中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (24): 3880-3885.doi: 10.12307/2022.570
• 脐带脐血干细胞 umbilical cord blood stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
脐带间充质干细胞对衰老胸腺上皮细胞的作用及影响
杨再玲1,2,田 川2,吕冠柯1,潘 杭1,2,朱向情2,王金祥2,王 凯2,阮光萍2,何志旭3,舒丽萍1,潘兴华2
- 1贵州医科大学,组织工程与干细胞实验中心,贵州省贵阳市 550004;2中国人民解放军联勤保障部队第九二〇医院干细胞与免疫细胞生物医药技术国家地方联合工程实验室、云南省细胞治疗技术转化医学重点实验室、昆明市干细胞与再生医学重点实验室、基础医学实验室,云南省昆明市 650032;3遵义医科大学附属医院儿科学教研室,贵州省遵义市 563100
Effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on aging thymus epithelial cells
Yang Zailing1, 2, Tian Chuan2, Lyu Guanke1, Pan Hang1, 2, Zhu Xiangqing2, Wang Jinxiang2, Wang Kai2, Ruan Guangping2, He Zhixu3, Shu Liping1, Pan Xinghua2
- 1Tissue Engineering and Stem Cell Experimental Center, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2Stem Cells and Immune Cells Biomedical Techniques Integrated Engineering Laboratory of State and Regions, Cell Therapy Technology Transfer Medical Key Laboratory of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China; 3Department of Pediatrics, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563100, Guizhou Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
胸腺上皮细胞:是胸腺微环境的最主要成分。根据表型和定位,胸腺上皮细胞可分为皮质胸腺上皮细胞和髓质胸腺上皮细胞。
Ki67:是人类第10号染色体上MKI-67基因所编码的一种蛋白,与细胞增殖密切相关并且可能是细胞增殖所必需的核蛋白。
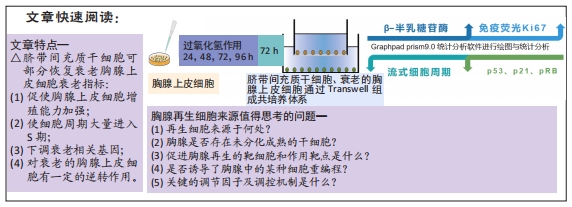
背景:据文献报道,胸腺上皮细胞数量减少、功能紊乱是胸腺退化的重要因素之一,可导致胸腺发育、增殖缺陷以及外周T细胞功能障碍。课题组前期研究发现间充质干细胞在体内可以逆转衰老胸腺的结构和功能,具体作用机制尚不清楚。
目的:探讨脐带间充质干细胞在体外对衰老胸腺上皮细胞的作用及影响。
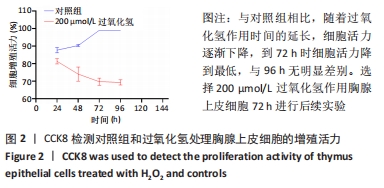
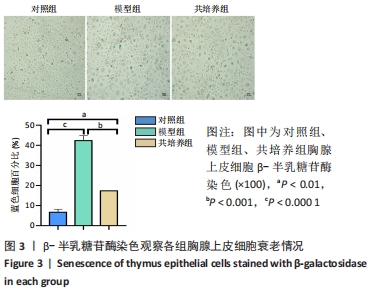
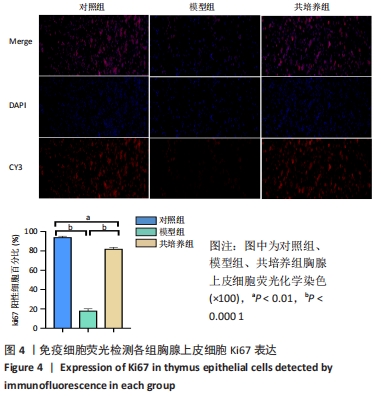
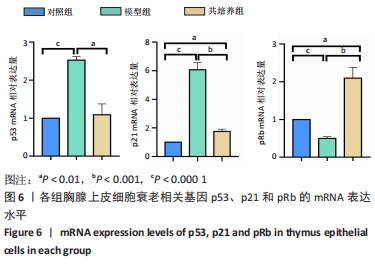
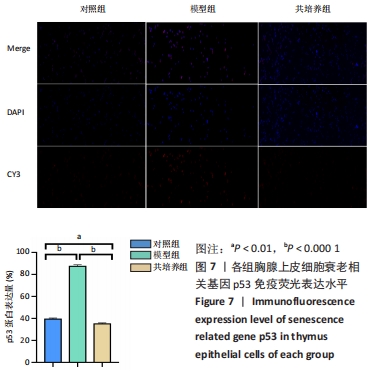
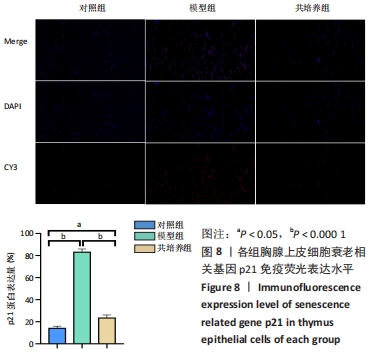
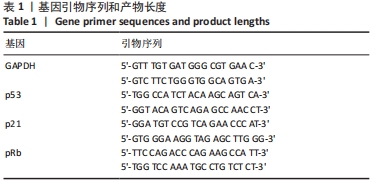
方法:将 200 μmol/L 过氧化氢分别作用于第4代胸腺上皮细胞24,48,72,96 h,通过CCK8法检测细胞活力,筛选200 μmol/L 过氧化氢作用72 h为制备衰老模型合适时间。取第4代脐带间充质干细胞,与衰老的胸腺上皮细胞共培养48 h后进行β-半乳糖苷酶染色检测衰老细胞变化;免疫荧光ki-67染色检测细胞增殖活性;流式细胞仪分析细胞周期变化;免疫组织化学染色法检测p53、p21蛋白阳性表达量;RT-PCR 检测衰老相关基因p21、p53以及pRb的mRNA表达水平。
结果与结论:与模型组相比,脐带间充质干细胞共培养组衰老胸腺上皮细胞β-半乳糖苷酶表达降低,细胞增殖能力升高,G2期细胞减少而S期细胞增多,免疫荧光p53、p21表达降低,p53、p21 mRNA 表达水平降低而pRb mRNA表达水平升高。共培养组β-半乳糖苷酶表达、细胞增殖能力、p53、p21、pRb表达等结果向着对照组趋势靠近。结果表明,脐带间充质干细胞能调控胸腺上皮细胞的衰老相关指标表达,促进胸腺上皮细胞的增殖与分裂,以逆转胸腺上皮细胞的衰老。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7642-5270 (杨再玲)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: