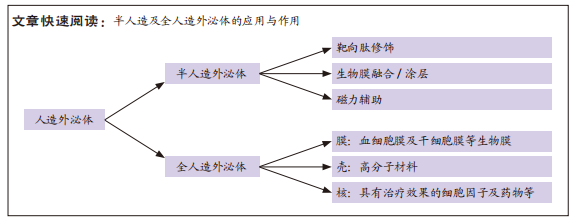
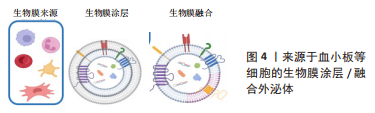
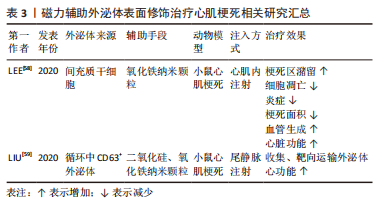
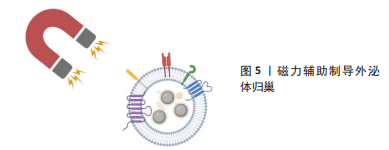
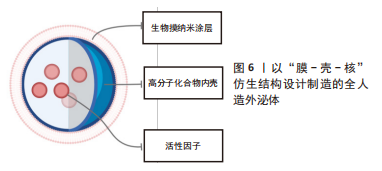
[1] THOMAS H, DIAMOND J, VIECO A, et al. Global Atlas of Cardiovascular Disease 2000-2016: the Path to Prevention and Control. Glob Heart. 2018;13(3):143-163.
[2] 中国心血管健康与疾病报告编写组.中国心血管健康与疾病报告2020概要[J].中国循环杂志,2021,36(6):25.
[3] JAMES SL, ABATE D, ABATE KH, et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1789-1858.
[4] ONG SB, HERNANDEZ-RESENDIZ S, CRESPO-AVILAN GE, et al. Inflammation following acute myocardial infarction: multiple players, dynamic roles, and novel therapeutic opportunities. Pharmacol Ther. 2018;186:73-87.
[5] FRANGOGIANNIS NG. Regulation of the inflammatory response in cardiac repair. Circ Res. 2012;110(1):159-173.
[6] GUO R, MORIMATSU M, FENG T, et al. Stem cell-derived cell sheet transplantation for heart tissue repair in myocardial infarction. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):19.
[7] HONG KU, LI QH, GUO Y, et al. A highly sensitive and accurate method to quantify absolute numbers of c-kit+ cardiac stem cells following transplantation in mice. Basic Res Cardiol. 2013;108(3):346.
[8] DUELEN R, SAMPAOLESI M. Stem cell technology in cardiac regeneration: a pluripotent stem cell promise. EBioMedicine. 2017;16:30-40.
[9] STREMERSCH S, DE SMEDT SC, RAEMDONCK K. Therapeutic and diagnostic applications of extracellular vesicles. J Control Release. 2016;244(Pt B):167-183.
[10] WANG X, ZHU Y, WU C, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes carry microRNA-671 to alleviate myocardial infarction through inactivating the TGFBR2/Smad2 axis. Inflammation. 2021;44(5):1815-1830.
[11] CHEN L, WANG Y, PAN Y, et al. Cardiac progenitor-derived exosomes protect ischemic myocardium from acute ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;431(3):566-571.
[12] HUANG P, WANG L, LI Q, et al. Atorvastatin enhances the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes in acute myocardial infarction via up-regulating long non-coding RNA H19. Cardiovasc Res. 2020;116(2):353-367.
[13] ARSLAN F, LAI RC, SMEETS MB, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes increase ATP levels, decrease oxidative stress and activate PI3K/Akt pathway to enhance myocardial viability and prevent adverse remodeling after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2013;10(3):301-312.
[14] GAO L, WANG L, WEI Y, et al. Exosomes secreted by hiPSC-derived cardiac cells improve recovery from myocardial infarction in swine. Sci Transl Med. 2020; 12(561):eaay1318.
[15] HUANG P, WANG L, LI Q, et al. Combinatorial treatment of acute myocardial infarction using stem cells and their derived exosomes resulted in improved heart performance. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):300.
[16] KOOIJMANS SA, ALEZA CG, ROFFLER SR, et al. Display of GPI-anchored anti-EGFR nanobodies on extracellular vesicles promotes tumour cell targeting. J Extracell Vesicles. 2016;5:31053.
[17] NAKASE I, NOGUCHI K, AOKI A, et al. Arginine-rich cell-penetrating peptide-modified extracellular vesicles for active macropinocytosis induction and efficient intracellular delivery. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):1991.
[18] PENG Q, MU H. The potential of protein-nanomaterial interaction for advanced drug delivery. J Control Release. 2016;225:121-132.
[19] JANG SC, GHO YS. Could bioengineered exosome-mimetic nanovesicles be an efficient strategy for the delivery of chemotherapeutics? Nanomedicine (Lond). 2014;9(2):177-180.
[20] JANG SC, KIM OY, YOON CM, et al. Bioinspired exosome-mimetic nanovesicles for targeted delivery of chemotherapeutics to malignant tumors. ACS Nano. 2013;7(9):7698-7710.
[21] NASIRI KENARI A, KASTANIEGAARD K, GREENING DW, et al. Proteomic and post-translational modification profiling of exosome-mimetic nanovesicles compared to exosomes. Proteomics. 2019;19(8):e1800161.
[22] LUNAVAT TR, JANG SC, NILSSON L, et al. RNAi delivery by exosome-mimetic nanovesicles - Implications for targeting c-Myc in cancer. Biomaterials. 2016;102:231-238.
[23] YANG Z, XIE J, ZHU J, et al. Functional exosome-mimic for delivery of siRNA to cancer: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J Control Release. 2016;243:160-171.
[24] GAO J, DONG X, WANG Z. Generation, purification and engineering of extracellular vesicles and their biomedical applications. Methods. 2020;177:114-125.
[25] MENG W, HE C, HAO Y, et al. Prospects and challenges of extracellular vesicle-based drug delivery system:considering cell source. Drug Deliv. 2020;27(1):585-598.
[26] LIU Y, WANG Y, LV Q, et al. Exosomes: from garbage bins to translational medicine. Int J Pharm. 2020;583:119333.
[27] ZHUANG X, XIANG X, GRIZZLE W, et al. Treatment of brain inflammatory diseases by delivering exosome encapsulated anti-inflammatory drugs from the nasal region to the brain. Mol Ther. 2011;19(10):1769-1779.
[28] LEE Y, EL ANDALOUSSI S, WOOD MJ. Exosomes and microvesicles:extracellular vesicles for genetic information transfer and gene therapy. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21(R1):R125-R134.
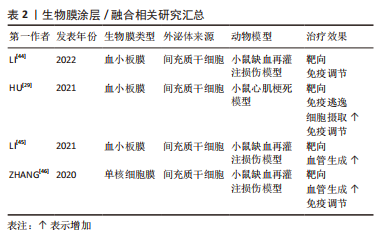
[29] HU S, WANG X, LI Z, et al. Platelet membrane and stem cell exosome hybrid enhances cellular uptake and targeting to heart injury. Nano Today. 2021;39:101210.
[30] XU X, LIANG Y, LI X, et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of kartogenin for chondrogenesis of synovial fluid-derived mesenchymal stem cells and cartilage regeneration. Biomaterials. 2021;269:120539.
[31] DUAN L, XU L, XU X, et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of gene vectors for gene therapy. Nanoscale. 2021;13(3):1387-1397.
[32] WEI W, AO Q, WANG X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: a promising biological tool in nanomedicine. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:590470.
[33] TSIAPALIS D, O’DRISCOLL L. Mesenchymal stem cell derived extracellular vesicles for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications. Cells. 2020;9(4):991.
[34] MAN K, BRUNET M Y, JONES M C, et al. Engineered extracellular vesicles:tailored-made nanomaterials for medical applications. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020;10(9):1838.
