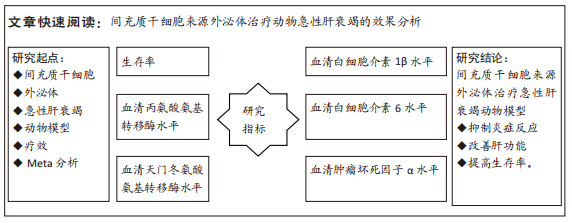
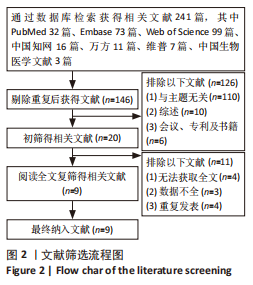
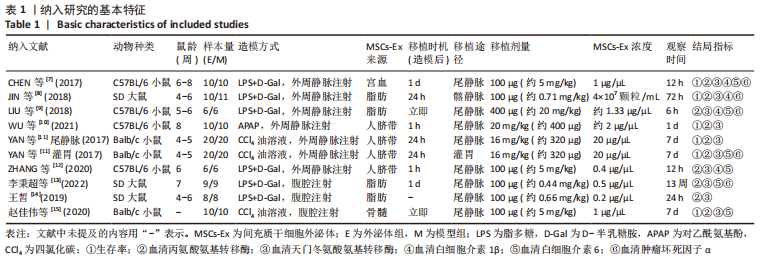
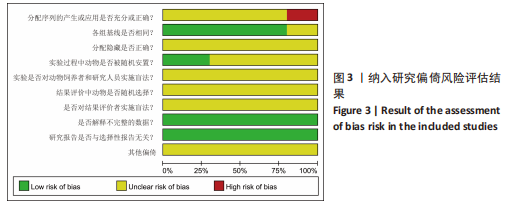
[1] 中华医学会感染病学分会肝衰竭与人工肝学组,中华医学会肝病学分会重型肝病与人工肝学组.肝衰竭诊治指南(2018年版) [J] .中华肝脏病杂志,2019,27(1):18-26.
[2] SHOKRAVI S, BORISOV V, ZAMAN BA, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) and their exosome in acute liver failure (ALF): a comprehensive review. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022; 13(1):192.
[3] SHI M, LI YY, XU RN, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy in decompensated liver cirrhosis: a long-term follow-up analysis of the randomized controlled clinical trial. Hepatol Int. 2021;15(6):1431-1441.
[4] PSARAKI A, NTARI L, KARAKOSTAS C, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: The regenerative impact in liver diseases. Hepatology. 2022;75(6):1590-1603.
[5] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977.
[6] 罗秋敏,朱姝,彭亮,等.间充质干细胞源性外泌体治疗肝衰竭的研究进展[J].中华肝脏病杂志,2022,30(3):249-252.
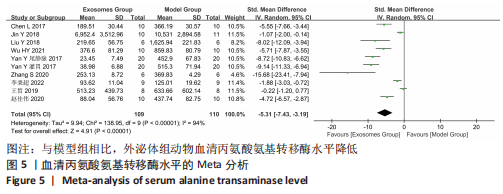
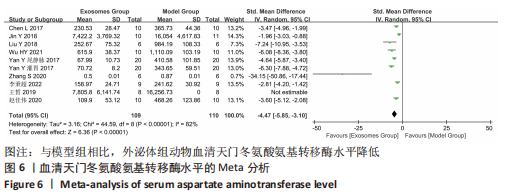
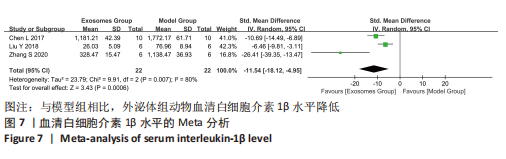
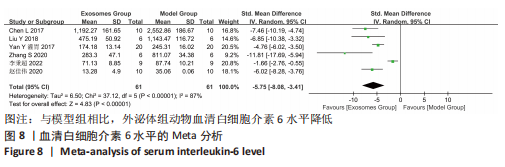
[7] CHEN L, XIANG B, WANG X, et al. Exosomes derived from human menstrual blood-derived stem cells alleviate fulminant hepatic failure. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):9.
[8] JIN Y, WANG J, LI H, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Secreted by Human Adipose-derived Stem Cells (hASCs) Improve Survival Rate of Rats with Acute Liver Failure by Releasing lncRNA H19. EBioMedicine. 2018;34:231-242.
[9] LIU Y, LOU G, LI A, et al. AMSC-derived exosomes alleviate lipopolysaccharide/d-galactosamine-induced acute liver failure by miR-17-mediated reduction of TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages. EBioMedicine. 2018; 36:140-150.
