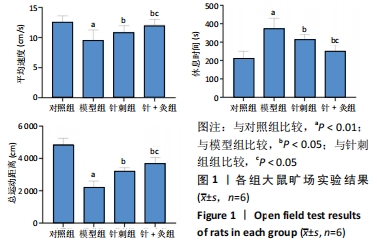
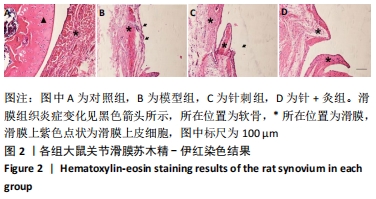
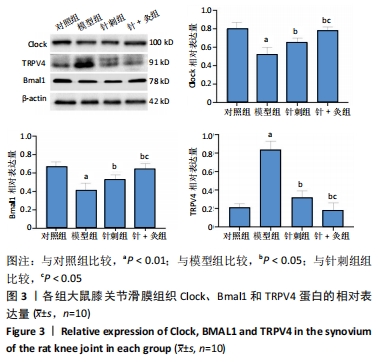
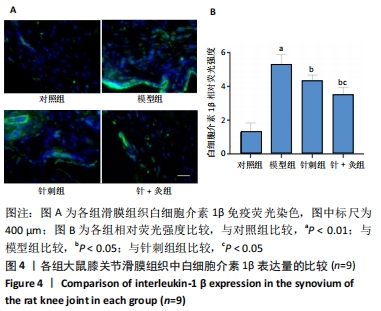
[1] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393 (10182):1745-1759.
[2] THOMAS E, PEAT G, CROFT P. Defining and mapping the person with osteoarthritis for population studies and public health. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014;53(2):338-345.
[3] ALSHAMI AM. Knee osteoarthritis related pain: a narrative review of diagnosis and treatment. Int J Health Sci (Qassim). 2014;8(1):85-104.
[4] FERKET BS, FELDMAN Z, ZHOU J, et al. Impact of total knee replacement practice: cost effectiveness analysis of data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. BMJ. 2017;356:j1131
[5] CHEN N, WANG J, MUCELLI A, et al. Electro-Acupuncture is beneficial for knee osteoarthritis: the evidence from meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Chin Med. 2017;45(5):965-985.
[6] 杨冬梅,林诗彬,梁振波,等.温针灸治疗膝关节骨性关节炎疗效的超声监测[J].重庆医学,2016,45(27):3860-3862.
[7] 何兆雍. 温针灸治疗膝骨性关节病的Meta分析及系统回顾[D]. 广州:广州中医药大学,2018.
[8] LEVICK JR. Microvascular architecture and exchange in synovial joints. Microcirculation. 1995;2(3):217-233.
[9] HAND LE, DICKSON SH, FREEMONT AJ, et al. The circadian regulator Bmal1 in joint mesenchymal cells regulates both joint development and inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019 6;21(1):5.
[10] ZHOU Y, TAO H, LI Y, et al. Berberine promotes proliferation of sodium nitroprusside-stimulated rat chondrocytes and osteoarthritic rat cartilage via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016;789: 109-118.
[11] 郭义.实验针灸学[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,2008.
[12] WEBER AE, BOLIA IK, TRASOLINI NA. Biological strategies for osteoarthritis: from early diagnosis to treatment. Int Orthop. 2021; 45(2):335-344.
[13] 丁呈彪,周云.膝骨性关节炎患者滑膜炎的发病机制及研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(51):8327-8332.
[14] 赵烨,刘永辉,毛书歌,等.骨性关节炎的滑膜病变机制及中药治疗进展[J].中国高新科技,2020(18):159-160.
[15] ZHANG L, XING R, HUANG Z, et al. Inhibition of Synovial Macrophage Pyroptosis Alleviates Synovitis and Fibrosis in Knee Osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2019;2019:2165918.
[16] GOSSAN N, BOOT-HANDFORD R, MENG QJ. Ageing and osteoarthritis: a circadian rhythm connection. Biogerontology. 2015;16(2):209-219.
[17] LEE C, ETCHEGARAY JP, CAGAMPANG FR, et al. Posttranslational mechanisms regulate the mammalian circadian clock. Cell. 2001;107(7): 855-867.
