[1] YING W, FU W, LEE YS, et al. The role of macrophages in obesity-associated islet inflammation and β-cell abnormalities. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020;16(2):81-90.
[2] FUCHS A, SAMOVSKI D, SMITH GI, et al. Associations Among Adipose Tissue Immunology, Inflammation, Exosomes and Insulin Sensitivity in People With Obesity and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology. 2021;161(3):968-981.e12.
[3] SUN H, SAEEDI P, KARURANGA S, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183:109119.
[4] MARCELIN G, GAUTIER EL, CLÉMENT K. Adipose Tissue Fibrosis in Obesity: Etiology and Challenges. Annu Rev Physiol. 2022;84:135-155.
[5] SPERRIN M, MARSHALL AD, HIGGINS V, et al. Slowing down of adult body mass index trend increases in England: a latent class analysis of cross-sectional surveys (1992-2010). Int J Obes (Lond). 2014;38(6):818-824.
[6] LIU W, LI D, CAO H, et al. Expansion and inflammation of white adipose tissue - focusing on adipocyte progenitors. Biol Chem. 2020;402(2):123-132.
[7] THOMAS D, APOVIAN C. Macrophage functions in lean and obese adipose tissue. Metabolism. 2017;72:120-143.
[8] LI S, GAO H, HASEGAWA Y, et al. Fight against fibrosis in adipose tissue remodeling. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2021;321(1):E169-E175.
[9] HEINONEN S, JOKINEN R, RISSANEN A, et al. White adipose tissue mitochondrial metabolism in health and in obesity. Obes Rev. 2020;21(2): e12958.
[10] KITA S, MAEDA N, SHIMOMURA I. Interorgan communication by exosomes, adipose tissue, and adiponectin in metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2019; 129(10):4041-4049.
[11] MOTA M, BANINI BA, CAZANAVE SC, et al. Molecular mechanisms of lipotoxicity and glucotoxicity in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism. 2016;65(8):1049-1061.
[12] MILJKOVIC I, KUIPERS AL, CVEJKUS R, et al. Myosteatosis increases with aging and is associated with incident diabetes in African ancestry men. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2016;24(2):476-482.
[13] KOENEN M, HILL MA, COHEN P, et al. Obesity, Adipose Tissue and Vascular Dysfunction. Circ Res. 2021;128(7):951-968.
[14] LAWLER HM, UNDERKOFLER CM, KERN PA, et al. Adipose Tissue Hypoxia, Inflammation, and Fibrosis in Obese Insulin-Sensitive and Obese Insulin-Resistant Subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101(4): 1422-1428.
[15] HOTAMISLIGIL GS. Inflammation, metaflammation and immunometabolic disorders. Nature. 2017;542(7640):177-185.
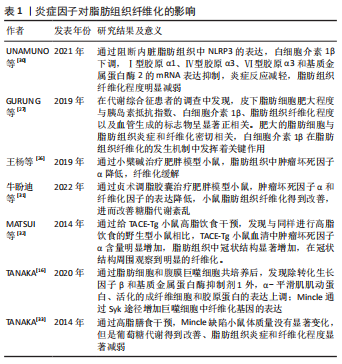
[16] TANAKA M. Molecular mechanism of obesity-induced adipose tissue inflammation; the role of Mincle in adipose tissue fibrosis and ectopic lipid accumulation. Endocr J. 2020;67(2):107-111.
[17] 陆敏,袁琳,胡娜,等.双歧杆菌三联活菌对肥胖小鼠慢性低度炎症的影响[J].卫生研究,2022,51(5):797-802.
[18] HAKA AS, BARBOSA-LORENZI VC, LEE HJ, et al. Exocytosis of macrophage lysosomes leads to digestion of apoptotic adipocytes and foam cell formation. J Lipid Res. 2016;57(6):980-992.
[19] 罗维,艾磊,王俐颖,等.下坡跑调节TRIB3/AKT通路和巨噬细胞极化改善肥胖小鼠脂肪组织慢性炎症[J].北京体育大学学报,2021,44(10): 110-120.
[20] WEISBERG SP, MCCANN D, DESAI M, et al. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest. 2003;112(12): 1796-1808.
[21] SCHERER PE. The Multifaceted Roles of Adipose Tissue-Therapeutic Targets for Diabetes and Beyond: The 2015 Banting Lecture. Diabetes. 2016;65(6): 1452-1461.
[22] HAMMARSTEDT A, GOGG S, HEDJAZIFAR S, et al. Impaired Adipogenesis and Dysfunctional Adipose Tissue in Human Hypertrophic Obesity. Physiol Rev. 2018;98(4):1911-1941.
[23] LUO T, NOCON A, FRY J, et al. AMPK Activation by Metformin Suppresses Abnormal Extracellular Matrix Remodeling in Adipose Tissue and Ameliorates Insulin Resistance in Obesity. Diabetes. 2016;65(8):2295-2310.
[24] WANG PY, FENG JY, ZHANG Z, et al. The adipokine orosomucoid alleviates adipose tissue fibrosis via the AMPK pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022; 43(2):367-375.
[25] JONES JEC, RABHI N, OROFINO J, et al. The Adipocyte Acquires a Fibroblast-Like Transcriptional Signature in Response to a High Fat Diet. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):2380.
[26] 王杨,孔敏,宋晓瑜,等.小檗碱对肥胖小鼠脂肪组织纤维化及肠道菌群的调节作用研究[J].食品研究与开发,2019,40(20):201-206.
[27] GURUNG P, MOUSSA K, ADAMS-HUET B, et al. Increased mast cell abundance in adipose tissue of metabolic syndrome: relevance to the proinflammatory state and increased adipose tissue fibrosis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2019;316(3):E504-E509.
[28] SOTÁK M, RAJAN MR, CLARK M, et al. Healthy Subcutaneous and Omental Adipose Tissue Is Associated with High Expression of Extracellular Matrix Components. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(1):520.
[29] ABDENNOUR M, REGGIO S, LE NAOUR G, et al. Association of adipose tissue and liver fibrosis with tissue stiffness in morbid obesity: links with diabetes and BMI loss after gastric bypass. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(3):898-907.
[30] UNAMUNO X, GÓMEZ-AMBROSI J, RAMÍREZ B, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome blockade reduces adipose tissue inflammation and extracellular matrix remodeling. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021;18(4):1045-1057.
[31] 牛盼迪,郑皎碧,张盛昔,等.贞术调脂胶囊对脂肪组织纤维化小鼠的改善作用[J].中药材,2022,45(9):2216-2220.
[32] MATSUI Y, TOMARU U, MIYOSHI A, et al. Overexpression of TNF-α converting enzyme promotes adipose tissue inflammation and fibrosis induced by high fat diet. Exp Mol Pathol. 2014;97(3):354-358.
[33] TANAKA M, IKEDA K, SUGANAMI T, et al. Macrophage-inducible C-type lectin underlies obesity-induced adipose tissue fibrosis. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4982.
[34] KHORAMIPOUR K, CHAMARI K, HEKMATIKAR AA, et al. Adiponectin: Structure, Physiological Functions, Role in Diseases, and Effects of Nutrition. Nutrients. 2021;13(4):1180.
[35] LUO L, LI J, WU Y, et al. Adiponectin, but Not TGF-β1, CTGF, IL-6 or TNF-α, May Be a Potential Anti-Inflammation and Anti-Fibrosis Factor in Keloid. J Inflamm Res. 2021;14:907-916.
[36] WANG X, YANG J, WU L, et al. Adiponectin inhibits the activation of lung fibroblasts and pulmonary fibrosis by regulating the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway. Bioengineered. 2022;13(4):10098-10110.
[37] RAMOS-TOVAR E, MURIEL P. Molecular Mechanisms That Link Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Fibrosis in the Liver. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020; 9(12):1279.
