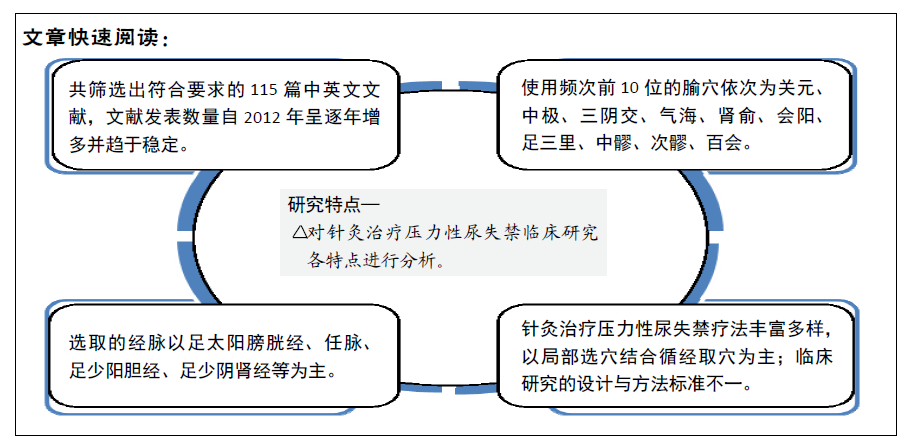
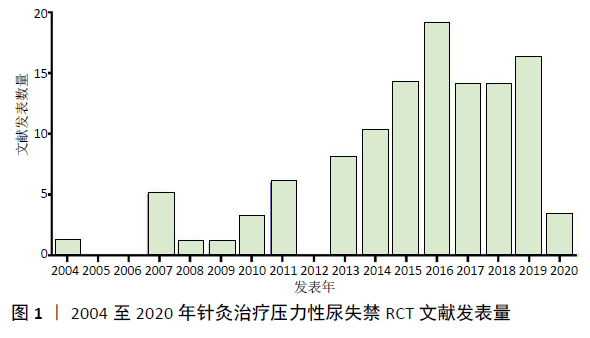
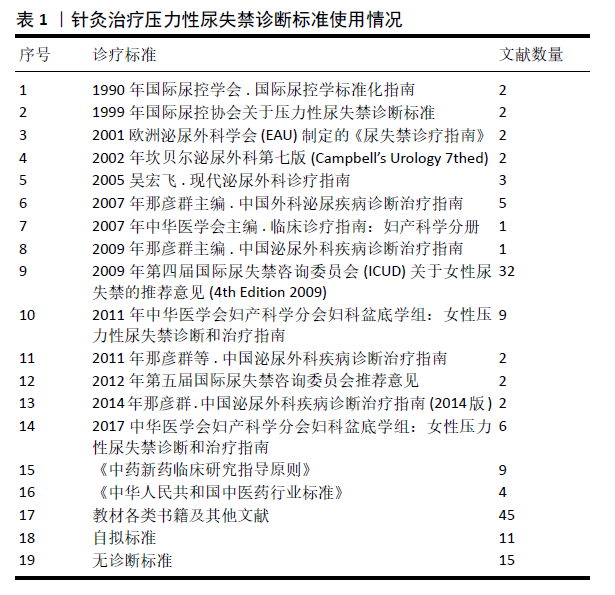
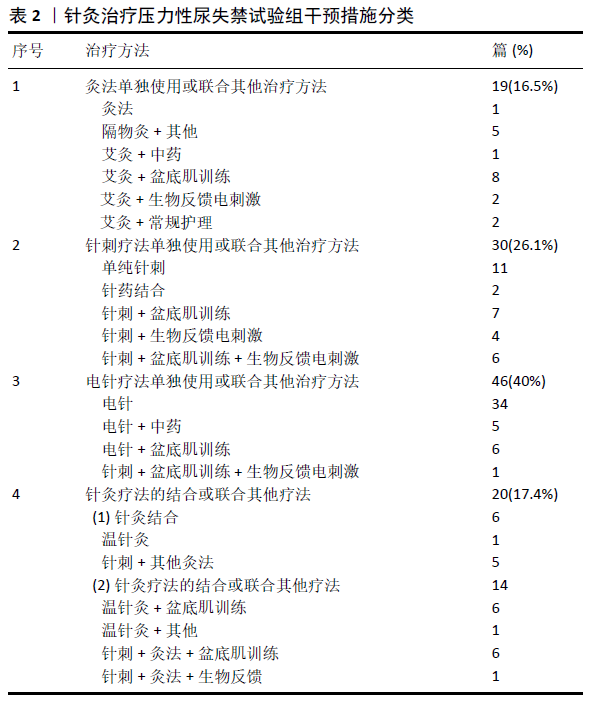
[1] REYNOLDS WS, DMOCHOWSKI RR, PENSON DF. Epidemiology of stress urinary incontinence in women. Curr Urol Rep. 2011;12(5):370-376.
