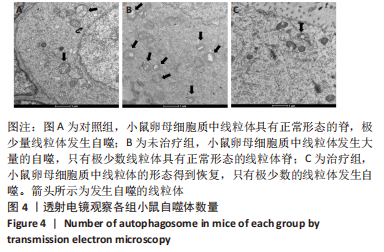
[1] PARKER J, O’BRIEN C, HAWRELAK J, et al. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: An Evolutionary Adaptation to Lifestyle and the Environment. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(3):1336.
[2] BATRA M, BHATNAGER R, KUMAR A, et al. Interplay between PCOS and microbiome: The road less travelled. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2022; 88(2):e13580.
[3] HOSSEINKHANI A, ASADI N, PASALAR M, et al. Traditional Persian Medicine and management of metabolic dysfunction in polycystic ovary syndrome. J Tradit Complement Med. 2017;8(1):17-23.
[4] DING J, SHANSHAN M, MENGCHENG C, et al. Integrated Network Pharmacology and Clinical Study to Reveal the Effects and Mechanisms of Bushen Huoxue Huatan Decoction on Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:2635375.
[5] MILLS G, BADEGHIESH A, SUARTHANA E, et al. Polycystic ovary syndrome as an independent risk factor for gestational diabetes and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: a population-based study on 9.1 million pregnancies. Hum Reprod. 2020;35(7):1666-1674.
[6] GU Y, ZHOU G, ZHOU F, et al. Life Modifications and PCOS: Old Story But New Tales. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:808898.
[7] ARMANINI D, BOSCARO M, BORDIN L, et al. Controversies in the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Treatment of PCOS: Focus on Insulin Resistance, Inflammation, and Hyperandrogenism. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(8):4110.
[8] SHIN TH, LEE BC, CHOI SW, et al. Human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate atopic dermatitis via regulation of B lymphocyte maturation. Oncotarget. 2017;8(1):512-522.
[9] 邹旺辉,钱楠楠,张萌,等.间充质干细胞临床前研究启示:间充质干细胞的细胞功能与JAK/STAT信号通路的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(19):3048-3055.
[10] KADAM P, NTEMOU E, ONOFRE J, et al. Does co-transplantation of mesenchymal and spermatogonial stem cells improve reproductive efficiency and safety in mice? Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):310.
[11] YANG Z, DU X, WANG C, et al. Therapeutic effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles on premature ovarian insufficiency in mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):250.
[12] MOHAMED Y, BASYONY MA, EL-DESOUKI NI, et al. The potential therapeutic effect for melatonin and mesenchymal stem cells on hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomedicine (Taipei). 2019;9(4):24.
[13] GENTILE P. Breast Cancer Therapy: The Potential Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Translational Biomedical Research. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(5):1179.
[14] LIU F, HU S, YANG H, et al. Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Integrated with Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Secretome to Treat Endometrial Injury in a Rat Model of Asherman’s Syndrome. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8(14): e1900411.
[15] ZHANG H, LUO Q, LU X, et al. Effects of hPMSCs on granulosa cell apoptosis and AMH expression and their role in the restoration of ovary function in premature ovarian failure mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):20.
[16] ARRIVABENE NEVES C, DOS SANTOS SILVA L, DE CARVALHO CES, et al. Culture of goat preantral follicles in situ associated with mesenchymal stem cell from bone marrow. Zygote. 2020;28(1):65-71.
[17] 李仲康,郑嘉华,田彦鹏,等.间充质干细胞治疗卵巢早衰的最新进展及机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(1):141-147.
[18] KOBAYASHI M, YOSHINO O, NAKASHIMA A, et al. Inhibition of autophagy in theca cells induces CYP17A1 and PAI-1 expression via ROS/p38 and JNK signalling during the development of polycystic ovary syndrome. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2020;508:110792.
[19] YEFIMOVA MG, LEFEVRE C, BASHAMBOO A, et al. Granulosa cells provide elimination of apoptotic oocytes through unconventional autophagy-assisted phagocytosis. Hum Reprod. 2020;35(6):1346-1362.
[20] MALAMOULI M, LEVINGER I, MCAINCH AJ, et al. The mitochondrial profile in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: impact of exercise. J Mol Endocrinol. 2022;68(3):R11-R23.
[21] VAN PHAM P, TRUONG NC, LE PT, et al. Isolation and proliferation of umbilical cord tissue derived mesenchymal stem cells for clinical applications. Cell Tissue Bank. 2016;17(2):289-302.
[22] DOU L, ZHENG Y, LI L, et al. The effect of cinnamon on polycystic ovary syndrome in a mouse model. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2018;16(1):99.
[23] JIANG W, XU J. Immune modulation by mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(1):e12712.
[24] WANG Y, CHEN X, CAO W, et al. Plasticity of mesenchymal stem cells in immunomodulation: pathological and therapeutic implications. Nat Immunol. 2014;15(11):1009-1016.
[25] LIU Q, ZHANG J, TANG Y, et al. The Effects of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation on Female Fertility Restoration in Mice. Curr Gene Ther. 2022;22(4):319-330.
[26] PASQUALI R, ZANOTTI L, FANELLI F, et al. Defining Hyperandrogenism in Women With Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Challenging Perspective. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101(5):2013-2022.
[27] BEDNARSKA S, SIEJKA A. The pathogenesis and treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome: What’s new? Adv Clin Exp Med. 2017;26(2):359-367.
[28] COLLÉE J, MAWET M, TEBACHE L, et al. Polycystic ovarian syndrome and infertility: overview and insights of the putative treatments. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2021;37(10):869-874.
[29] URBISZ AZ, CHAJEC Ł, MAŁOTA K, et al. All for one: changes in mitochondrial morphology and activity during syncytial oogenesis. Biol Reprod. 2022;106(6):1232-1253.
[30] HARVEY AJ. Mitochondria in early development: linking the microenvironment, metabolism and the epigenome. Reproduction. 2019;157(5):R159-R179.
[31] SARPARANTA J, GARCÍA-MACIA M, SINGH R. Autophagy and Mitochondria in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2017;13(4):352-369.
[32] BHARDWAJ JK, PALIWAL A, SARAF P, et al. Role of autophagy in follicular development and maintenance of primordial follicular pool in the ovary. J Cell Physiol. 2022;237(2):1157-1170.
[33] HU J, DING X, TIAN S, et al. TRIM39 deficiency inhibits tumor progression and autophagic flux in colorectal cancer via suppressing the activity of Rab7. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(4):391.
[34] SHEN Q, LIU Y, LI H, et al. Effect of mitophagy in oocytes and granulosa cells on oocyte quality. Biol Reprod. 2021;104(2):294-304. |