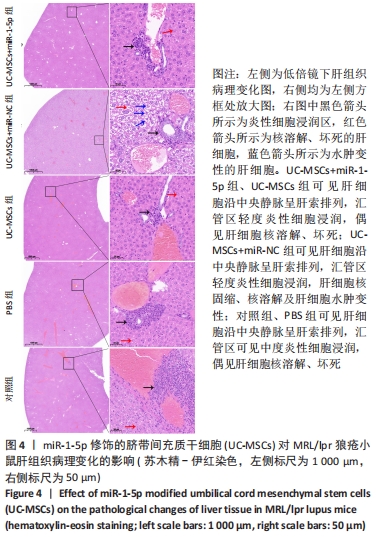
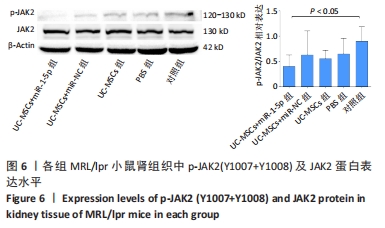
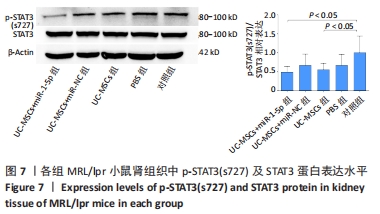
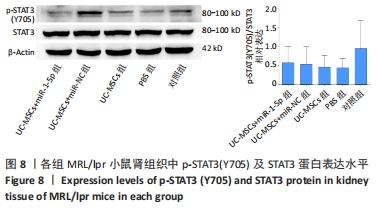
[1] TRENTIN F, ZUCCHI D, SIGNORINI V, et al. One year in review 2021: systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2021;39(2):231-241.
[2] WU YR, HSING CH, CHIU CJ, et al. Roles of IL-1 and IL-10 family cytokines in the progression of systemic lupus erythematosus: Friends or foes. IUBMB Life. 2022;74(2):143-156.
[3] ROGER I, MILARA J, MONTERO P, et al. The Role of JAK/STAT Molecular Pathway in Vascular Remodeling Associated with Pulmonary Hypertension. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(9):4980.
[4] ITALIANI P, MANCA ML, ANGELOTTI F, et al. IL-1 family cytokines and soluble receptors in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):27.
[5] ALUNNO A, PADJEN I, FANOURIAKIS A, et al. Pathogenic and Therapeutic Relevance of JAK/STAT Signaling in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Integration of Distinct Inflammatory Pathways and the Prospect of Their Inhibition with an Oral Agent. Cells. 2019;8(8):898.
[6] XIANG M, FENG Y, WANG Y, et al. Correlation between circulating interleukin-18 level and systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):4707.
[7] VERMEIRE S, SCHREIBER S, PETRYKA R, et al. Clinical remission in patients with moderate-to-severe Crohn’s disease treated with filgotinib (the FITZROY study): results from a phase 2, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;389(10066):266-275.
[8] WU YN, ZHANG R, SONG XC, et al. C6orf120 gene knockout in rats mitigates concanavalin Ainduced autoimmune hepatitis via regulating NKT cells. Cell Immunol. 2022;371:104467.
[9] MUSTAFA M, BAWAZIR YM. Acute liver failure as the first feature of systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Int. 2021;41(2):469-474.
[10] MOK CC. The Jakinibs in systemic lupus erythematosus: progress and prospects. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2019;28(1):85-92.
[11] WANG DH, WALLACE DJ. New Insights Into Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Therapies: 2010-2020. J Clin Rheumatol. 2022;28(1): e217-e221.
[12] XIE Q, LIU R, JIANG J, et al. What is the impact of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on clinical treatment. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):519.
[13] ZHANG Y, XIA Y, NI S, et al. Transplantation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviates pneumonitis of MRL/lpr mice. J Thorac Dis. 2014;6(2):109-117.
[14] WANG D, NIU L, FENG X, et al. Long-term safety of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells transplantation for systemic lupus erythematosus: a 6-year follow-up study. Clin Exp Med. 2017;17(3): 333-340.
[15] QU Q, WANG L, BING W, et al. miRNA-126-3p carried by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell enhances endothelial function through exosome-mediated mechanisms in vitro and attenuates vein graft neointimal formation in vivo. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):464.
[16] FUJII R, OSAKA E, SATO K, et al. MiR-1 Suppresses Proliferation of Osteosarcoma Cells by Up-regulating p21 via PAX3. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2019;16(1):71-79.
[17] XU C, LU Y, PAN Z, et al. The muscle-specific microRNAs miR-1 and miR-133 produce opposing effects on apoptosis by targeting HSP60, HSP70 and caspase-9 in cardiomyocytes. J Cell Sci. 2011;124(Pt 18):3187.
