[1] REFARDT J, WINZELER B, CHRIST-CRAIN M. Diabetes Insipidus: An Update. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2020;49(3):517-531.
[2] SELVARAJAH D, KAR D, KHUNTI K, et al. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: advances in diagnosis and strategies for screening and early intervention. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(12):938-948.
[3] SLOAN G, SELVARAJAH D, TESFAYE S. Pathogenesis, diagnosis and clinical management of diabetic sensorimotor peripheral neuropathy. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021;17(7):400-420.
[4] LIU S, HE CZ, CAI YT, et al. Evaluation of negative-pressure wound therapy for patients with diabetic foot ulcers: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017;13:533-544.
[5] JAVED S, HAYAT T, MENON L, et al. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy in people with type 2 diabetes: too little too late. Diabet Med. 2020;37(4):573-579.
[6] STINO AM, SMITH AG. Peripheral neuropathy in prediabetes and the metabolic syndrome. J Diabetes Investig. 2017;8(5):646-655.
[7] HE X, KUANG G, WU Y, et al. Emerging roles of exosomal miRNAs in diabetes mellitus. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(6):e468.
[8] 潘钟杰,秦志鸿,郑铁军,等.股骨头坏死发病机制中非编码RNA的靶标性[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(9):1441-1447.
[9] 万淑君,孔祥,吕坤.非编码RNA与糖尿病血管病变的关系[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版),2021,41(5):665-670.
[10] REGAZZI R. MicroRNAs as therapeutic targets for the treatment of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018;22(2):153-160.
[11] GAO C, FAN F, LIU X, et al. Exosomal miRNA Analysis of Aqueous Humour of Diabetes and Cataract Patients. Curr Eye Res. 2021;46(3): 324-332.
[12] HE X, KUANG G, WU Y, et al. Emerging roles of exosomal miRNAs in diabetes mellitus. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(6):e468.
[13] SCHERM MG, DANIEL C. miRNA Regulation of T Cells in Islet Autoimmunity and Type 1 Diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 2020;20(9):41.
[14] KAUR P, KOTRU S, SINGH S, et al. Role of miRNAs in diabetic neuropathy: mechanisms and possible interventions. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59(3):1836-1849.
[15] DISTEFANO JK, TAILA M, ALVAREZ ML. Emerging roles for miRNAs in the development, diagnosis, and treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Curr Diab Rep. 2013;13(4):582-591.
[16] LIU ZN, JIANG Y, LIU XQ, et al. MiRNAs in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Potential Mechanisms and Clinical Applications. J Diabetes Res. 2021;2021:4632745.
[17] JIN ZQ. MicroRNA targets and biomarker validation for diabetes-associated cardiac fibrosis. Pharmacol Res. 2021;174:105941.
[18] LI Y, XU Y, HOU Y, et al. Construction and Bioinformatics Analysis of the miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network in Diabetic Nephropathy. J Healthc Eng. 2021;2021: 8161701.
[19] CHEN Y, HE Y, ZHOU H. The potential role of lncRNAs in diabetes and diabetic microvascular complications. Endocr J. 2020;67(7):659-668.
[20] LEUNG A, AMARAM V, NATARAJAN R. Linking diabetic vascular complications with LncRNAs. Vascul Pharmacol. 2019;114:139-144.
[21] BISWAS S, COYLE A, CHEN S, et al. Expressions of Serum lncRNAs in Diabetic Retinopathy - A Potential Diagnostic Tool. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13: 851967.
[22] LONG J, DANESH FR. Values and Limitations of Targeting lncRNAs in Diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetes. 2018;67(4):552-553.
[23] COELLAR JD, LONG J, DANESH FR. Long Noncoding RNAs and Their Therapeutic Promise in Diabetic Nephropathy. Nephron. 2021;145(4): 404-414.
[24] LI J, WEI M, LIU X, et al. The progress, prospects, and challenges of the use of non-coding RNA for diabetic wounds. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021;24:554-578.
[25] GONG Q, LU Z, HUANG Q, et al. Altered microRNAs expression profiling in mice with diabetic neuropathic pain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;456(2): 615-620.
[26] DU H, LIU Z, TAN X, et al. Identification of the Genome-wide Expression Patterns of Long Non-coding RNAs and mRNAs in Mice with Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Neuropathic Pain. Neuroscience. 2019;402:90-103.