[18] ZHANG Z, ZENG P, GAO W, et al. Circadian clock: a regulator of the immunity in cancer. Cell Commun Signal. 2021;19(1):37.
[19] BEKKI H, DUFFY T, OKUBO N, et al. Suppression of circadian clock protein cryptochrome 2 promotes osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(7):966-976.
[20] DUDEK M, ANGELUCCI C, PATHIRANAGE D, et al. Circadian time series proteomics reveals daily dynamics in cartilage physiology. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(5):739-749.
[21] CHO H, ZHAO X, HATORI M, et al. Regulation of circadian behaviour and metabolism by REV-ERB-α and REV-ERB-β. Nature. 2012;485(7396): 123-127.
[22] MORRIS JL, LETSON HL, GILLMAN R, et al. The CNS theory of osteoarthritis: Opportunities beyond the joint. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019;49(3):331-336.
[23] GOSSAN N, ZEEF L, HENSMAN J, et al. The circadian clock in murine chondrocytes regulates genes controlling key aspects of cartilage homeostasis. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(9):2334-2345.
[24] AKAGI R, AKATSU Y, FISCH KM, et al. Dysregulated circadian rhythm pathway in human osteoarthritis: NR1D1 and BMAL1 suppression alters TGF-β signaling in chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017; 25(6):943-951.
[25] MA Z, JIN X, QIAN Z, LI F, et al. Deletion of clock gene Bmal1 impaired the chondrocyte function due to disruption of the HIF1α-VEGF signaling pathway. Cell Cycle. 2019;18(13):1473-1489.
[26] 蔡国伟,李柏村,李佳,等.温针灸对骨关节炎大鼠软骨组织Clock、Bmal1蛋白的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2019,39(10): 1225-1229.
[27] 贾振华,黄渊,唐景峰,等. TRP通道超家族的基本特征及其与疾病的关系[J].生命科学,2020,32 (9):29-40.
[28] 刘天珍,王鸣刚,崔冰冰,等.TRPV4在氧化应激相关疾病中的作用及其机制研究进展[J].解放军医药杂志,2020,32(11):113-116.
[29] SEGOND VON BANCHET G, BOETTGER MK, KÖNIG C, et al. Neuronal IL-17 receptor upregulates TRPV4 but not TRPV1 receptors in DRG neurons and mediates mechanical but not thermal hyperalgesia. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013;52:152-160.
[30] KOCHUKOV MY, MCNEARNEY TA, YIN H, et al. Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-α) Enhances Functional Thermal and Chemical Responses of TRP Cation Channels in Human Synoviocytes. Mol Pain. 2009;20(5):49.
[31] 魏歆然,魏高文,郑雪娜,等.不同经穴组合针刺对失眠大鼠下丘脑生物钟基因Clock和Bmal 1表达的影响[J].针刺研究,2017, 42(5):429-433.
[32] 郭保君,余思奕,申治富,等.针刺跷脉对失眠大鼠视交叉上核内生物钟基因Period 1及Period 2的影响[J].针刺研究,2017,42(6): 507-509.
[33] CHENG AH, CHENG HM. Genesis of the Master Circadian Pacemaker in Mice. Front Neurosci. 2021;15:659974.
[34] IHARA T, MITSUI T, NAKAMURA Y, et al. The Circadian expression of Piezo1, TRPV4, Connexin26, and VNUT, associated with the expression levels of the clock genes in mouse primary cultured urothelial cells. Neurourol Urodyn. 2018;37(3):942-951.
[35] CUESTA M, AUNGIER J, MORTON AJ. Behavioral therapy reverses circadian deficits in a transgenic mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2014;63:85-91.
[36] RIVAS GBS, TELES-DE-FREITAS R, PAVAN MG,et al. Effects of Light and Temperature on Daily Activity and Clock Gene Expression in Two Mosquito Disease Vectors. J Biol Rhythms. 2018;33(3):272-288.
[37] SIMONI A, WOLFGANG W, TOPPING MP, et al. A mechanosensory pathway to the Drosophila circadian clock. Science. 2014;343(6170): 525-528.
|