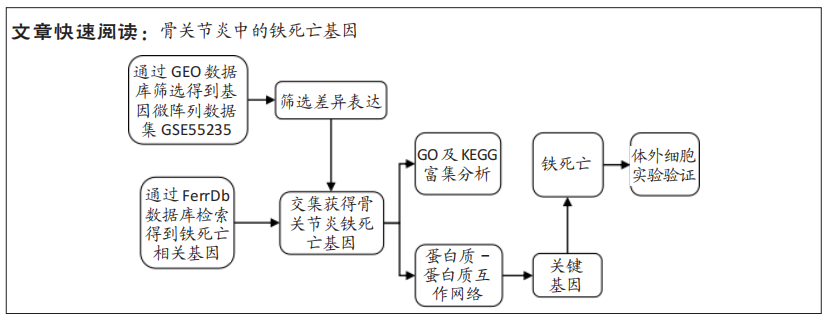
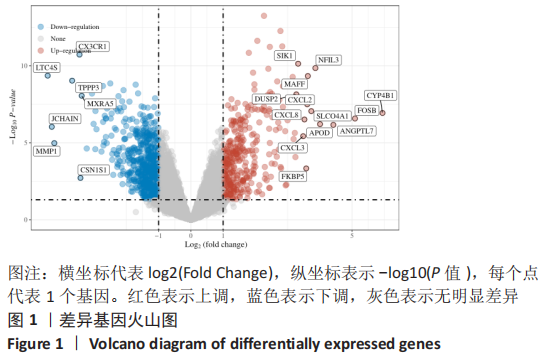
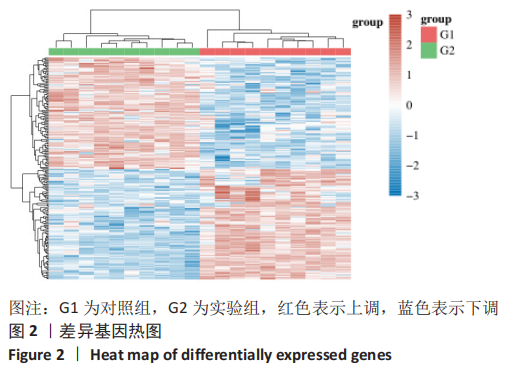
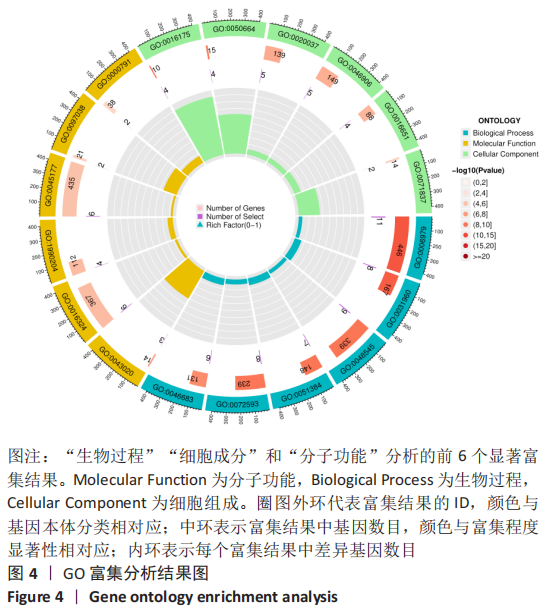
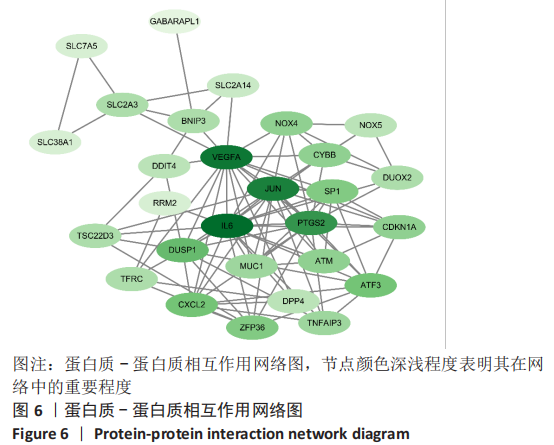
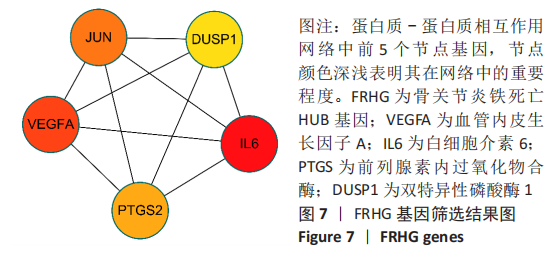
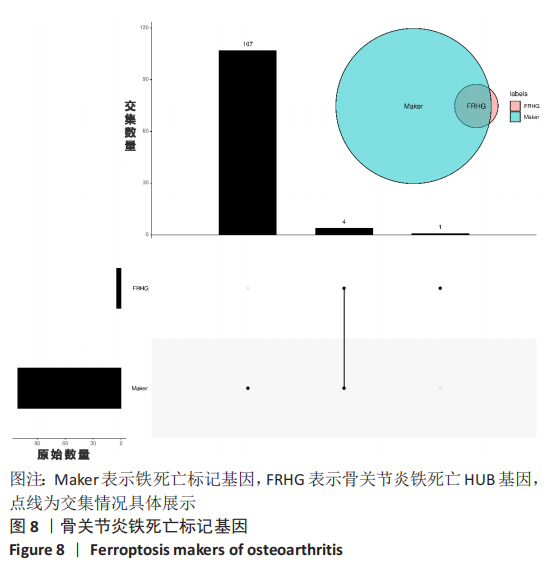
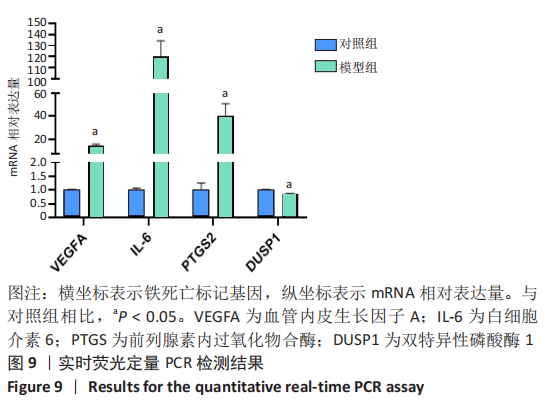
|
[1] STOCKWELL BR, JIANG X, GU W. Emerging mechanisms and disease relevance of ferroptosi. Trends Cell Biol. 2020;30(6):478-490.
[2] JIANG X, STOCKWELL BR, CONRAD M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22(4):266-282.
[3] YAO X, SUN K, YU S, et al. Chondrocyte ferroptosis contribute to the progression of osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. 2020;27:33-43.
[4] TANG D, CHEN X, KANG R, et al. Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res. 2021;31(2):107-125.
[5] GUO Z, LIN J, SUN K, et al. Deferoxamine alleviates osteoarthritis by inhibiting chondrocyte ferroptosis and activating the nrf2 pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:791376.
[6] ZHU H, YAN X, ZHANG M, et al. miR-21-5p protects IL-1β-induced human chondrocytes from degradation. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):118.
[7] 魏丽杰.降钙素对IL-1β诱导的大鼠软骨细胞炎性反应的影响[D].唐山:河北联合大学,2014.
[8] MIAO Y, CHEN Y, XUE F, et al. Contribution of ferroptosis and GPX4’s dual functions to osteoarthritis progression. EBioMedicine. 2022;76: 103847.
[9] JI Q, ZHENG Y, ZHANG G, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq analysis reveals the progression of human osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(1):100-110.
[10] KUMAR S, ADJEI IM, BROWN SB, et al. Manganese dioxide nanoparticles protect cartilage from inflammation-induced oxidative stress. Biomaterials. 2019;224:119467.
