[1] SHARIATI A, NEMATI R, SADEGHIPOUR Y, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) for neurodegenerative disease: a promising frontier. Eur J Cell Biol. 2020;99(6):151097.
[2] MAQSOOD M, KANG M, WU X, et al. Adult mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes: Sources, characteristics, and application in regenerative medicine. Life Sci. 2020;256:118002.
[3] ATRI C, GUERFALI FZ, LAOUINI D. Role of human macrophage polarization in inflammation during infectious diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(6):1801.
[4] YUNNA C, MENGRU H, LEI W, et al. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020; 877:173090.
[5] HE X, DONG Z, CAO Y, et al. MSC-derived exosome promotes M2 polarization and enhances cutaneous wound healing. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:7132708.
[6] PAJARINEN J, LIN T, GIBON E, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-macrophage crosstalk and bone healing. Biomaterials. 2019;196:80-89.
[7] LU D, XU Y, LIU Q, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-macrophage crosstalk and maintenance of inflammatory microenvironment homeostasis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:681171.
[8] 谢丽,孟芮,商澎.细胞共培养技术在骨组织生物学中的应用[J].中国细胞生物学报, 2013,35(2):216-223.
[9] LAWRENCE TS, BEERS WH, GILULA NB. Transmission of hormonal stimulation by cell-to-cell communication. Nature. 1978;272(5653):501-506.
[10] PANDURANGAN M, HWANG I. Application of cell co-culture system to study fat and muscle cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014;98(17):7359-7364.
[11] 张楚晗,张东敏,徐稳安.牙髓再生组织工程中的细胞共培养体系[J].中国组织工程研究, 2023,27(15):2379-2384.
[12] LU LY, LOI F, NATHAN K, et al. Pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages promote osteogenesis by mesenchymal stem cells via the COX-2-prostaglandin E2 pathway. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(11): 2378-2385.
[13] LI Y, ZHANG D, XU L, et al. Cell-cell contact with proinflammatory macrophages enhances the immunotherapeutic effect of mesenchymal stem cells in two abortion models. Cell Mol Immunol. 2019;16(12):908-920.
[14] 高弘斐,张潜,陈龙,等.间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞共培养体系的细胞因子表达模式研究[J].免疫学杂志,2017,33(11):930-936.
[15] YUAN Y, NI S, ZHUGE A, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells reprogram M1 macrophage metabolism via PHD2/HIF-1α pathway in colitis mice. Front Immunol. 2022;13:859806.
[16] YAO H, YUAN X, WU Z, et al. Fabrication and performance evaluation of gelatin/sodium alginate hydrogel-based macrophage and MSC cell-encapsulated paracrine system with potential application in wound healing. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2):1240.
[17] ROMERO-LÓPEZ M, LI Z, RHEE C, et al. Macrophage effects on mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis in a three-dimensional in vitro bone model. Tissue Eng Part A. 2020;26(19-20):1099-1111.
[18] SALDAÑA L, VALLÉS G, BENSIAMAR F, et al. Paracrine interactions between mesenchymal stem cells and macrophages are regulated by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):14618.
[19] TANG H, HUSCH JFA, ZHANG Y, et al. Coculture with monocytes/macrophages modulates osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells on poly (lactic-co-glycolic) acid/polycaprolactone scaffolds. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(5):785-798.
[20] LUO ML, JIAO Y, GONG WP, et al. Macrophages enhance mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis via down-regulation of reactive oxygen species. J Dent. 2020;94:103297.
[21] SWARTZLANDER MD, BLAKNEY AK, AMER LD, et al. Immunomodulation by mesenchymal stem cells combats the foreign body response to cell-laden synthetic hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2015;41:79-88.
[22] ZHANG Y, BÖSE T, UNGER RE, et al. Macrophage type modulates osteogenic differentiation of adipose tissue MSCs. Cell Tissue Res. 2017;369(2):273-286.
[23] SPILLER KL, KOH TJ. Macrophage-based therapeutic strategies in regenerative medicine. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017;122:74-83.
[24] TANG H, ZHANG Y, JANSEN JA, et al. Effect of monocytes/macrophages on the osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in 3D co-culture spheroids. Tissue Cell. 2017;49(4):461-469.
[25] HUANG SC, EVERTS B, IVANOVA Y, et al. Cell-intrinsic lysosomal lipolysis is essential for alternative activation of macrophages. Nat Immunol. 2014;15(9):846-855.