[2] 李志毅,朱兰.女性压力性尿失禁流行病学现状[J].实用妇产科杂志, 2018,34(3):161-162.
[3] COYNE KS, KVASZ M, IRELAND AM, et al. Urinary incontinence and its relationship to mental health and health-related quality of life in men and women in Sweden, the United Kingdom,and the United States. Eur Urol. 2012;61:88-95.
[4] 中华医学会妇产科学分会妇科盆底学组.女性压力性尿失禁诊断和治疗指南(2017)[J].中华妇产科杂志,2017,52(5):289-293
[5] LIU Z, LIU Y, XU H, et al. Effect of Electroacupuncture on Urinary Leakage Among Women With Stress Urinary Incontinence:A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2017;317(24):2493-2501.
[6] WANG S, LV J, FENG X, et al. Efficacy of electrical pudendal nerve stimulation in treating female stress incontinence. Urology. 2016;91:64-69.
[7] WANG S, ZHANG S. Simultaneous perineal ultrasound and vaginal pressure measurement prove the action of electrical pudendal nerve stimulation in treating female stress incontinence. BJU Int. 2012;110(9):1338-1343.
[8] ABRAMS P, ANDERSSON K E, BIRDER L, et al. Fourth International Consultation on Incontinence Recommendations of the International Scientific Committee:Evaluation and treatment of urinary incontinence,pelvic organ prolapse,and fecal incontinence. Neurourol.Urodyn. 2010;29:213-240.
[9] 中华医学会妇产科学分会妇科盆底学组.女性压力性尿失禁诊断和治疗指南(试行)[J].中华妇产科杂志,2011,46(10):796-798.
[10] 乔雪奇,安军明.热敏灸联合盆底肌锻炼治疗女性压力性尿失禁[J].河南中医,2019,39(10):1575-1578.
[11] 陈艳明,董玉喜,易姣姣.温针灸治疗女性压力性尿失禁30例临床观察[J].湖南中医杂志,2019,35(6):69-70.
[12] 王子臣,杨晓锋,左晓玲,等.沈氏芒针治疗女性压力性尿失禁的临床研究[J].河北中医药学报,2019,34(1):34-36.
[13] 毕伟莲.电针治疗女性压力性尿失禁[J].中华中医药学刊,2007,25(6): 1284-1285.
[14] 肖春风,李建坤,韦哲,等.艾灸关元穴治疗老年女性压力性尿失禁30例[J].国际中医中药杂志,2013,35(5):442.
[15] 刘样,胡蓉,袁光辉,等.艾灸配合盆底肌训练治疗产后压力性尿失禁临床观察[J].上海针灸杂志,2018,37(2):192-195.
[16] 王伟,姜义明,王蓉,等.电针治疗轻中度女性压力性尿失禁疗效观察[J].上海针灸杂志,2016,35(1):47-49.
[17] 李爽.针药结合治疗肾阳虚型围绝经期压力性尿失禁的临床疗效观察[D].哈尔滨:黑龙江中医药大学,2018.
[18] 戚莹莹.电针结合中药治疗女性单纯压力性尿失禁的临床疗效观察[D].哈尔滨:黑龙江中医药大学,2017.
[19] LIU Z, XU H, CHEN Y, et al. The efficacy and safety of electroacupuncture for women with pure stress urinary incontinence: study protocol for a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2013;14:315.
