, PANYATHANMAPORN T. Influence of raw powder preparation routes on properties of hydroxyapatite fabricated by 3D printing technique. Mater Sci Eng C. 2010;30(4):610-617. [30] WEI Q, WANG Y, CHAI W, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation and experimental study of the bonding properties of polymer binders in 3D powder printed hydroxyapatite bioceramic bone scaffolds. Ceram Int. 2017;43(16):13702-13709. [31] ZHOU Z, LENNON A, BUCHANAN F, et al. Binder jetting additive manufacturing of hydroxyapatite powders: effects of adhesives on geometrical accuracy and green compressive strength. Addit Manuf. 2020;36:101645. [32] CHAVEZ LA, IBAVE P, WILBURN B, et al. The influence of printing parameters, post-processing, and testing conditions on the properties of binder jetting additive manufactured functional ceramics. Ceramics. 2020;3(1):65-77. [33] DADKHAH M, TULLIANI JM, SABOORI A, et al. Additive manufacturing of ceramics: advances, challenges, and outlook. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2023;43(15):6635-6664. [34] ZHOU M, ZHU W, YU S, et al. Selective laser sintering of carbon nanotube–coated thermoplastic polyurethane:Mechanical, electrical, and piezoresistive properties. Compos Part C: Open Access. 2022;7:100212. [35] SOLEYMANI S, NAGHIB SM. 3D and 4D printing hydroxyapatite-based scaffolds for bone tissue engineering and regeneration. Heliyon. 2023;9(9):e19363. [36] CHEN AN, WU JM, LIU K, et al. High-performance ceramic parts with complex shape prepared by selective laser sintering: a review. Adv Appl Ceram. 2017; 117(2):100-117. [37] CHEN Z, LI Z, LI J, et al. 3D printing of ceramics: a review. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2019; 39(4):661-687. [38] LIN K, LIU J, WU JM, et al. Selective laser sintered nano-HA/PDLLA composite microspheres for bone scaffolds applications. Rapid Prototyp J. 2020;26(6):1131-1143. [39] SASKA S, PIRES LC, COMINOTTE MA, et al. Three-dimensional printing and in vitro evaluation of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) scaffolds functionalized with osteogenic growth peptide for tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;89: 265-273. [40] SHUAI C, SHUAI C, FENG P, et al. Antibacterial capability, physicochemical properties, and biocompatibility of nTiO(2) incorporated polymeric scaffolds. Polymers (Basel). 2018;10(3):328. [41] PAXTON NC, DINORO J, REN J, et al. Additive manufacturing enables personalised porous high-density polyethylene surgical implant manufacturing with improved tissue and vascular ingrowth. Appl Mater Today. 2021;22:100965. [42] MUMITH A, CHEONG VS, FROMME P, et al. The effect of strontium and silicon substituted hydroxyapatite electrochemical coatings on bone ingrowth and osseointegration of selective laser sintered porous metal implants. PLoS One. 2020;15(1):e0227232. [43] HAN J, WU J, XIANG X, et al. Biodegradable BBG/PCL composite scaffolds fabricated by selective laser sintering for directed regeneration of critical-sized bone defects. Mater Des. 2023;225:111543. [44] IMANIAN ME, BIGLARI FR. Modeling and prediction of surface roughness and dimensional accuracy in SLS 3D printing of PVA/CB composite using the central composite design. J Manuf Process. 2022;75:154-169. [45] 冯东,王博,刘琦,等.高分子基功能复合材料的熔融沉积成型研究进展[J].复合材料学报,2021,38(5):1371-1386. [46] CALÌ M, PASCOLETTI G, GAETA M, et al. New filaments with natural fillers for FDM 3D printing and their applications in biomedical field. Procedia Manuf. 2020;51: 698-703. [47] LIGON SC, LISKA R, STAMPFL J, et al. Polymers for 3D printing and customized additive manufacturing. Chem Rev. 2017;117(15):10212. [48] KIM CG, HAN KS, LEE S, et al. Fabrication of biocompatible polycaprolactone–hydroxyapatite composite filaments for the FDM 3D printing of bone scaffolds. Appl Sci. 2021;11(14):6351. [49] COCKERILL I, SU Y, SINHA S, et al. Porous zinc scaffolds for bone tissue engineering applications: a novel additive manufacturing and casting approach. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;110:110738. [50] DHANDAPANI R, KRISHNAN PD, ZENNIFER A, et al. Additive manufacturing of biodegradable porous orthopaedic screw. Bioact Mater. 2020;5(3):458-467. [51] WINARSO R, ANGGORO PW, ISMAIL R, et al. Application of fused deposition modeling (FDM) on bone scaffold manufacturing process: a review. Heliyon. 2022;8(11):e11701. [52] WASTI S, ADHIKARI S. Use of biomaterials for 3D printing by fused deposition modeling technique: a review. Front Chem. 2020;8:315. [53] 牟宇松,姜沅政,李红宾,等.基于FDM技术的连续纤维增强复合材料研究进展[J].工程塑料应用,2021,49(12):153-156, 161. [54] MALIK HH, DARWOOD AR, SHAUNAK S, et al. Three-dimensional printing in surgery:a review of current surgical applications. J Surg Res. 2015;199(2):512-522. [55] 曹嘉欣. SLA-3D打印光敏树脂的改性及其性能研究[D].西安:西安科技大学,2020. [56] LAKKALA P, MUNNANGI SR, BANDARI S, et al. Additive manufacturing technologies with emphasis on stereolithography 3D printing in pharmaceutical and medical applications: a review. Int J Pharm X. 2023;5:100159. [57] JACOBS P. Rapid prototyping manufacturing-Fundamentals of stereolithography. J Manuf Syst. 1993;12(5):430-433. [58] ALEXANDER AE, WAKE N, CHEPELEV L, et al. A guideline for 3D printing terminology in biomedical research utilizing ISO/ASTM standards. 3D Print Med. 2021;7(1):8. [59] THAVORNYUTIKARN B, TESAVIBUL P, SITTHISERIPRATIP K, et al. Porous 45S5 Bioglass(R)-based scaffolds using stereolithography: effect of partial pre-sintering on structural and mechanical properties of scaffolds. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;75:1281-1288. [60] CHEN Q, ZOU B, LAI Q, et al. SLA-3d printing and compressive strength of PEGDA/nHAP biomaterials. Ceram Int. 2022;48(20):30917-30926. [61] 赵丽.面向医用植入体的氧化锆基陶瓷材料3D打印残余应力产生机理研究[D].济南:山东大学,2021. [62] CARTER SD, COSTA PF, VAQUETTE C, et al. Additive Biomanufacturing: an advanced approach for periodontal tissue regeneration. Ann Biomed Eng. 2017;45(1):12-22. [63] LU F, WU R, SHEN M, et al. Rational design of bioceramic scaffolds with tuning pore geometry by stereolithography:Microstructure evaluation and mechanical evolution. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2021;41(2):1672-1682. [64] WALLACE J, WANG MO, THOMPSON P, et al. Validating continuous digital light processing (cDLP) additive manufacturing accuracy and tissue engineering utility of a dye-initiator package. Biofabrication. 2014;6(1):015003. [65] GARDAN J. Additive manufacturing technologies:state of the art and trends. Int. J Prod Res. 2015;54(9-10):3118-3132. [66] PREOBRAZHENSKIY II, TIKHONOV AA, EVDOKIMOV PV, et al. DLP printing of hydrogel/calcium phosphate composites for the treatment of bone defects. Open Ceramics. 2021;6:100115. [67] WU Y, CAO Q, WANG Y, et al. Optimized fabrication of DLP-based 3D printing calcium phosphate ceramics with high-precision and low-defect to induce calvarial defect regeneration. Mater Des. 2023;233:112230. [68] 欧俊,黄民忠,黄瑶,等.基于DLP技术打印制备聚合物转化陶瓷基复合材料的研究[J].陶瓷学报,2023,44(1):154-162. [69] SONG P, LI M, ZHANG B, et al. DLP fabricating of precision GelMA/HAp porous composite scaffold for bone tissue engineering application. Composites Part B. 2022;244:110163. [70] BRIGHENTI R, MARSAVINA L, MARGHITAS MP, et al. The effect of process parameters on mechanical characteristics of specimens obtained via DLP additive manufacturing technology. Mater Today Proc. 2023;78:331-336. [71] FAZAL F, DIAZ SANCHEZ FJ, WAQAS M, et al. A modified 3D printer as a hybrid bioprinting-electrospinning system for use in vascular tissue engineering applications. Med Eng Phys. 2021;94:52-60. [72] MOVAHEDI M, ASEFNEJAD A, RAFIENIA M, et al. Potential of novel electrospun core-shell structured polyurethane/starch (hyaluronic acid) nanofibers for skin tissue engineering:In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;146:627-637. [73] TAO F, CHENG Y, TAO H, et al. Carboxymethyl chitosan/sodium alginate-based micron-fibers fabricated by emulsion electrospinning for periosteal tissue engineering. Mater Des. 2020;194:108849. [74] GUPTA D, VENUGOPAL J, MITRA S, et al. Nanostructured biocomposite substrates by electrospinning and electrospraying for the mineralization of osteoblasts. Biomaterials. 2009;30(11):2085-2094. [75] 姚子琪,马东明,雷文龙,等.熔体静电纺丝直写技术在组织工程中的应用进展[J].化工进展,2019,38(8):7. [76] WANG Z, WANG H, XIONG J, et al. Fabrication and in vitro evaluation of PCL/gelatin hierarchical scaffolds based on melt electrospinning writing and solution electrospinning for bone regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C. 2021;128(4):112287. [77] PENSA NW, CURRY AS, BONVALLET PP, et al. 3D printed mesh reinforcements enhance the mechanical properties of electrospun scaffolds. Biomater Res. 2019;23(1):22. [78] RAJZER I, KUROWSKA A, JABŁOŃSKI A, et al. Layered gelatin/PLLA scaffolds fabricated by electrospinning and 3D printing- for nasal cartilages and subchondral bone reconstruction. Mater Des. 2018;155(OCT.):297-306. [79] SUN B, LONG YZ, ZHANG HD, et al. Advances in three-dimensional nanofibrous macrostructures via electrospinning. Prog Polym Sci. 2014;39(5):862-890. [80] SILL TJ, VON RECUM HA. Electrospinning:applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2008;29(13):1989-2006. |