[27] GUO G, REN S, KANG Y, et al. Microarray analyses of lncRNAs and mRNAs expression profiling associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy in rats. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(9):15347-15359.
[28] ZHANG Y, ZHU Z, LIU X, et al. Integrated analysis of long noncoding RNAs and mRNA expression profiles reveals the potential role of lncRNAs in early stage of post-peripheral nerve injury in Sprague-Dawley rats. Aging (Albany NY). 2021; 13(10):13909-13925.
[29] FENG Y, GE Y, WU M, et al. Long Non Coding RNAs Regulate Inflammation in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy by Acting as ceRNAs Targeting miR-146a-5p. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020;13:413-422.
[30] ASHJARI D, KARAMALI N, RAJABINEJAD M, et al. The axis of long non-coding RNA MALAT1/miR-1-3p/CXCR4 is dysregulated in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Heliyon. 2022;8(3):e09178.
[31] WANG B, YAO J, YAO X, et al. Swertiamarin alleviates diabetic peripheral neuropathy in rats by suppressing NOXS/ ROS/NLRP3 signal pathway. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021;41(6):937-941.
[32] JUCHNICKA I, KUZMICKI M. Influence of MiRNAs in gestational diabetes mellitus development. Ginekol Pol. 2021;92(8):579-582.
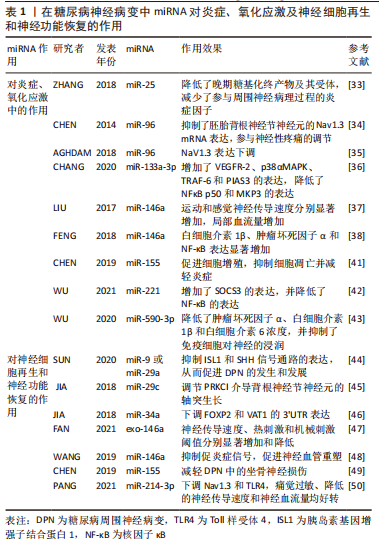
[33] ZHANG Y, SONG C, LIU J, et al. Inhibition of miR-25 aggravates diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Neuroreport. 2018;29(11):945-953.
[34] CHEN HP, ZHOU W, KANG LM, et al. Intrathecal miR-96 inhibits Nav1.3 expression and alleviates neuropathic pain in rat following chronic construction injury. Neurochem Res. 2014;39(1):76-83.
[35] AGHDAM AM, SHAHABI P, KARIMI-SALES E,et al. Swimming Exercise Induced Reversed Expression of miR-96 and Its Target Gene NaV1.3 in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Rats. Chin J Physiol. 2018;61(2):124-129.
[36] CHANG LL, WANG HC, TSENG KY, et al. Upregulation of miR-133a-3p in the Sciatic Nerve Contributes to Neuropathic Pain Development. Mol Neurobiol. 2020;57(9):3931-3942.
[37] LIU XS, FAN B, SZALAD A, et al. MicroRNA-146a Mimics Reduce the Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Diabetes. 2017;66(12): 3111-3121.
[38] FENG Y, CHEN L, LUO Q, et al. Involvement of microRNA-146a in diabetic peripheral neuropathy through the regulation of inflammation. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018;12:171-177.
[39] LUO Q, FENG Y, XIE Y, et al. Nanoparticle-microRNA-146a-5p polyplexes ameliorate diabetic peripheral neuropathy by modulating inflammation and apoptosis. Nanomedicine. 2019;17:188-197.
[40] YOUSEFZADEH N, ALIPOUR MR, SOUFI FG. Deregulation of NF-кB-miR-146a negative feedback loop may be involved in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy. J Physiol Biochem. 2015;71(1):51-58.
[41] CHEN J, LI C, LIU W, et al. miRNA-155 silencing reduces sciatic nerve injury in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J Mol Endocrinol. 2019;63(3):227-238.
[42] WU X, WANG X, YIN Y, et al. Investigation of the role of miR-221 in diabetic peripheral neuropathy and related molecular mechanisms. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2021;30(6):623-632.