[26] JIN HJ, BAE YK, KIM M, et al. Comparative analysis of human mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord blood as sources of cell therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(9):17986-18001.
[27] PESHKOVA M, KORNEEV A, SULEIMANOV S, et al. MSCs’ conditioned media cytokine and growth factor profiles and their impact on macrophage polarization. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023; 14(1):142.
[28] ALANAZI A, ALASSIRI M, JAWDAT D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy: a review of clinical trials for multiple sclerosis. Regen Ther. 2022;21:201-209.
[29] CORTÉS-MORALES VA, CHÁVEZ-SÁNCHEZ L, ROCHA-ZAVALETA L, et al. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells derived from cervical cancer promote M2 macrophage polarization. Cells. 2023; 12(7):1047.
[30] JIN L, DENG Z, ZHANG J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells promote type 2 macrophage polarization to ameliorate the myocardial injury caused by diabetic cardiomyopathy. J Transl Med. 2019;17(1):251.
[31] XIA TT, HU R, SHAO CJ, et al. Stanniocalcin-1 secreted by human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells regulates interleukin-10 expression via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in alveolar macrophages. Cytokine. 2023;162:156114.
[32] KO JH, OH JY. Mesenchymal stromal cells regulate THP-1-differentiated macrophage cytokine production by activating Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 pathway. Cytotherapy. 2023;25(8):858-865.
[33] ZHOU T, SUN Y, WANG Y, et al. Umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells enhance lipopolysaccharide-induced IL-10 and IL-37 production in THP-1 cells. Inflammation. 2019; 42(3):987-993.
[34] LIU H, YANG R, ZHAO S, et al. Collagen scaffolds derived from bovine skin loaded with MSC optimized M1 macrophages remodeling and chronic diabetic wounds healing. Bioeng Transl Med. 2022;8(3):e10467.
[35] CHEN X, YANG B, TIAN J, et al. Dental follicle stem cells ameliorate lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation by secreting TGF-β3 and TSP-1 to elicit macrophage M2 polarization. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(5):2290-2308.
[36] WANG M, CHEN F, WANG J, et al. Calcium phosphate altered the cytokine secretion of macrophages and influenced the homing of mesenchymal stem cells. J Mater Chem B. 2018; 6(29):4765-4774.
[37] FREYTES DO, KANG JW, MARCOS-CAMPOS I, et al. Macrophages modulate the viability and growth of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 2013;114(1):220-229.
[38] LIU F, QIU H, XUE M, et al. MSC-secreted TGF-β regulates lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophage M2-like polarization via the Akt/FoxO1 pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):345.
[39] CHOI H, LEE RH, BAZHANOV N, et al. Anti-inflammatory protein TSG-6 secreted by activated MSCs attenuates zymosan-induced mouse peritonitis by decreasing TLR2/NF-κB signaling in resident macrophages. Blood. 2011;118(2):330-338.
[40] SHI MM, ZHU YG, YAN JY, et al. Role of miR-466 in mesenchymal stromal cell derived extracellular vesicles treating inoculation pneumonia caused by multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(1):e287.
[41] HOU L, ZHU Z, JIANG F, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles alleviated silica induced lung inflammation and fibrosis in mice via circPWWP2A/miR-223-3p/NLRP3 axis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023;251:114537.
[42] XU H, ZHU Y, HSIAO AW, et al. Bioactive glass-elicited stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles regulate M2 macrophage polarization and angiogenesis to improve tendon regeneration and functional recovery. Biomaterials. 2023;294:121998.
[43] ZHENG C, SUI B, ZHANG X, et al. Apoptotic vesicles restore liver macrophage homeostasis to counteract type 2 diabetes. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10(7):e12109.
[44] XIA L, ZHANG C, LV N, et al. AdMSC-derived exosomes alleviate acute lung injury via transferring mitochondrial component to improve homeostasis of alveolar macrophages. Theranostics. 2022;12(6):2928-2947.
[45] TEO KYW, ZHANG S, LOH JT, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell exosomes mediate M2-like macrophage polarization through CD73/Ecto-5’-nucleotidase activity. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(5):1489.
[46] LI J, PAN Y, YANG J, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α-primed mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote M2 macrophage polarization via Galectin-1 and modify intrauterine adhesion on a novel murine model. Front Immunol. 2022;13:945234.