| [1] | 杨玉芳, 杨芷姗, 段棉棉, 刘毅恒, 唐正龙, 王 宇. 促红细胞生成素在骨组织工程中的应用及前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1443-1449. |
| [2] | 陈凯佳, 刘景云, 曹 宁, 孙建波, 周 燕, 梅建国, 任 强. 组织工程技术在股骨头坏死治疗中的应用及前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1450-1456. |
| [3] | 梅静怡, 刘 江, 肖 聪, 刘 鹏, 周浩浩, 林展翼. 组织工程血管构建过程中平滑肌细胞增殖变化及代谢模式[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1043-1049. |
| [4] | 王姗姗, 舒 晴, 田 峻. 物理因子促进干细胞的成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1083-1090. |
| [5] | 沈子青, 夏 天, 单一波, 朱睿君, 万昊鑫, 丁 浩, 潘 枢, 赵 军. 负载外泌体水凝胶修饰3D打印支架构建血管化的气道替代物[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 697-705. |
| [6] | 朱礼威, 王江玥, 白 丁. 纳米复合甲基丙烯酰明胶水凝胶在不同骨缺损环境中应用的价值[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 753-758. |
| [7] | 尹 彤, 杨吉垒, 李友瑞, 刘卓冉, 姜 明. 核壳结构纳米纤维在口腔组织再生中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 766-770. |
| [8] | 陈小芳, 郑国爽, 李茂源, 于炜婷. 可注射海藻酸钠水凝胶的制备及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 789-794. |
| [9] | 王嘉旎, 陈俊宇. 金属离子促血管生成机制及在骨组织工程中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 804-812. |
| [10] | 杨雨晴, 陈志宇. 早期短暂M1巨噬细胞在骨组织工程中的作用及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 594-601. |
| [11] | 于朋鑫, 韩禹秋, 郭丽娜, 王秀丽. 大鼠肠道平滑肌胶原条带构建及周期性拉伸培养的体外评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(35): 5630-5635. |
| [12] | 李昱林, 俞海鹏, 唐华菁, 张梓桐, 林兴南. 小檗碱促进骨再生的机制、安全性及在骨组织工程中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(35): 5702-5708. |
| [13] | 商永慧, 李 帅, 刘义琮, 赵启航, 刘 文. 正畸减数患者后牙前移对颞下颌关节应力影响的三维有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(34): 5516-5520. |
| [14] | 黄柯琪, 李加根, 陈尚桐, 容向宾. 长链非编码RNA在骨关节炎中的发病机制及中药干预[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(34): 5571-5576. |
| [15] | 杨小倩, 宋爱梅, 宋 晖. 间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞的共培养技术[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(31): 5055-5062. |
支架是设计用于模拟骨组织的细胞外基质的临时机械结构,使得骨重建过程可以在这个环境下发生。支架工程的主要理念是仿生天然组织的细胞外基质,确保支架表现出的结构和功能与细胞外基质所起的作用相似。用于组织工程生物学的理想支架需具备许多性能,其中关键的性能之一是生物相容性。生物相容性允许细胞在支架表面黏附、迁移和增殖而不产生阳性免疫应答和严重炎症反应[2]。生物可降解性是组织工程支架的另一个重要性能,当形成组织时,不应存在对支架的外来材料的触发炎症反应。此外,理想的组织工程支架也需要有一定的多孔结构,多孔结构可以促进营养物和代谢废物的扩散,不过孔间需要一定的互连性以进行适当的细胞渗透、血管化和营养输送[3]。另外支架也需要具有足够的机械性能,以承受载荷并在新组织形成时提供足够的机械支撑。
第一批试图使用实验室制造材料的骨头来修复丢失或损坏骨的报告,可以追溯到20世纪初,当时外科医生开始研究使用磷酸钙作为骨移植材料[4]。此后,用于治疗骨缺损的植入物不断发展,从旨在简单地替换丢失的骨头,到用生物互作用物质填充缺损体积来实现功能骨的再生,再到使用生物活性材料的组织。在这个过程中,骨组织工程引入了不同的材料和不同的方法,并在20世纪90年代成为一个独立的研究领域[5]。如今的材料合成和处理技术、骨组织支架制备技术以及对骨生物学和结构的深入了解,为设计更复杂的材料以及骨组织工程支架提供了新的可能。作为天然骨组织潜在的有机和无机成分的生物相容性材料已得到广泛研究,这些材料可大致分为金属、高分子材料、陶瓷以及它们的复合材料[6]。文章针对高分子材料与陶瓷材料,综述了相关支架制备方法的研究。高分子材料通常与金属、生物玻璃和陶瓷或离子共沉淀用于原位矿化,通过静电纺丝、气体发泡及低温凝胶化等方法制备多孔支架。采用化学交联及离子交联、粘合交联等多种交联技术可以增强材料性能和控制分解速率。聚合物支架的多孔结构为新形成的成骨细胞提供了外壳和足够的细胞附着位点,还可以浸渍药物,添加生长因子以及提供暂时的骨机械支撑[7]。生物陶瓷主要通过粉末床工艺制造,如粘合剂喷射及选择性激光烧结等,其中以羟基磷灰石和磷酸三钙为代表的陶瓷材料,由于骨传导性能优异,可不同程度融入宿主骨,广泛用作骨替代材料[8]。