[43] WU Y, GU Y, SHI B. miR-590-3p Alleviates diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain by targeting RAP1A and suppressing infiltration by the T cells. Acta Biochim Pol. 2020;67(4):587-593.
[44] SUN Q, ZENG J, LIU Y, et al. microRNA-9 and -29a regulate the progression of diabetic peripheral neuropathy via ISL1-mediated sonic hedgehog signaling pathway. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(12):11446-11465.
[45] JIA L, WANG L, CHOPP M, et al. MiR-29c/PRKCI Regulates Axonal Growth of Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurons Under Hyperglycemia. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(1):851-858.
[46] JIA L, CHOPP M, WANG L, et al. MiR-34a Regulates Axonal Growth of Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurons by Targeting FOXP2 and VAT1 in Postnatal and Adult Mouse. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(12):9089-9099.
[47] FAN B, CHOPP M, ZHANG ZG, et al. Treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy with engineered mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes enriched with microRNA-146a provide amplified therapeutic efficacy. Exp Neurol. 2021;341: 113694.
[48] WANG L, CHOPP M, LU X, et al. miR-146a mediates thymosin β4 induced neurovascular remodeling of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type-II diabetic mice. Brain Res. 2019;1707:198-207.
[49] CHEN J, LIU W, YI H, et al. MicroRNA-155 mimics ameliorates nerve conduction velocities and suppresses hyperglycemia-induced pro-inflammatory genes in diabetic peripheral neuropathic mice. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(6):3905-3918.
[50] PANG B, QIAO L, WANG S, et al. MiR-214-3p plays a protective role in diabetic neuropathic rats by regulating Nav1.3 and TLR4. Cell Biol Int. 2021;45(11): 2294-2303.
[51] LI Z, LI X, CHEN X, et al. Emerging roles of long non-coding RNAs in neuropathic pain. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(1):e12528.
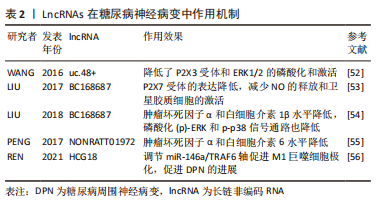
[52] WANG S, XU H, ZOU L, et al. LncRNA uc.48+ is involved in diabetic neuropathic pain mediated by the P2X3 receptor in the dorsal root ganglia. Purinergic Signal. 2016;12(1):139-48.
[53] LIU C, TAO J, WU H, et al. Effects of LncRNA BC168687 siRNA on Diabetic Neuropathic Pain Mediated by P2X7 Receptor on SGCs in DRG of Rats. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:7831251.
[54] LIU C, LI C, DENG Z, et al. Long Non-coding RNA BC168687 is Involved in TRPV1-mediated Diabetic Neuropathic Pain in Rats. Neuroscience. 2018;374:214-222.
[55] PENG H, ZOU L, XIE J, et al. lncRNA NONRATT021972 siRNA Decreases Diabetic Neuropathic Pain Mediated by the P2X3 Receptor in Dorsal Root Ganglia. Mol Neurobiol. 2017;54:511-523.
[56] REN W, XI G, LI X, et al. Long non-coding RNA HCG18 promotes M1 macrophage polarization through regulating the miR-146a/TRAF6 axis, facilitating the progression of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(1): 471-482.
[57] YU W, ZHAO GQ, CAO RJ, et al. LncRNA NONRATT021972 Was Associated with Neuropathic Pain Scoring in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Behav Neurol. 2017; 2017:2941297.
[58] LIU S, ZOU L, XIE J, et al. LncRNA NONRATT021972 siRNA regulates neuropathic pain behaviors in type 2 diabetic rats through the P2X7 receptor in dorsal root ganglia. Mol Brain. 2016;9:44.
[59] LU J, HUANG Y, ZHANG X, et al. Noncoding RNAs involved in DNA methylation and histone methylation, and acetylation in diabetic vascular complications. Pharmacol Res. 2021;170:105520.
[60] FILARDI T, CATANZARO G, MARDENTE S, et al. Non-Coding RNA: Role in Gestational Diabetes Pathophysiology and Complications. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(11):4020.
[61] MEYDAN C, ÜÇEYLER N, SOREQ H. Non-coding RNA regulators of diabetic polyneuropathy. Neurosci Lett. 2020;731:135058. |