[47] KANG M, HUANG CC, LU Y, et al. Bone regeneration is mediated by macrophage extracellular vesicles. Bone. 2020;141:115627.
[48] NICOLAIDOU V, WONG MM, REDPATH AN, et al. Monocytes induce STAT3 activation in human mesenchymal stem cells to promote osteoblast formation. PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e39871.
[49] DENG H, WU L, LIU M, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes attenuate LPS-induced ARDS by modulating macrophage polarization through inhibiting glycolysis in macrophages. Shock. 2020;54(6):828-843.
[50] CAI W, ZHANG J, YU Y, et al. Mitochondrial transfer regulates cell fate through metabolic remodeling in osteoporosis. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(4):e2204871.
[51] TEISSIER V, GAO Q, SHEN H, et al. Metabolic profile of mesenchymal stromal cells and macrophages in the presence of polyethylene particles in a 3D model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):99.
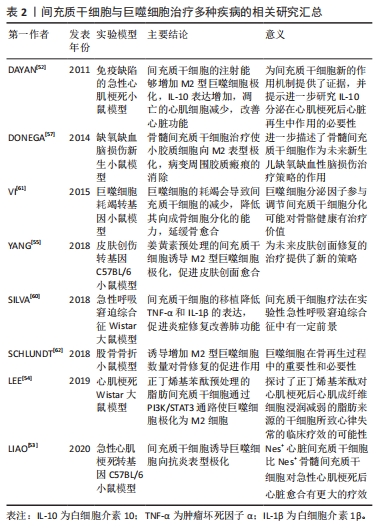
[52] DAYAN V, YANNARELLI G, BILLIA F, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells mediate a switch to alternatively activated monocytes/macrophages after acute myocardial infarction. Basic Res Cardiol. 2011;106(6):1299-1310.
[53] LIAO Y, LI G, ZHANG X, et al. Cardiac nestin+ mesenchymal stromal cells enhance healing of ischemic heart through periostin-mediated M2 macrophage polarization. Mol Ther. 2020; 28(3):855-873.
[54] LEE TM, HARN HJ, CHIOU TW, et al. Preconditioned adipose-derived stem cells ameliorate cardiac fibrosis by regulating macrophage polarization in infarcted rat hearts through the PI3K/STAT3 pathway. Lab Invest. 2019;99(5):634-647.
[55] YANG Z, HE C, HE J, et al. Curcumin-mediated bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell sheets create a favorable immune microenvironment for adult full-thickness cutaneous wound healing. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):21.
[56] DI G, DU X, QI X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells promote diabetic corneal epithelial wound healing through TSG-6-dependent stem cell activation and macrophage switch. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017;58(10):4344-4354.
[57] DONEGA V, NIJBOER CH, VAN TILBORG G, et al. Intranasally administered mesenchymal stem cells promote a regenerative niche for repair of neonatal ischemic brain injury. Exp Neurol. 2014;261:53-64.
[58] LI Y, LIU J, LIAO G, et al. Early intervention with mesenchymal stem cells prevents nephropathy in diabetic rats by ameliorating the inflammatory microenvironment. Int J Mol Med. 2018; 41(5):2629-2639.
[59] ASAMI T, ISHII M, NAMKOONG H, et al. Anti-inflammatory roles of mesenchymal stromal cells during acute Streptococcus pneumoniae pulmonary infection in mice. Cytotherapy. 2018;20(3):302-313.
[60] SILVA JD, LOPES-PACHECO M, PAZ AHR, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, adipose tissue, and lung tissue differentially mitigate lung and distal organ damage in experimental acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med. 2018;46(2):e132-e140.
[61] VI L, BAHT GS, WHETSTONE H, et al. Macrophages promote osteoblastic differentiation in-vivo: implications in fracture repair and bone homeostasis. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(6):1090-102.
[62] SCHLUNDT C, EL KHASSAWNA T, SERRA A, et al. Macrophages in bone fracture healing: their essential role in endochondral ossification. Bone. 2018;106:78-89.
[63] NATHAN K, LU LY, LIN T, et al. Precise immunomodulation of the M1 to M2 macrophage transition enhances mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis and differs by sex. Bone Joint Res. 2019;8(10):481-488.
|
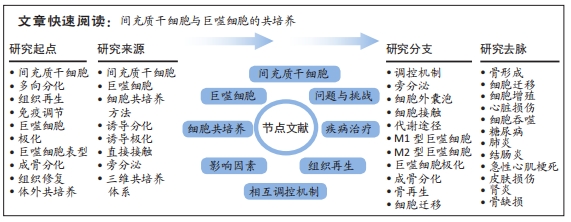
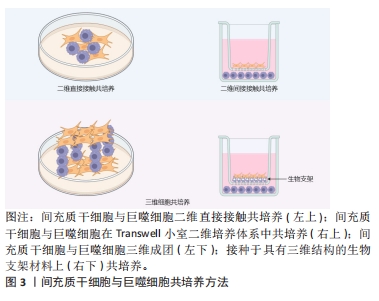
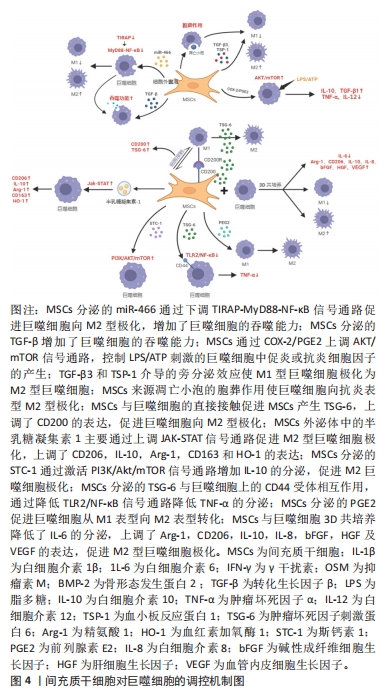

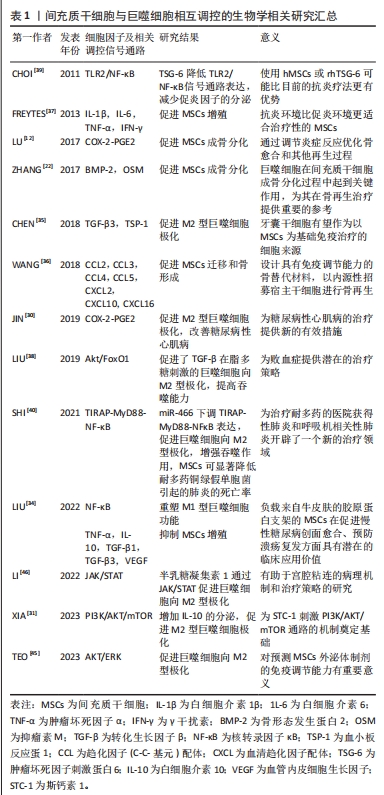


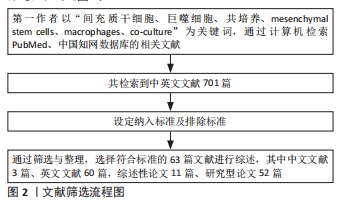
 细胞共培养理论和技术仍需成熟完善,且间充质干细胞和巨噬细胞在体内局部微环境中相互作用是高度复杂、动态和多方面的,相互调控的具体作用机制仍有许多不明确之处,相互作用的最终结果取决于多种因素,而最终结果并非总是有益的,且目前多数研究均仅停留在基础研究阶段,尚未进入早期临床试验阶段,其中仍存在一些问题有待研究。显然需要更多的研究来确定特定疾病和疾病阶段中的这些因素对两种细胞相互作用的影响,并使这种相互作用可以预测和改变,确保有利的结果,优化间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞临床运用方式,对于其治疗的发展具有重要意义。
细胞共培养理论和技术仍需成熟完善,且间充质干细胞和巨噬细胞在体内局部微环境中相互作用是高度复杂、动态和多方面的,相互调控的具体作用机制仍有许多不明确之处,相互作用的最终结果取决于多种因素,而最终结果并非总是有益的,且目前多数研究均仅停留在基础研究阶段,尚未进入早期临床试验阶段,其中仍存在一些问题有待研究。显然需要更多的研究来确定特定疾病和疾病阶段中的这些因素对两种细胞相互作用的影响,并使这种相互作用可以预测和改变,确保有利的结果,优化间充质干细胞与巨噬细胞临床运用方式,对于其治疗的发展具有重要意义。