[18] HAN C, SHEN JK, HORNICEK FJ, et al. Regulation of microRNA-1 (miR-1) expression in human cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2017;1860(2):227-232.
[19] GEORGANTAS RW, STREICHER K, GREENBERG SA, et al. Inhibition of myogenic microRNAs 1, 133, and 206 by inflammatory cytokines links inflammation and muscle degeneration in adult inflammatory myopathies. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(4):1022-1033.
[20] NAVARRO QUIROZ E, NAVARRO QUIROZ R, PACHECO LUGO L, et al. Integrated analysis of microRNA regulation and its interaction with mechanisms of epigenetic regulation in the etiology of systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS One. 2019;14(6):e0218116.
[21] 胡明智,张晶莹,杨国安,等.miR-1-5p修饰脐带间充质干细胞对系统性红斑狼疮T淋巴细胞亚群的免疫调节[J].中国组织工程研究, 2021,25(31):4928-4938.
[22] ZHONG Z, LI H, ZHONG H, et al. Clinical efficacy and safety of rituximab in lupus nephritis. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13:845-856.
[23] ZHOU T, ZHANG X, LIN W, et al. Multitarget Therapy: An Effective and Safe Therapeutic Regimen for Lupus Nephritis. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2019;22(1):365-375.
[24] ZAMANI P, OSKUEE RK, ATKIN SL, et al. MicroRNAs as important regulators of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2020; 150:50-61.
[25] SONDERGAARD HB, AIRAS L, CHRISTENSEN JR, et al. Pregnancy-Induced Changes in microRNA Expression in Multiple Sclerosis. Front Immunol. 2021;11:552101.
[26] ZILAHI E, ADAMECZ Z, BODOKI L, et al. Dysregulated expression profile of myomiRs in the skeletal muscle of patients with polymyositis. EJIFCC. 2019; 30(2):237-245.
[27] TIAN M, ZHOU Y, JIA H, et al. The Clinical Significance of Changes in the Expression Levels of MicroRNA-1 and Inflammatory Factors in the Peripheral Blood of Children with Acute-Stage Asthma. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:7632487.
[28] GUAN YT, XIE Y, LI DS, et al. Comparison of biological characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells derived from the human umbilical cord and decidua parietalis. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(1):633-639.
[29] YANG Y, ZHAO Y, ZHANG L, et al. The Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of Liver Diseases: Mechanism, Efficacy, and Safety Issues. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:655268.
[30] LI Y, WANG F, LIANG H, et al. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation therapy for type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):273.
[31] SCHIESS M, SUESCUN J, DOURSOUT MF, et al. Allogeneic Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Safety in Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease. Mov Disord. 2021;36(8):1825-1834.
[32] COZENE BM, RUSSO E, ANZALONE R, et al. Mitochondrial activity of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Brain Circ. 2021;7(1): 33-36.
[33] GU F, WANG D, ZHANG H, et al. Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for lupus nephritis patients refractory to conventional therapy. Clin Rheumatol. 2014;33(11):1611-1619.
[34] WANG D, ZHANG H, LIANG J, et al. A Long-Term Follow-Up Study of Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell Transplantation in Patients with Drug-Resistant Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Stem Cell Reports. 2018;10(3):933-941.
[35] ZHAO C, ZHANG L, KONG W, et al. Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibit Cadherin-11 Expression by Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Immunol Res. 2015;2015: 137695.
[36] BI ZM, ZHOU QF, GENG Y, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate experimental cirrhosis through activation of keratinocyte growth factor by suppressing microRNA-199. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016;20(23):4905-4912.
[37] ABBASZADEH H, GHORBANI F, DERAKHSHANI M, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: A novel therapeutic paradigm. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(2):706-717.
[38] DE ALMEIDA PE, RANSOHOFF JD, NAHID A, et al. Immunogenicity of pluripotent stem cells and their derivatives. Circ Res. 2013;112(3):549-561.
[39] YANG C, CHEN Y, ZHONG L, et al. Homogeneity and heterogeneity of biological characteristics in mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cords and exfoliated deciduous teeth. Biochem Cell Biol. 2020; 98(3):415-425.
[40] ZHANG B, ZHANG J, SHI H, et al. A novel method to isolate mesenchymal stem cells from mouse umbilical cord. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(1):861-869.
[41] VAN PEL M, FIBBE WE, SCHEPERS K. The human and murine hematopoietic stem cell niches: are they comparable? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2016;1370(1):55-64.
[42] BERNARDO ME, FIBBE WE. Mesenchymal stromal cells: sensors and switchers of inflammation. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;13(4):392-402.