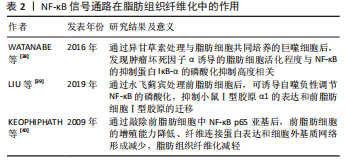
[38] WATANABE Y, NAGAI Y, HONDA H, et al. Isoliquiritigenin Attenuates Adipose Tissue Inflammation in vitro and Adipose Tissue Fibrosis through Inhibition of Innate Immune Responses in Mice. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23097.
[39] LIU X, XU Q, LONG X, et al. Silibinin-induced autophagy mediated by PPARα-sirt1-AMPK pathway participated in the regulation of type I collagen-enhanced migration in murine 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019;450(1-2):1-23.
[40] KEOPHIPHATH M, ACHARD V, HENEGAR C, et al. Macrophage-secreted factors promote a profibrotic phenotype in human preadipocytes. Mol Endocrinol. 2009;23(1):11-24.
[41] ONG CH, THAM CL, HARITH HH, et al. TGF-β-induced fibrosis: A review on the underlying mechanism and potential therapeutic strategies. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021;911:174510.
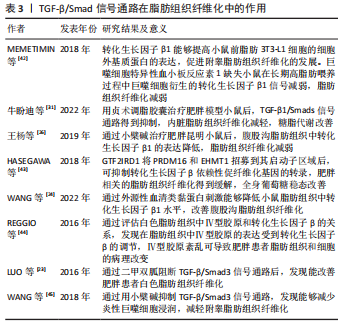
[42] MEMETIMIN H, LI D, TAN K, et al. Myeloid-specific deletion of thrombospondin 1 protects against inflammation and insulin resistance in long-term diet-induced obese male mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2018;315(6):E1194-E1203.
[43] HASEGAWA Y, IKEDA K, CHEN Y, et al. Repression of Adipose Tissue Fibrosis through a PRDM16-GTF2IRD1 Complex Improves Systemic Glucose Homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2018;27(1):180-194.e6.
[44] REGGIO S, ROUAULT C, POITOU C, et al. Increased Basement Membrane Components in Adipose Tissue During Obesity: Links With TGFβ and Metabolic Phenotypes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101(6):2578-2587.
[45] WANG L, YE X, HUA Y, et al. Berberine alleviates adipose tissue fibrosis by inducing AMP-activated kinase signaling in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;105:121-129.
[46] LU HD, LIU ZC, ZHOU LY, et al. Influence of the TLR4-mediated p38MAPK signaling pathway on chronic intermittent hypoxic-induced rat’s oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines in rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(1):352-360.
[47] OZAKI KI, AWAZU M, TAMIYA M, et al. Targeting the ERK signaling pathway as a potential treatment for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2016;310(8):E643-E651.
[48] HUANG J, LIU C, MING XF, et al. Inhibition of p38mapk Reduces Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Aging Mediated by Arginase-II. Pharmacology. 2020;105(9-10):491-504.
[49] ZHANG X, XU A, CHUNG SK, et al. Selective inactivation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase in adipose tissue protects against diet-induced obesity and improves insulin sensitivity in both liver and skeletal muscle in mice. Diabetes. 2011;60(2):486-495.
[50] VAN PELT DW, GUTH LM, WANG AY, et al. Factors regulating subcutaneous adipose tissue storage, fibrosis, and inflammation may underlie low fatty acid mobilization in insulin-sensitive obese adults. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2017;313(4):E429-E439.
[51] SUGA H, ETO H, SHIGEURA T, et al. IFATS collection: Fibroblast growth factor-2-induced hepatocyte growth factor secretion by adipose-derived stromal cells inhibits postinjury fibrogenesis through a c-Jun N-terminal kinase-dependent mechanism. Stem Cells. 2009;27(1):238-249.
[52] MALEKPOUR-DEHKORDI Z, TEIMOURIAN S, NOURBAKHSH M, et al. Metformin reduces fibrosis factors in insulin resistant and hypertrophied adipocyte via integrin/ERK, collagen VI, apoptosis, and necrosis reduction. Life Sci. 2019;233:116682. |