中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (26): 4141-4146.doi: 10.12307/2022.815
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
针灸足三里对佐剂性关节炎模型大鼠胃肠动力的调节作用
李 佳1,李柏村2,蔡国伟2,李 静2
- 1湖北中医药大学针灸骨伤学院/针灸治未病湖北省协同创新中心,湖北省武汉市 430061;2华中科技大学同济医学院附属协和医院针灸科,湖北省武汉市 430022
Effect of acupuncture and moxibustion at Zusanli on gastrointestinal motility in adjuvant arthritis rats
Li Jia1, Li Baicun2, Cai Guowei2, Li Jing2
- 1School of Acupuncture and Moxibustion and Orthopedics/Hubei Collaborative Innovation Center for Preventive Treatment of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Wuhan 430061, Hubei Province, China; 2Department of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Wuhan Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, Hubei Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
佐剂性关节炎大鼠模型:又称是弗氏佐剂关节炎,是免疫性关节炎动物模型的基本方法。通过在大鼠足跖底部注射药物,从而足跖部明显肿胀,出现继发性炎性反应,表现为前肢或对侧肢体甚至耳、尾部红肿或炎性结节出现,模拟出人类风湿关节炎状况。
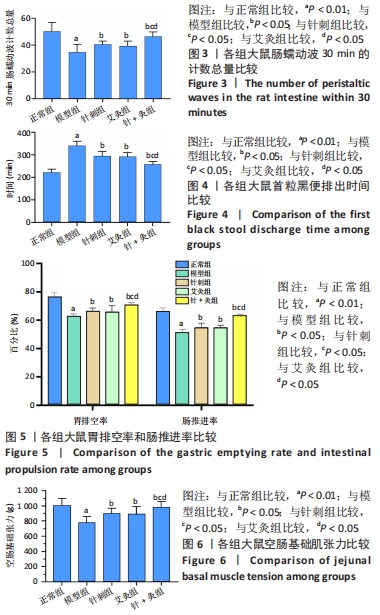
胃肠动力:可反映胃肠功能,是胃肠部肌肉的收缩蠕动力,包括胃肠部肌肉收缩的力量和频率。在此文中通过结肠蠕动波测定方法检测大鼠肠蠕动波次数、活性炭悬液灌胃法检测首粒黑便排出时间以及离体灌流装置检测大鼠空肠平滑肌肌条收缩水平,进一步说明佐剂性关节炎模型大鼠存在胃肠功能障碍。
背景:类风湿关节炎患者存在胃肠动力不足的问题逐渐受到关注,针灸作为类风湿关节炎的一种治疗方法,是否能够改善其胃肠动力不足的问题,值得进一步探究。
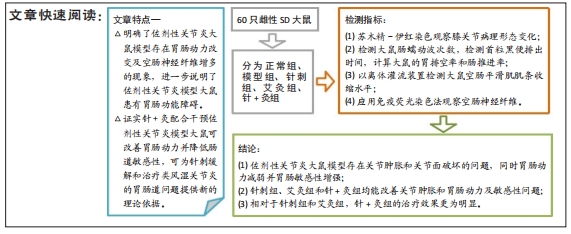
目的:制备佐剂性关节炎大鼠模型,探讨针灸足三里对大鼠胃肠动力的影响。
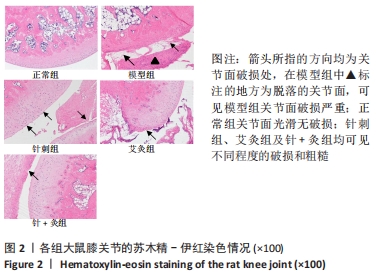
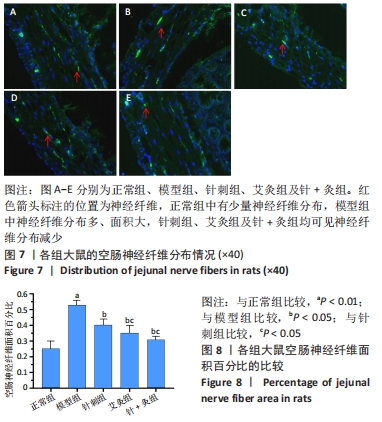
方法:将60只清洁级健康3月龄雌性SD大鼠随机分为5组,即正常组、模型组、针刺组、艾灸组和针+灸组,每组12只,除正常组外其余4组均采用弗氏完全佐剂建立佐剂性关节炎模型。针刺组、艾灸组和针+灸组于造模第1天取足三里穴治疗,15 min/次,1次/d,一共14 d。针刺组大鼠采用针刺干预,艾灸组大鼠则用艾灸干预,而针+灸组大鼠在使用针刺的基础上联合使用艾灸方法。所有大鼠于相应处理结束后,采用跖围法测大鼠跖围长度,采用苏木精-伊红染色观察其膝关节的病理形态变化,运用结肠蠕动波测定方法检测大鼠肠蠕动波次数,应用活性炭悬液灌胃法观察首粒黑便排出时间,计算大鼠的胃排空率和肠推进率,以离体灌流装置检测大鼠空肠平滑肌肌条收缩水平,应用免疫荧光染色法观察空肠神经纤维。
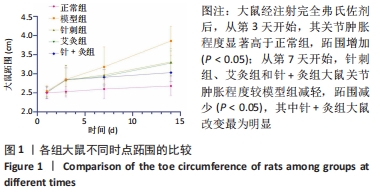
结果与结论:①针灸足三里治疗后,大鼠跖关节肿胀程度明显降低,软骨破坏和炎性细胞明显减少,肠蠕动波次数增加,全胃肠活性炭排出时间缩短,胃排空率和肠推进率得到提升,空肠平滑肌肌条收缩基础张力增强,空肠神经纤维减少;②3组针灸方法中针+灸干预最为明显;③提示针灸足三里对佐剂性关节炎大鼠肠动力障碍具有防治作用,并且针刺联合艾灸疗效优于单纯针刺或艾灸治疗。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0444-2263 (李佳)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: