1.1 设计 随机对照动物实验,两两比较使用最小显著性差异法 (LSD)。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2022年 10-12 月在首都医科大学附属北京潞河医院中心实验室完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 实验动物 成年雌性 SD 大鼠36只,6-8周龄,体质量 (220±20) g,由北京维通利华公司提供,动物许可证号:SCXK(京)2021-0011,饲养环境:湿度 40%-47%,温度 20-25 ℃,光照12 h阴暗12 h。实验方案经首都医科大学动物实验伦理委员会批准(批准号:AEEI-2023-005)。实验过程遵循了国际兽医学编辑协会《关于动物伦理与福利的作者指南共识》和本地及国家法规。实验动物在异氟烷、空气混合物麻醉下进行所有手术,并尽一切努力最大限度地减少其疼痛、痛苦和死亡。
1.3.2 主要药物与试剂 利鲁唑(中国食品药品检定研究院,图1为结构式);环糊精(利鲁唑的溶剂,美国 Sigma 公司);苏木精-伊红染色试剂盒(中国索莱宝公司);ELISA 试剂盒 IL-1β、IL-18(中国武汉华美公司);兔抗鼠NLRP3、Caspase-1、GSDMD抗体、小鼠单克隆抗体Iba1 抗体(美国Abcam公司);兔抗鼠IL-1β抗体、山羊抗兔二抗、山羊抗鼠二抗(中国武汉三鹰公司);DAPI(中国上海碧云天生物技术有限公司);BCA 蛋白浓度测定试剂盒(美国 Thermo Fisher Scientific 公司);RIPA 裂解液(中国上海碧云天生物技术有限公司);Triton X-100(美国 Sigma 公司);封闭用正常山羊血清原液(中国北京中杉金桥生物技术有限公司)。
1.3.3 实验主要仪器设备 第3代脊髓挫伤打击器(美国新泽西州立罗格斯大学);激光共聚焦显微镜(日本尼康公司);低温高速离心机(德国 Eppendorf 公司);冰冻切片机(德国Leica公司);超声破碎器(美国 Thermo Fisher Scientific 公司);荧光显微镜(日本尼康公司);酶标仪(美国 Thermo Fisher Scientific 公司)。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 大鼠分组、脊髓损伤模型制备及利鲁唑给药方式 36只雌性 SD大鼠采用随机数字表法随机分成 3 组(n=12):假手术组单纯椎板开窗,不做脊髓打击;模型组打击脊髓+腹腔注射利鲁唑的溶剂环糊精溶液4 mg/kg(利鲁唑组按照4 mg/kg利鲁唑给药,模型组也是按照大鼠体质量计算出假设注射利鲁唑的量,给予注射同体积的环糊精);利鲁唑组打击脊髓+腹腔注射利鲁唑溶液4 mg/kg。术前禁食6 h后,吸入异氟烷与空气混合物麻醉、备皮消毒,以T10为中心行背部正中切口,长约2 cm,逐层分离肌肉及软组织,充分暴露 T9-T11节段,及时止血,咬骨钳去除 T10 棘突及椎板,保留硬膜囊完整,充分暴露 T10 脊髓后,假手术组直接逐层缝合切口,其他两组使用modelⅢ脊髓挫伤打击器(10 g,2.5 cm)打击T10,观察到损伤局部迅速出现充血水肿(图2),双后肢抽搐,尾巴摆动,则造模成功。依次缝合肌肉、筋膜和皮肤,消毒后将大鼠置于电热毯等待完全苏醒。术后每天2次按摩膀胱辅助排尿,直至建立完整的排尿反射。模型组及利鲁唑组脊髓损伤后立即腹腔注射给药,每天2次,连续3 d。