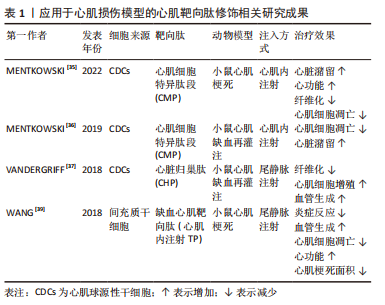
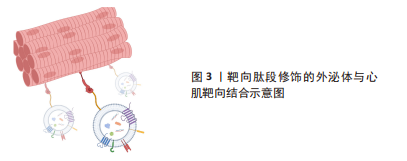
[35] MENTKOWSKI KI, TARVIRDIZADEH T, MANZANERO CA, et al. Surface engineering enhances the therapeutic potential of extracellular vesicles following acute myocardial infarction. BioRxiv. 2022. doi: /10.1101/2022.01.31.478512.
[36] MENTKOWSKI KI, LANG JK. Exosomes engineered to express a cardiomyocyte binding peptide demonstrate improved cardiac retention in vivo. Sci Rep. 2019; 9(1):10041.
[37] VANDERGRIFF A, HUANG K, SHEN D, et al. Targeting regenerative exosomes to myocardial infarction using cardiac homing peptide. Theranostics. 2018;8(7):1869-1878.
[38] CIULLO A, BIEMMI V, MILANO G, et al. Exosomal expression of CXCR4 targets cardioprotective vesicles to myocardial infarction and improves outcome after systemic administration. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(3):468.
[39] WANG X, CHEN Y, ZHAO Z, et al. Engineered exosomes with ischemic myocardium-targeting peptide for targeted therapy in myocardial infarction. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018;7(15):e008737.
[40] KANKI S, JAALOUK DE, LEE S, et al. Identification of targeting peptides for ischemic myocardium by in vivo phage display. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011;50(5):841-848.
[41] ANTES J, MIDDLETON RC, LUTHER KM, et al. Targeting extracellular vesicles to injured tissue using membrane cloaking and surface display. J Nanobiotechnology. 2018;16(1):61.
[42] KIM H, YUN N, MUN D, et al. Cardiac-specific delivery by cardiac tissue-targeting peptide-expressing exosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;499(4):803-808.
[43] ZHU LP, TIAN T, WANG JY, et al. Hypoxia-elicited mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes facilitates cardiac repair through miR-125b-mediated prevention of cell death in myocardial infarction. Theranostics. 2018;8(22):6163-6177.
[44] LI Q, HUANG Z, WANG Q, et al. Targeted immunomodulation therapy for cardiac repair by platelet membrane engineering extracellular vesicles via hitching peripheral monocytes. Biomaterials. 2022;284:121529.
[45] LI Q, SONG Y, WANG Q, et al. Engineering extracellular vesicles with platelet membranes fusion enhanced targeted therapeutic angiogenesis in a mouse model of myocardial ischemia reperfusion. Theranostics. 2021;11(8):3916-3931.
[46] ZHANG N, SONG Y, HUANG Z, et al. Monocyte mimics improve mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicle homing in a mouse MI/RI model. Biomaterials. 2020;255:120168.
[47] FANG R H, KROLL A V, GAO W, et al. Cell membrane coating nanotechnology. Adv Mater. 2018;30(23):e1706759.
[48] SUN J, MUZ B, ALHALLAK K, et al. Targeting CD47 as a Novel Immunotherapy for Multiple Myeloma. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(2):305.
[49] BARKAL AA, BREWER RE, MARKOVIC M, et al. CD24 signalling through macrophage Siglec-10 is a target for cancer immunotherapy. Nature. 2019;572(7769):392-396.
[50] FANG RH, JIANG Y, FANG JC, et al. Cell membrane-derived nanomaterials for biomedical applications. Biomaterials. 2017;128:69-83.
[51] LI H, JIN K, LUO M, et al. Size dependency of circulation and biodistribution of biomimetic nanoparticles: red blood cell membrane-coated nanoparticles. Cells. 2019;8(8):881.
[52] BEN-AKIVA E, MEYER RA, YU H, et al. Biomimetic anisotropic polymeric nanoparticles coated with red blood cell membranes for enhanced circulation and toxin removal. Sci Adv. 2020;6(16):eaay9035.
[53] HU CM, FANG RH, WANG KC, et al. Nanoparticle biointerfacing by platelet membrane cloaking. Nature. 2015;526(7571):118-121.
[54] WANG D, WANG S, ZHOU Z, et al. White blood cell membrane-coated nanoparticles: recent development and medical applications. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(7):e2101349.
[55] YAO C, WU W, TANG H, et al. Self-assembly of stem cell membrane-camouflaged nanocomplex for microRNA-mediated repair of myocardial infarction injury. Biomaterials. 2020;257:120256.
[56] FANG RH, HU CM, LUK BT, et al. Cancer cell membrane-coated nanoparticles for anticancer vaccination and drug delivery. Nano Lett. 2014;14(4):2181-2188.
[57] MODERY-PAWLOWSKI CL, KUO HH, BALDWIN WM, et al. A platelet-inspired paradigm for nanomedicine targeted to multiple diseases. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2013;8(10):1709-1727.
[58] LEE JR, PARK BW, KIM J, et al. Nanovesicles derived from iron oxide nanoparticles-incorporated mesenchymal stem cells for cardiac repair. Sci Adv. 2020;6(18):eaaz0952.
[59] LIU S, CHEN X, BAO L, et al. Treatment of infarcted heart tissue via the capture and local delivery of circulating exosomes through antibody-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles. Nat Biomed Eng. 2020;4(11):1063-1075.
[60] ZHANG X, ZHANG Y, ZHANG R, et al. Biomimetic design of artificial hybrid nanocells for boosted vascular regeneration in ischemic tissues. Adv Mater. 2022; 34(14):e2110352.
[61] CHEN J, SONG Y, WANG Q, et al. Targeted neutrophil-mimetic liposomes promote cardiac repair by adsorbing proinflammatory cytokines and regulating the immune microenvironment. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):218.
[62] BAO L, DOU G, TIAN R, et al. Engineered neutrophil apoptotic bodies ameliorate myocardial infarction by promoting macrophage efferocytosis and inflammation resolution. Bioact Mater. 2022;9:183-197.
[63] XU L, CHEN Y, JIN Q, et al. Biomimetic PLGA microbubbles coated with platelet membranes for early detection of myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury. Mol Pharm. 2021;18(8):2974-2985.
[64] XUE Y, ZENG G, CHENG J, et al. Engineered macrophage membrane-enveloped nanomedicine for ameliorating myocardial infarction in a mouse model. Bioeng Transl Med. 2021;6(2):e10197.
[65] ZHANG R, LUO W, ZHANG Y, et al. Particle-based artificial three-dimensional stem cell spheroids for revascularization of ischemic diseases. Sci Adv. 2020; 6(19):eaaz8011.
[66] SU T, HUANG K, MA H, et al. Platelet-inspired nanocells for targeted heart repair after ischemia/reperfusion injury. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29(4):1803567.
[67] KOOIJMANS SA, VADER P, VAN DOMMELEN SM, et al. Exosome mimetics: a novel class of drug delivery systems. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:1525-1541.
[68] ZANINETTI C, SACHS L, PALANKAR R. Role of platelet cytoskeleton in platelet biomechanics: current and emerging methodologies and their potential relevance for the investigation of inherited platelet disorders. Hamostaseologie. 2020;40(3):337-347.
[69] GAO J, SONG Y, WANG Q, et al. Precisely co-delivery of protein and ROS scavenger with platesomes for enhanced endothelial barrier preservation against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. Chem Eng J. 2022;44(2):446.
[70] WANG J, DONG Y, LI Y, et al. Designer exosomes for active targeted chemo-photothermal synergistic tumor therapy. Adv Funct Mater. 2018;28(18):1707360.
[71] BUNGGULAWA EJ, WANG W, YIN T, et al. Recent advancements in the use of exosomes as drug delivery systems. J Nanobiotechnology. 2018;16(1):81.
[72] ARYANI A, DENECKE B. Exosomes as a nanodelivery system: a key to the future of neuromedicine? Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53(2):818-834.
[73] MURALIDHARAN-CHARI V, CLANCY JW, SEDGWICK A, et al. Microvesicles: mediators of extracellular communication during cancer progression. J Cell Sci. 2010;123(Pt 10):1603-1611. |