另外,制备组织工程支架的方法也在不断优化,文章以近5年报道为主,就适用于骨组织工程支架的制备方法进行了总结,应用的材料主要以高分子材料和陶瓷为主。文章的针对性较强,由于大多选用近几年的文章,也具有一定的时效性。通过详细提供每种制备方法的优缺点、应用现状和影响因素,为现有制备方式的逐步改进和新的制备方法的开发奠定一定的基础。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 主要由第一作者在2023年8月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 主要搜索时间段为2008年1月至2023年 8月,同时纳入少数远期经典及特别相关文献。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中国知网、万方数据、PubMed、ScienceDirect数据库。
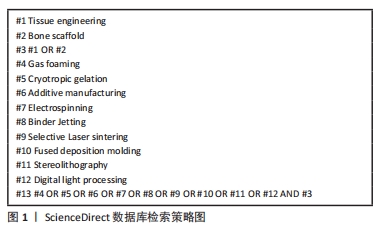
1.1.4 检索词及检索策略 以“Tissue engineering,Bone scaffold,Gas foaming,Cryotropic gelation,Additive manufacturing,Electrospinning,Binder Jetting,Selective Laser sintering,Fused deposition molding,Stereolithography,Digital light processing”为英文检索词,以“组织工程,骨支架,气体发泡,低温凝胶,增材制造,静电纺丝,粘合剂喷射,选择性激光烧结,熔融沉积成型,立体光刻,数字光处理”为中文检索词。以ScienceDirect数据库检索策略为例,检索词搭配见图1。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.7 检索文献量 初步检索文献300余篇。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①与骨组织工程支架材料相关;②含多个关键词的相关文献;③优先考虑近几年的文章。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①重复性研究;②与文章内容相关性不高的文献。
1.3 文献质量评估和数据的提取 对初步纳入的关键词进行检索后,阅读文章摘要进行快速排除,舍去时间较早、内容重复、内容相关性不高的文章,最终纳入标准文献80篇,其中中国知网数据库6篇,万方数据库5篇,PubMed数据库22篇,ScienceDirect数据库47篇。另外中文文献11篇,英文文献69篇。
目前报告的绝大多数文献对临床的适用性都是探索性的。在对细胞进行体外培养时,研究者通常是评价在短期内支架的生物性能,缺少在更长时间的探索以及与各种制造技术在同种材料下的比较。另外新的研究层出不穷,在新材料新方法的研究上难免会有不足。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 大部分研究者对支架制备方法的综述上都涵盖金属材料,由于金属与高分子材料、陶瓷在物理性能和生物相容性方面差异显著,显得在描述制备方法上比较宽泛。文章以近5年研究为主,就适用于骨组织工程支架的制备方法进行了总结,应用的材料主要以高分子材料和陶瓷为主。文章的针对性较强,由于大多选用近几年的文章,也具有一定的时效性。
3.3 综述的局限性 关于骨组织工程支架的文章很多,进行筛选时难免有一定的主观性。此外并没有对金属材料的制备方法进行研究,在高分子材料或陶瓷材料与金属材料复合方面缺失,有一定的局限性。
3.4 综述的重要意义 由于目前报告的绝大多数文献对临床的适用性都是探索性的,希望可以通过详细提供每种制造方法的工艺流程、在制备骨组织工程支架过程的优劣势、在骨组织工程的应用进展以及影响骨组织工程支架性能的因素等几个方面,能够为研究人员制备理想的骨组织工程支架提供思路和方法,设计出克服当前方法限制的新的制造技术,并期待能有超出骨组织修复预期的创新型应用。
3.5 结论及展望 文章主要从制备方法的工艺流程、制备过程的优劣势、在骨组织工程的应用进展以及影响骨组织工程支架性能的因素等几个方面进行了综述。相较一些传统的制造方法,增材制造方法在速度、精度和使用的材料范围方面确实更具优势。另外增材制造技术还提供了制造高度复杂的几何形状和拓扑优化结构的可行性,实现精确调节和构造结构的高重复性。可以肯定地说,增材制造技术所需的资源和劳动力更少。此外静电纺丝是生产一系列纤维垫的最具适应性和前景的技术之一,它可以用不同的方法,将材料特征与各种形态学特征结合,用于先进的组织工程。通过静电纺丝产生的纳米纤维支架是与细胞质基质微观结构非常惊人相似的生物材料,相信电纺纳米纤维支架能够在不久的将来,提供组织工程和生物医学应用所需的广泛功能。
未来骨支架会向有着相匹配的力学性能、降解速率可控、促进骨再生性能强和附有特定功能的方向发展。此外在生产过程中,应更好地解决材料性能的选择问题,以避免复杂化,更好地了解和理解它们的特性将使生产具有增强功能的支架成为可能。另外目前的临床病例数量明显较少,因此难以准确评价制造工艺的临床成功,随着新制造技术的适应,未来可能会集中在临床环境中探索新兴骨支架的材料及制备工艺。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
骨组织工程支架:是一种用于促进骨再生和修复的三维结构,它可以提供机械支撑和生物活性,为细胞附着、增殖和分化提供合适的环境。增材制造技术:也称为3D打印,通过逐层加工材料来建立三维实体。与传统的减材制造(如切割、铸造等)不同,增材制造技术通过将材料逐层叠加,直接将数字模型转化为实体产品,具有更高的制造自由度。
文章以近5年文章为主,就适用于骨组织工程支架的制备方法进行了总结,应用的材料主要以高分子材料和陶瓷为主。文章的针对性较强,由于大多选用近几年的文章,也具有一定的时效性。通过总结各制备方法的优劣势、应用现状和影响支架的因素,为从事相关骨组织工程的学者提供有价值的参考。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||