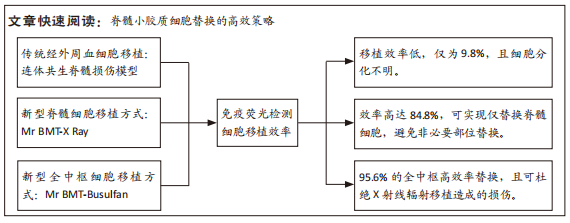
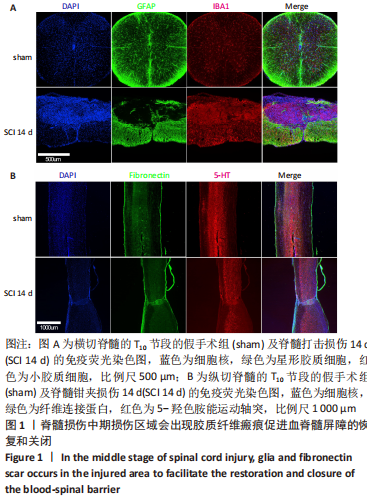
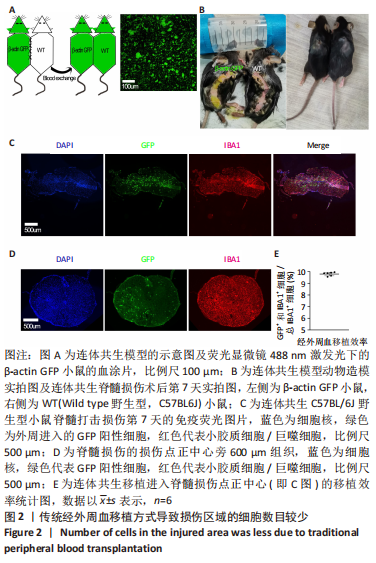
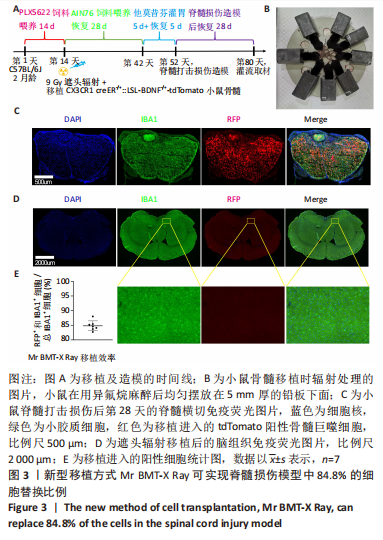
[1] LEE BB, CRIPPS RA, FITZHARRIS M, et al. The global map for traumatic spinal cord injury epidemiology: update 2011, global incidence rate. Spinal Cord. 2014;52(2):110-116.
[2] KWON BK, TETZLAFF W, GRAUER JN, et al. Pathophysiology and pharmacologic treatment of acute spinal cord injury. Spine J. 2004;4(4): 451-464.
[3] KIYOTAKE EA, MARTIN MD, DETAMORE MS. Regenerative rehabilitation with conductive biomaterials for spinal cord injury. Acta Biomater. 2022;139: 43-64.
[4] XIANG L, CHEN Y. Stem cell transplantation for treating spinal cord injury: A literature comparison between studies of stem cells obtained from various sources. Neural Regen Res. 2012;7(16):1256-1263.
[5] RAMALHO BDS, ALMEIDA FM, SALES CM, et al. Injection of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by intravenous or intraperitoneal routes is a viable alternative to spinal cord injury treatment in mice. Neural Regen Res. 2018; 13(6):1046-1053.
[6] ZHANG SX, HUANG F, GATES M, et al. Role of endogenous Schwann cells in tissue repair after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(2):177-185.
[7] ASSINCK P, DUNCAN GJ, HILTON BJ, et al. Cell transplantation therapy for spinal cord injury. Nat Neurosci. 2017;20(5):637-647.
[8] WANG J, CHU R, NI N, et al. The effect of Matrigel as scaffold material for neural stem cell transplantation for treating spinal cord injury. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):2576.
[9] HONMOU O, YAMASHITA T, MORITA T, et al. Intravenous infusion of auto serum-expanded autologous mesenchymal stem cells in spinal cord injury patients: 13 case series. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2021;203:106565.
[10] XU Z, RAO Y, HUANG Y, et al. Efficient Strategies for Microglia Replacement in the Central Nervous System. Cell Rep. 2020;32(6):108041.
[11] SHEN Y, JIANG X, MENG L, et al. Transplantation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Prevents Radiation-Induced Artery Injury by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:5942916.
[12] LI Y, HE X, KAWAGUCHI R, et al. Microglia-organized scar-free spinal cord repair in neonatal mice. Nature. 2020;587(7835):613-618.
[13] WILKINSON FL, SERGIJENKO A, LANGFORD-SMITH KJ, et al. Busulfan conditioning enhances engraftment of hematopoietic donor-derived cells in the brain compared with irradiation. Mol Ther. 2013;21(4):868-876.
[14] KIERDORF K, KATZMARSKI N, HAAS CA, et al. Bone marrow cell recruitment to the brain in the absence of irradiation or parabiosis bias. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58544.
[15] YOUSHANI AS, ROWLSTON S, O’LEARY C, et al. Non-myeloablative busulfan chimeric mouse models are less pro-inflammatory than head-shielded irradiation for studying immune cell interactions in brain tumours. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;16(1):25.
[16] XU Z, ZHOU X, PENG B, et al. Microglia replacement by bone marrow transplantation (Mr BMT) in the central nervous system of adult mice. STAR Protoc. 2021;2(3):100666.
[17] WEN S, ZOU ZR, CHENG S, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 improves energy metabolism after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(6):1332-1338.
[18] LI Q, GUO Y, XU C, et al. Therapy of spinal cord injury by folic acid polyethylene glycol amine-modified zeolitic imidazole framework-8 nanoparticles targeted activated M/Ms. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:959324.
[19] KAMRAN P, SERETI KI, ZHAO P, et al. Parabiosis in mice: a detailed protocol. J Vis Exp. 2013;(80):50556.
[20] ZHOU T, LI Y, LI X, et al. Microglial debris is cleared by astrocytes via C4b-facilitated phagocytosis and degraded via RUBICON-dependent noncanonical autophagy in mice. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):6233.
[21] FIGLEY SA, KHOSRAVI R, LEGASTO JM, et al. Characterization of vascular disruption and blood-spinal cord barrier permeability following traumatic spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2014;31(6):541-552.
[22] BELLVER-LANDETE V, BRETHEAU F, MAILHOT B, et al. Microglia are an essential component of the neuroprotective scar that forms after spinal cord injury. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):518.
[23] DEPAUL MA, PALMER M, LANG BT, et al. Intravenous multipotent adult progenitor cell treatment decreases inflammation leading to functional recovery following spinal cord injury. Sci Rep. 2015;5:16795.
[24] HUANG Y, XU Z, XIONG S, et al. Repopulated microglia are solely derived from the proliferation of residual microglia after acute depletion. Nat Neurosci. 2018;21(4):530-540.
[25] GUIMARÃES RM, DAVOLI-FERREIRA M, FONSECA MM, et al. Frontline Science: Blood-circulating leukocytes fail to infiltrate the spinal cord parenchyma after spared nerve injury. J Leukoc Biol. 2019;106(3):541-551.
[26] NIU C, YU J, ZOU T, et al. Identification of hematopoietic stem cells residing in the meninges of adult mice at steady state. Cell Rep. 2022;41(6):111592.
[27] SAHU A, CLEMENS ZJ, SHINDE SN, et al. Regulation of aged skeletal muscle regeneration by circulating extracellular vesicles. Nat Aging. 2021;1(12): 1148-1161.
[28] MA S, WANG S, YE Y, et al. Heterochronic parabiosis induces stem cell revitalization and systemic rejuvenation across aged tissues. Cell Stem Cell. 2022;29(6):990-1005.e10.
[29] RITFELD GJ, PATEL A, CHOU A, et al. The role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in bone marrow stromal cell-mediated spinal cord repair. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(11):2209-2220.
[30] ZHANG J, RONG P, ZHANG L, et al. IL4-driven microglia modulate stress resilience through BDNF-dependent neurogenesis. Sci Adv. 2021;7(12):eabb9888.
[31] GENSEL JC, ZHANG B. Macrophage activation and its role in repair and pathology after spinal cord injury. Brain Res. 2015;1619:1-11.
[32] KIGERL KA, GENSEL JC, ANKENY DP, et al. Identification of two distinct macrophage subsets with divergent effects causing either neurotoxicity or regeneration in the injured mouse spinal cord. J Neurosci. 2009;29(43): 13435-13444.
[33] MIRON VE, BOYD A, ZHAO JW, et al. M2 microglia and macrophages drive oligodendrocyte differentiation during CNS remyelination. Nat Neurosci. 2013;16(9):1211-1218.
[34] SHIBUYA Y, KUMAR KK, MADER MM, et al. Treatment of a genetic brain disease by CNS-wide microglia replacement. Sci Transl Med. 2022;14(636): eabl9945.
[35] PARIHAR VK, MAROSO M, SYAGE A, et al. Persistent nature of alterations in cognition and neuronal circuit excitability after exposure to simulated cosmic radiation in mice. Exp Neurol. 2018;305:44-55.
[36] PARIHAR VK, ALLEN BD, CARESSI C, et al. Cosmic radiation exposure and persistent cognitive dysfunction. Sci Rep. 2016;6:34774.
[37] LU P, WOODRUFF G, WANG Y, et al. Long-distance axonal growth from human induced pluripotent stem cells after spinal cord injury. Neuron. 2014;83(4):789-796.
[38] MARQUARDT LM, DOULAMES VM, WANG AT, et al. Designer, injectable gels to prevent transplanted Schwann cell loss during spinal cord injury therapy. Sci Adv. 2020;6(14):eaaz1039.
[39] CUSIMANO M, BIZIATO D, BRAMBILLA E, et al. Transplanted neural stem/precursor cells instruct phagocytes and reduce secondary tissue damage in the injured spinal cord. Brain. 2012;135(Pt 2):447-460.
[40] SAILOR KA, AGORANOS G, LÓPEZ-MANZANEDA S, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation chemotherapy causes microglia senescence and peripheral macrophage engraftment in the brain. Nat Med. 2022;28(3):517-527.
[41] DISERBO M, AGIN A, LAMPROGLOU I, et al. Blood-brain barrier permeability after gamma whole-body irradiation: an in vivo microdialysis study. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2002;80(7):670-678.
[42] LI YQ, CHEN P, JAIN V, et al. Early radiation-induced endothelial cell loss and blood-spinal cord barrier breakdown in the rat spinal cord. Radiat Res. 2004;161(2):143-152.
[43] LAMPRON A, LESSARD M, RIVEST S. Effects of myeloablation, peripheral chimerism, and whole-body irradiation on the entry of bone marrow-derived cells into the brain. Cell Transplant. 2012;21(6):1149-1159.
|