[11] LEPETSOS P, PAPAVASSILIOU KA, PAPAVASSILIOU AG. Redox and NF-κB signaling in osteoarthritis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;132:90-100.
[12] ARRA M, SWARNKAR G, KE K, et al. LDHA-mediated ROS generation in chondrocytes is a potential therapeutic target for osteoarthritis. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):3427.
[13] DEYLE GD, ALLEN CS, ALLISON SC, et al. Physical therapy versus glucocorticoid injection for osteoarthritis of the knee. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(15):1420-1429.
[14] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and treatment of hip and knee osteoarthritis: a review. JAMA. 2021;325(6):568-578.
[15] BENNELL KL, HUNTER DJ. Physical therapy before the needle for osteoarthritis of the knee. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(15):1470-1471.
[16] CHEN H, YU J, ZHANG J, et al. Monitoring metabolites using an NAD(P)H-sensitive polymer dot and a metabolite-specific enzyme. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021;60(35):19331-19336.
[17] FILAIRE E, TOUMI H. Reactive oxygen species and exercise on bone metabolism: friend or enemy? Joint Bone Spine. 2012;79(4):341-346.
[18] HOSSEINZADEH A, BAHRAMPOUR JUYBARI K, KAMARUL T, et al. Protective effects of atorvastatin on high glucose-induced oxidative stress and mitochondrial apoptotic signaling pathways in cultured chondrocytes. J Physiol Biochem. 2019;75(2):153-162.
[19] RAYEGAN S, DEHPOUR AR, SHARIFI AM. Studying neuroprotective effect of Atorvastatin as a small molecule drug on high glucose-induced neurotoxicity in undifferentiated PC12 cells: role of NADPH oxidase. Metab Brain Dis. 2017;32(1):41-49.
