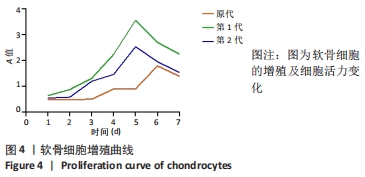
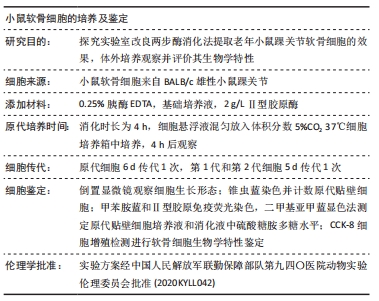
[1] ZHANG Y, GUO WM, WANG MG, et al. Co-culture systems-based strategies for articular cartilage tissue engineering. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(3):1940-1951.
[2] WANG HR, ZHU ZH, WU JN, et al. Effect of type II diabetes-induced osteoarthritis on articular cartilage aging in rats: A study in vivo and in vitro.Exp Gerontol. 2021;150:111354.
[3] LIAO YH, LONG JS T, GALLO CJR, et al. Isolation and Culture of Murine Primary Chondrocytes: Costal and Growth Plate Cartilage. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2230:415-423.
[4] WANG RK, JIANG W, ZHANG L, et al. Intra-articular delivery of extracellular vesicles secreted by chondrogenic progenitor cells from MRL/MpJ superhealer mice enhances articular cartilage repair in a mice injury model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):1-14.
[5] RUAN G, XU J, WANG K, et al. Associations between knee structural measures, circulating inflammatory factors and MMP13 in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(8):1063-1069.
[6] TAN SHARON SH, TJIO CKE, WONG JRY, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosomes for Cartilage Regeneration: A Systematic Review of Preclinical In Vivo Studies. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2018;233(3):1940-1951.
[7] KAROL J, ALINA J, BARBARA B. Cell cultures in drug discovery and development: The need of reliable in vitro-in vivo extrapolation for pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics assessment. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018;147:297-312.
[8] LAVENDER C, SINAADIL SA, SINGH V, et al. Autograft Cartilage Transfer Augmented With Bone Marrow Concentrate and Allograft Cartilage Extracellular Matrix. Arthrosc Tech. 2020;9(2):e199-e203.
[9] ALTMAN RD, MANJOO A, FIERLINGER A, et al. The mechanism of action for hyaluronic acid treatment in the osteoarthritic knee:a systematic review. BMC Musculoskeletal Disord. 2015;16:321.
[10] CHANG KV, HUNG CY, ALIWARGA F, et al. Comparative effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma injections for treating knee joint cartilage degenerative pathology:a systematic review and meta- analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2014;95(3):562- 575.
[11] ZHOU QF, CAI YZH, JIANG YZ, et al. Exosomes in osteoarthritis and cartilage injury: advanced development and potential therapeutic strategies. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(11):1811-1820.
[12] XIE F, LIU YL, CHEN XY, et al. Role of MicroRNA, LncRNA, and Exosomes in the Progression of Osteoarthritis: A Review of Recent Literature. Orthop Surg. 2020;12:708-716.
[13] LI JS, DING ZY, LI YZ, et al. BMSCs-Derived Exosomes Ameliorate Pain Via Abrogation of Aberrant Nerve Invasion in Subchondral Bone in Lumbar Facet Joint Osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(3):670-679.
[14] ZHANG R, MA J, HAN J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell related therapies for cartilage lesions and osteoarthritis. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(10):6275-6289.
[15] RYU JH, CHUN JS. Opposing roles of WNT-5A and WNT-11 in interleukin-1beta regulation of type II collagen expression in articular chondrocytes. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(31):22039-22047.
[16] KOROSTYNSKI M, MALEK N, PIECHOTA M, et al. Cell-type-specific gene expression patterns in the knee cartilage in an osteoarthritis rat model. Funct Integr Genomics. 2018;18(1):79-87.
[17] WATT FE. Osteoarthritis biomarkers: year in review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(3):312-318.
[18] MI B, LIU G, ZHOU W, et al. Identification of genes and pathways in the synovia of women with osteoarthritis by bioinformatics analysis. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(3):4467-4473.
[19] MOON SM, SA LE, HAN SH, et al. Aqueous extract of codium fragile alleviates osteoarthritis through the MAPK/NF-κB pathways in IL- 1β-induced rat primary chondrocytes and a rat osteoarthritis model. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;97:264-270.
[20] LI ZM, LI M. Improvement in orthopedic outcome score and reduction in IL-1β, CXCL13, and TNF-α in synovial fluid of osteoarthritis patients following arthroscopic knee surgery. Genet Mol Res. 2017;16(3):16039487.
[21] WALY NE, REFAIY A, ABOREHAB NM. IL-10 and TGF-β: roles in chondroprotective effects of glucosamine in experimental osteoarthritis?. Pathophysiology. 2017;24(1):45-49.
[22] BARRETO G, SENTURK B, COLOMBO L, et al. Lumican is upregulated in osteoarthritis and contributes to TLR4-induced pro-inflammatory activation of cartilage degradation and macrophage polarization. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(1):92-101.
[23] MORELAND LW. Intra- articular hyaluronan (hyaluronic acid) and hylans for the treatment of osteoarthritis:mechanisms of action. Am J Transl Res. 2003;5(2):54-67.
[24] 郑晓芬. 骨关节炎发病机制和治疗的最新进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(20):3255- 3262.
[25] HOSEIN PJ, MARAGULIA JC, SALZBERG MP, et al. A multicentre study of primary breast diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era. Br J Haematol. 2014;165(3):358-363.
[26] ZHAO C, JIN YP, WEN M, et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells promote chondrogenesis and suppress inflammation by upregulating miR-145 and miR-221. Mol Med Rep. 2020;21(4):1881-1889.
[27] GREEN WT. Behavior of articular chondrocytes in cell culture. Clin Orthop. 1971;75:248-260.
[28] KLAGSBRUN M. Large- scale preparation of chondrocy tes. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:560-564.
[29] SHIMOMURA Y, YONEDA T, SUZUKI F. Osteogenesis by chondrocytes from grow th cartilage of rat rib. Calcif Tissue Res. 1975;19:179-187.
[30] QI H, LIU DP, XIAO DW, et al. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells inhibit mitochondrial dysfunction-induced apoptosis of chondrocytes via p38, ERK, and Akt pathways. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2019;55(3): 203-210.
[31] 魏钰, 魏民. 人骨关节炎软骨细胞的体外分离与培养[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(25):4056-4061.
[32] 李文辉. 软骨组织工程种子细胞及其培养方法[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2003,5(3):90-92.
[33] 杜国庆, 桑晓文, 王楠, 等. 大鼠半月板纤维软骨细胞的体外培养和生物学特征鉴定[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2019,19(15):2829-2833.
[34] NIPHA C, PHONGSAKORN K, PARINYA N. Three-dimensional cell culture systems as an in vitro platform for cancer and stem cell modeling. World J Stem Cells. 2019;11(12):1065-1083.
[35] 刘小荣,张笠,高武,等. 新西兰兔关节软骨细胞分离培养与鉴定的实验研究[J]. 国际检验医学杂志,2012,33(19):2307-2308.
[36] RODRIGUES A, PAP S. The effect of long- term culture on the ability of human articular chondrocytes to generate tissue engineered cartilage// Stard GB, Horch R, Tanczos E (eds).Biologicalmatrices And tissue Reconstruction. 1998:163-168.
[37] SCHIPHOF D, VAN DEN DRIEST JJ, RUNHAAR J. Osteoarthritis year in review 2017: rehabilitation and outcomes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(3): 326-340.
[38] DEHNE T, KARLSSON C, RINGE J, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation potential of osteoarthritic chondrocytes and their possible use in matrix-associated autologous chondrocyte transplantation. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(5):R133.
[39] HE P, ZHANG Z, LIAO W, et al. Screening of gene signatures for rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics analysis. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(2):1587-1593.
[40] LIU Y, JING J, YU H, et al. Expression profiles of long non-coding RNAs in the cartilage of patients with knee osteoarthritis and normal individuals. Exp Ther Med. 2021;21(4):365-375.
[41] GIBSON AL, HUI MC, FOOTE AT, et al. Wnt7a inhibits IL-1β induced catabolic gene expression and prevents articular cartilage damage in experimental osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2017;7:41823.
|