[10] WU HY, ZHANG XC, JIA BB, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure through activating ERK and IGF-1R/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J Pharmacol Sci. 2021; 147(1):143-155.
[11] YAN Y, JIANG W, TAN Y, et al. hucMSC Exosome-Derived GPX1 Is Required for the Recovery of Hepatic Oxidant Injury. Mol Ther. 2017;25(2):465-479.
[12] ZHANG S, JIANG L, HU H, et al. Pretreatment of exosomes derived from hUCMSCs with TNF-α ameliorates acute liver failure by inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 in macrophage. Life Sci. 2020; 246:117401.
[13] 李秉超,冯建恩,何云.人脂肪干细胞来源外泌体对急性肝衰竭大鼠炎症反应的抑制作用及相关机制[J].中西医结合肝病杂志,2022,32(2): 139-144.
[14] 王皙.人脂肪干细胞外泌体中microRNA-19b-3p的抑炎作用及对急性肝衰竭动物模型治疗的探索[D].贵阳:贵州医科大学,2019.
[15] 赵佳伟,贾蓉蓉,王景辉,等.间充质干细胞外泌体对小鼠急性肝衰竭的保护作用[J].现代生物医学进展,2020,20(7):1246-1252.
[16] LU FB, CHEN DZ, CHEN L, et al. Attenuation of Experimental Autoimmune Hepatitis in Mice with Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Carrying MicroRNA-223-3p. Mol Cells. 2019;42(12):906-918.
[17] ZHANG L, SONG Y, CHEN L, et al. MiR-20a-containing exosomes from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviates liver ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Cell Physiol. 2020; 235(4):3698-3710.
[18] ZHANG J, GAO J, LIN D, et al. Potential Networks Regulated by MSCs in Acute-On-Chronic Liver Failure: Exosomal miRNAs and Intracellular Target Genes. Front Genet. 2021;12:650536.
[19] HYUN J, WANG S, KIM J, et al. MicroRNA125b-mediated Hedgehog signaling influences liver regeneration by chorionic plate-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep. 2015;5:14135.
[20] SONG XJ, ZHANG L, LI Q, et al. hUCB-MSC derived exosomal miR-124 promotes rat liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy via downregulating Foxg1. Life Sci. 2021;265:118821.
[21] 郑嵘炅,邓泽润,韩丹,等.骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体调节大鼠肝细胞凋亡的机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(1):44-49.
[22] ZHENG J, LU T, ZHOU C, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protect Liver Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Reducing CD154 Expression on CD4+ T Cells via CCT2. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020; 7(18):1903746.
[23] JIANG W, TAN Y, CAI M, et al. Human Umbilical Cord MSC-Derived Exosomes Suppress the Development of CCl4-Induced Liver Injury through Antioxidant Effect. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018: 6079642.
[24] SAMERI MJ, SAVARI F, HOSEINYNEJAD K, et al. The hepato-protective effect of H2S-modified and non-modified mesenchymal stem cell exosomes on liver ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice: The role of MALAT1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022;635:194-202.
[25] MARDPOUR S, GHANIAN MH, SADEGHI-ABANDANSARI H, et al. Hydrogel-Mediated Sustained Systemic Delivery of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Improves Hepatic Regeneration in Chronic Liver Failure. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(41):37421-37433.
[26] ZHAO S, LIU Y, PU Z. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes attenuate D-GaIN/LPS-induced hepatocyte apoptosis by activating autophagy in vitro. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13: 2887-2897.
[27] LIN D, CHEN H, XIONG J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells exosomal let-7a-5p improve autophagic flux and alleviate liver injury in acute-on-chronic liver failure by promoting nuclear expression of TFEB. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(10):865.
[28] WU HH, LEE OK. Exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells induce the conversion of hepatocytes into progenitor oval cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):117.
[29] JUN JH, KIM JY, CHOI JH, et al. Exosomes from Placenta-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Are Involved in Liver Regeneration in Hepatic Failure Induced by Bile Duct Ligation. Stem Cells Int. 2020; 2020:5485738.
[30] ARABPOUR M, SAGHAZADEH A, REZAEI N. Anti-inflammatory and M2 macrophage polarization-promoting effect of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021; 97:107823.
[31] JIANG L, ZHANG S, HU H, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate acute liver failure by reducing the activity of the NLRP3 inflammasome in macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;508(3):735-741.
[32] TAMURA R, UEMOTO S, TABATA Y. Immunosuppressive effect of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on a concanavalin A-induced liver injury model. Inflamm Regen. 2016;36:26.
|