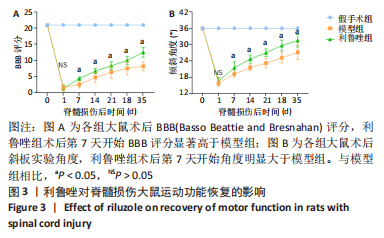
1.4.2 运动功能评分 造模术后即刻以及第1,7,14,21,35天进行功能学评分:①BBB(Basso Beattie and Bresnahan scale score)评分:采用双人双盲法,由非此组实验人员完成,分别独立观察各组大鼠下肢的活动情况,每只大鼠每次的观察时间不少于 5 min。②斜板实验评分:将脊髓损伤大鼠放置于斜板实验操作平台上,板面具有一定的摩擦力以利于大鼠保持位置。调试斜板与水平面的相对角度,观察脊髓损伤大鼠在斜面上保持平稳的最大角度(5 s内不掉落,即可认为能保持平稳),测量角度并重复3次取平均值。同样采用双人双盲法,由非此组实验人员完成。
1.4.3 灌注取材及切片 术后3,35 d,每组每个时间点随机选 6 只大鼠,异氟烷(鲁南贝特制药,山东临沂)吸入麻醉,诱导的浓度为4%,维持麻醉浓度为2%。取以损伤区为中心约1 cm长的脊髓组织。麻醉后灌入生理盐水(用于蛋白实验的3只取完组织立即放入-80 ℃冰箱保存),待血液置换完毕后用于组织学实验的3只大鼠灌注10%组织固定液固定,并室温下固定4 h;将脊髓组织置于30%蔗糖 PBS中脱水,行冰冻切片,切片厚度 10 μm。术后3 d 进行Western blot、ELISA检测及免疫荧光检测;术后35 d进行苏木精-伊红染色及电生理评估。
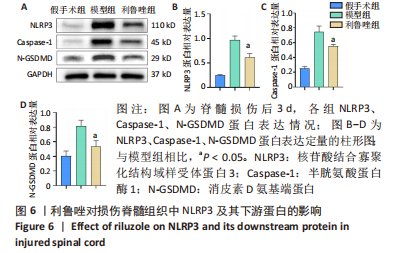
1.4.4 Western blot检测 按照 100 mg 组织∶400 µL Ripa裂解液(加入1%蛋白酶磷酸酶抑制剂)的比例冰上裂解蛋白30 min,于 4 ℃,12 000×g离心10 min,取上清液,BCA法配平各组蛋白浓度。蛋白样品(10 μg)经 SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳分离,并将蛋白转移至PVDF膜上,用 5% 脱脂牛奶室温封闭 1 h,然后加入 NLRP3(1∶1 000)、Caspase-1(1∶1 000)、GSDMD(1∶1 000)、GAPDH(1∶5 000)一抗于 4 ℃孵育过夜,加入二抗(1∶5 000)室温孵育2 h,通过化学发光法显示免疫反应条带。以 GAPDH 作为内参,用 Image J 获得条带的灰度值,蛋白表达水平用目的条带灰度值与内参条带灰度值的比值来确定。
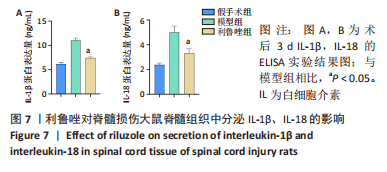
1.4.5 ELISA检测 从-80 ℃冰箱中取出之前配平的组织匀浆并稀释10倍,参照试剂盒操作指南进行实验。具体如下:设置标准品孔和样本孔,加入标准品溶液或样本溶液。于37 ℃
孵育箱中孵育 2 h,后加入生物素标记抗体工作液,37 ℃孵育1 h。洗板后每个孔内滴加辣根过氧化物酶标记亲和素工作液,37 ℃孵育1 h。洗板后每个孔内滴加底物溶液,37 ℃孵育20 min。取出酶标板后,立即向每个孔内按照顺序滴加终止溶液,将酶标板移至酶标仪中进行检测,选择 450 nm 的波长检测吸光度值。根据标准品孔的吸光度值绘制标准曲线,通过计算得出方程后将样本孔的吸光度值依次代入,最终得出每个样品的浓度(注意标准品双孔和样品所设的3孔,需先取平均值再进行计算)。
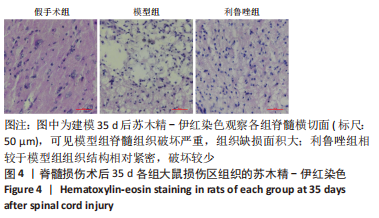
1.4.6 苏木精-伊红染色 将冰冻切片用4 ℃ PBS洗涤2 min,去除包埋剂,60 ℃ 烘片30 min。苏木精染液染色 5 min,冲洗,分化液分化,冲洗,蓝化液反蓝,伊红染色 2 min,漂洗,常规脱水、透明,滴入中性树脂封固,显微镜下观察脊髓组织病理学变化。
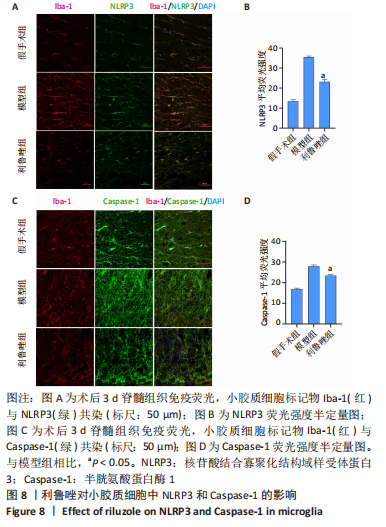
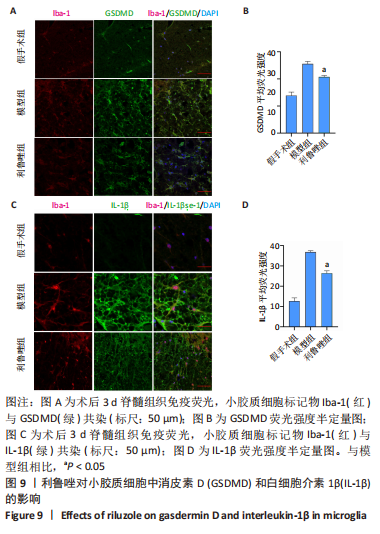
1.4.7 免疫荧光 组织切片室温下复温30 min,将脊髓组织切片置于 4 ℃ PBS中清洗2 min;60 ℃ 烘片30 min,再次PBS洗3遍。加入 0.5%TritonX-100与2%BSA 溶液进行抗原打孔、封闭1 h;加入一抗NLRP3、Caspase-1、GSDMD、IL-1β,置于 4 ℃孵育过夜;加入荧光二抗室温避光孵育 1 h,置于 PBS 中清洗 3 次,每次 5 min;加入 DAPI室温下避光染核 5 min,PBS 漂洗 3 次,于激光共聚焦显微镜下观察和拍照。
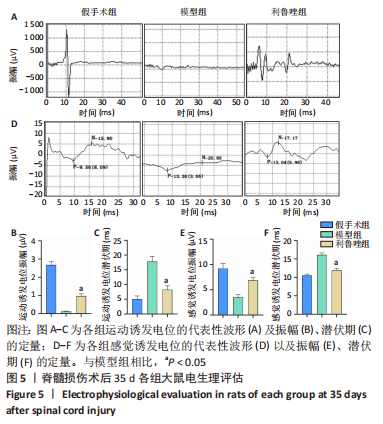
1.4.8 电生理实验 记录运动诱发电位和躯体感觉诱发电位,以评估脊髓损伤后运动和感觉系统的恢复。运动诱发电位和感觉诱发电位测定如前所述[15]。简单地说,大鼠被氧和异氟烷的混合物麻醉。然后在前囟门上方皮下插入刺激电极,并在每条跟腱中放置记录电极以记录运动诱发电位。同时,在双后肢骨骼肌中插入刺激电极,并在双侧感觉运动皮质皮下放置电极记录感觉诱发电位。用振幅和潜伏期分析神经恢复效果。
1.5 主要观察指标 通过Western blot、ELISA观察NLRP3、Caspase-1、GSDMD、IL-1β、IL-18蛋白表达情况;免疫荧光评估小胶质细胞焦亡情况;采用苏木精-伊红染色观察脊髓组织缺损情况,电生理评估神经传导功能恢复情况。
1.6 统计学分析 GraphPad Prism 8 用于统计学数据的处理分析。符合正态分布、方差齐性的计量资料采用单因素方差分析;正态分布、方差不齐或非正态分布的计量资料采用非参数检验。两组数据的比较通过双尾t检验进行;单因素方差分析用于比较两组以上的数据;BBB 评分和斜板实验评分的统计采用双因素方差分析。数据显示为均数±标准误,P < 0.05 为差异有显著性意义。文章统计学方法已经首都医科大学附属北京潞河医院生物统计学专家审核。