[20] KWOK SC, SAMUEL SP, HANDAL J. Atorvastatin activates heme oxygenase-1 at the stress response elements. J Cell Mol Med. 2012; 16(2):394-400.
[21] JAIKUMKAO K, PONGCHAIDECHA A, CHATTIPAKORN N, et al. Atorvastatin improves renal organic anion transporter 3 and renal function in gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Exp Physiol. 2016;101(6):743-753.
[22] HWANG HS, LEE MH, CHOI MH, et al. NOD2 signaling pathway is involved in fibronectin fragment-induced pro-catabolic factor expressions in human articular chondrocytes. BMB Rep. 2019;52(6): 373-378.
[23] YAN Z, QI W, ZHAN J, et al. Activating Nrf2 signalling alleviates osteoarthritis development by inhibiting inflammasome activation. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(22):13046-13057.
[24] MA D, ZHAO Y, SHE J, et al. NLRX1 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis and inflammation in chondrocytes by suppressing the activation of NF-κB signaling. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;71:7-13.
[25] LIU Y, PENG H, MENG Z, et al. Correlation of IL-17 Level in Synovia and Severity of Knee Osteoarthritis. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21:1732-1736.
[26] BOUAZIZ W, SIGAUX J, MODROWSKI D, et al. Interaction of HIF1α and β-catenin inhibits matrix metalloproteinase 13 expression and prevents cartilage damage in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(19): 5453-5458.
[27] HU S, ZHANG C, NI L, et al. Stabilization of HIF-1α alleviates osteoarthritis via enhancing mitophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(6):481.
[28] WU Y, WANG J, ZHAO T, et al. Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate exposure leads to ferroptosis via the HIF-1α/HO-1 signaling pathway in mouse testes. J Hazard Mater. 2022;426:127807.
[29] ANSARI MY, AHMAD N, HAQQI TM. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: role of polyphenols. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;129:110452.
[30] ZHANG J, FAN F, LIU A, et al. Icariin: a potential molecule for treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:811808.
[31] SHEN C, CAI GQ, PENG JP, et al. Autophagy protects chondrocytes from glucocorticoids-induced apoptosis via ROS/Akt/FOXO3 signaling. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(12):2279-2287.
[32] SERGI C, SHEN F, LIU SM. Insulin/IGF-1R, SIRT1, and FOXOs pathways-an intriguing interaction platform for bone and osteosarcoma. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019;10:93.
[33] HUANG Z, SHI X, LI X, et al. Network Pharmacology approach to uncover the mechanism governing the effect of simiao powder on knee osteoarthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:6971503.
[34] MA L, ZHAO X, LIU Y, et al. Dihydroartemisinin attenuates osteoarthritis by inhibiting abnormal bone remodeling and angiogenesis in subchondral bone. Int J Mol Med. 2021;47(3):4855.
[35] HAMILTON JL, NAGAO M, LEVINE BR, et al. Targeting VEGF and its receptors for the treatment of osteoarthritis and associated pain. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31(5):911-924.
[36] LIU Y, ZENG Y, SI HB, et al. Exosomes derived from human urine-derived stem cells overexpressing miR-140-5p alleviate knee osteoarthritis through downregulation of VEGFA in a rat model. Am J Sports Med. 2022;50(4):1088-1105.
[37] LATOURTE A, CHERIFI C, MAILLET J, et al. Systemic inhibition of IL-6/Stat3 signalling protects against experimental osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(4):748-755.
[38] MU Y, HAO W, LI S. Casticin protects against IL-1β-induced inflammation in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;842:314-320.
[39] WEN ZH, LIN YY, CHANG YC, et al. The COX-2 inhibitor etoricoxib reduces experimental osteoarthritis and nociception in rats: the roles of TGF-β1 and NGF expressions in chondrocytes. Eur J Pain. 2020; 24(1):209-222.
[40] NAKATA K, HANAI T, TAKE Y, et al. Disease-modifying effects of COX-2 selective inhibitors and non-selective NSAIDs in osteoarthritis: a systematic review . Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(10):1263-1273.
[41] PENG HZ, YUN Z, WANG W, et al. Dual specificity phosphatase 1 has a protective role in osteoarthritis fibroblastlike synoviocytes via inhibition of the MAPK signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(6):8441-8447.
[42] MAEKAWA A, SAWAJI Y, ENDO K, et al. Prostaglandin E2 induces dual-specificity phosphatase-1, thereby attenuating inflammatory genes expression in human osteoarthritic synovial fibroblasts. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2021;154:106550.
[43] JIANG W, JIN Y, ZHANG S, et al. PGE2 activates EP4 in subchondral bone osteoclasts to regulate osteoarthritis. Bone Res. 2022;10(1):27.
|