[43] MEZA-LEÓN B, GRATZINGER D, AGUILAR-NAVARRO AG, et al. Human, mouse, and dog bone marrow show similar mesenchymal stromal cells within a distinctive microenvironment. Exp Hematol. 2021;100:41-51.
[44] 郭波,刘佳,崔晓兰,等.人脐带间充质干细胞联合免疫干预治疗1型糖尿病小鼠的实验研究[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(13): 2016-2021.
[45] 李娟娟,王有为,马凤霞,等.比较人脐带和胎盘间充质干细胞对小鼠急性移植物抗宿主病的预防作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2017, 21(5): 693-700.
[46] LIU J, LU X, LOU Y, et al. Xenogeneic Transplantation of Human Placenta-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviates Renal Injury and Reduces Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Lupus Nephritis. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:9370919.
[47] MOYA A, PAQUET J, DESCHEPPER M, et al. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Failure to Adapt to Glucose Shortage and Rapidly Use Intracellular Energy Reserves Through Glycolysis Explains Poor Cell Survival After Implantation. Stem Cells. 2018;36(3):363-376.
[48] SAGE EK, THAKRAR RM, JANES SM. Genetically modified mesenchymal stromal cells in cancer therapy. Cytotherapy. 2016;18(11):1435-1445.
[49] FOPPIANI EM, CANDINI O, MASTROLIA I, et al. Impact of HOXB7 overexpression on human adipose-derived mesenchymal progenitors. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):101.
[50] DAMASCENO PKF, DE SANTANA TA, SANTOS GC, et al. Genetic Engineering as a Strategy to Improve the Therapeutic Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells in Regenerative Medicine. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:737.
[51] XIN P, XU X, DENG C, et al. The role of JAK/STAT signaling pathway and its inhibitors in diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;80:106210.
[52] JI J, WU Y, MENG Y, et al. JAK-STAT signaling mediates the senescence of bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2017; 49(3):208-215.
[53] SHAN J, JIN H, XU Y. T Cell Metabolism: A New Perspective on Th17/Treg Cell Imbalance in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1027.
[54] EGWUAGU CE. STAT3 in CD4+ T helper cell differentiation and inflammatory diseases. Cytokine. 2009;47(3):149-156.
[55] ZUO H, WENG K, LUO M, et al. A MicroRNA-1-Mediated Inhibition of the NF-κB Pathway by the JAK-STAT Pathway in the Invertebrate Litopenaeus vannamei. J Immunol. 2020;204(11):2918-2930.
[56] LI L, MA X, ZHAO YF, et al. MiR-1-3p facilitates Th17 differentiation associating with multiple sclerosis via targeting ETS1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(12):6881-6892.
[57] LIU D, ZHANG N, ZHANG X, et al. MiR-410 Down-Regulates the Expression of Interleukin-10 by Targeting STAT3 in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;39(1):303-315.
[58] WEBB GJ, SIMINOVITCH KA, HIRSCHFIELD GM. The immunogenetics of primary biliary cirrhosis: A comprehensive review. J Autoimmun. 2015;64:42-52.
[59] JOSHITA S, UMEMURA T, NAKAMURA M, et al. STAT4 gene polymorphisms are associated with susceptibility and ANA status in primary biliary cirrhosis. Dis Markers. 2014;2014:727393.
[60] FANG X, ZAMAN MH, GUO X, et al. Role of Hepatic Deposited Immunoglobulin G in the Pathogenesis of Liver Damage in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1457.
[61] 陈蓓迪.系统性红斑狼疮患者肠道微生物群特征的组学研究[D].北京:北京协和医学院,2021.
[62] 朱继开,钟煜,王璐璇,等.肠道杯状细胞与黏蛋白的研究进展[J].继续医学教育,2017,31(7):139-140.
[63] 黄春兰,曾悦.杯状细胞及肠道黏液屏障的功能研究[J].国际消化病杂志,2017,37(6):357-360.
[64] HENEGHAN AF, PIERRE JF, KUDSK KA. JAK-STAT and intestinal mucosal immunology. JAKSTAT. 2013;2(4):e25530.
[65] MA J, LAM IKY, LAU CS, et al. Elevated Interleukin-18 Receptor Accessory Protein Mediates Enhancement in Reactive Oxygen Species Production in Neutrophils of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients. Cells. 2021;10(5):964.
[66] VERWEYEN E, HOLZINGER D, WEINHAGE T, et al. Synergistic Signaling of TLR and IFNalpha/beta Facilitates Escape of IL-18 Expression from Endotoxin Tolerance. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;201(5):526-539.
[67] YASUDA K, NAKANISHI K, TSUTSUI H. Interleukin-18 in Health and Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(3):649.
|