[20] XU H, LIU B, WU J, et al.A Pilot randomized placebo controlled trial of electroacupuncture for women with pure stress urinary incontinence. PLoS One. 2016;11(3):e0150821.
[21] SU T, ZHOU J, LIU Z, et al. The efficacy of electroacupuncture for the treatment of simple female stress urinary incontinence-comparison with pelvic floor muscle training: study protocol for a multicenter randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2015;16:45.
[22] 王静.针刺后予雷火灸手法操作配合盆底肌群锻炼治疗压力性尿失禁效果观察[J].中医临床研究,2015,7(36):119-120.
[23] 胡丹,邓鹏,焦琳,等.热敏灸加腹针疗法联合盆底肌训练法治疗女性压力性尿失禁28例临床观察[J].中医杂志,2017,58(19):1662-1665.
[24] 胡丹,邓鹏,焦琳,等.热敏灸联合Kegel锻炼疗法治疗女性压力性尿失禁疗效观察[J].针刺研究,2017,42(4):338-341.
[25] 陈申旭,张馥晴,汪司右.电针阴部神经刺激疗法治疗女性压力性尿失禁临床研究[J].针灸临床杂志,2014,30(3):5-8.
[26] 河恩惠,陈胤希,田鸿芳,等.电针治疗女性压力性尿失禁不同针刺疗程的疗效观察[J].中国针灸,2016,36(4):351-354.
[27] 王琳琳,任志欣,朱敬云,等.电针联合透灸治疗产后压力性尿失禁疗效观察[J].中国针灸,2019,39(6):599-603.
[28] 郑慧敏,徐世芬,尹平,等.电针治疗轻中度女性压力性尿失禁的近远期疗效观察[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2015,10(2):191-193+209.
[29] 王伟,姜义明,王蓉,等.电针治疗轻中度女性压力性尿失禁疗效观察[J].上海针灸杂志,2016,35(1):47-49.
[30] 赵洁晶,崔秀敏,卢耀能,等.针刺联合隔附子饼灸治疗老年女性压力性尿失禁临床研究[J].世界中医药,2016,11(5):891-893.
[31] 张春敏.盆底康复训练联合针灸对产妇产后压力性尿失禁及盆底肌力的影响[J].中国妇幼保健,2018,33(9):1975-1978.
[32] 陈卓伟,王敦建,袁瑷芹.针刺夹脊穴配合盆底肌功能锻炼治疗产后压力性尿失禁疗效观察[J].上海针灸杂志,2017,36(3):308-311.
[33] 陈元霄,马睿杰.电针会阳、中髎穴结合头针治疗女性压力性尿失禁临床观察[J].上海针灸杂志,2015,34(12):1159-1161.
[34] 费凌志,王晓颖,张海峰.头针结合骶四针治疗女性压力性尿失禁临床研究[J].新中医,2020,52(1):142-145.
[35] 王频,杨华元,胡银娥.国家标准《针灸技术操作规范第11部分:电针》研制体会[J].中国针灸,2010,30(5):413-419.
[36] 郭盛楠,齐淑兰,杨立丽,等.中医药研究人员对随机对照试验质量评价工具/报告规范认识现状的横断面调查[J].中华中医药杂志,2018, 33(3):1077-1081.
[37] 谷鸿秋,王杨,李卫.Cochrane偏倚风险评估工具在随机对照研究Meta分析中的应用[J].中国循环杂志,2014,29(2):147-148.
[38] 莫倩,刘志顺.针灸治疗压力性尿失禁的诊疗特点分析[J].上海针灸杂志,2013,32(12):1060-1063.
[39] 王孟琦,王峰.近20年来针灸治疗压力性尿失禁的临床研究进展[J].中医药学报,2019,47(6):73-78.
[40] 陈妮妮,赵培培,杜莉,等.针灸治疗压力性尿失禁的随机对照试验文献计量研究[J].上海针灸杂志,2020,39(7):937-942.
[41] 赵琳,汪司右.不同治疗频次对女性压力性尿失禁疗效的影响[J].中国针灸,2013,33(12):1088-1090.
[42] DAVID MOHER,SALLY HOPEWELL,KENNETH F SCHULZ,等.CONSORT 2010说明与详述:报告平行对照随机临床试验指南的更新[J].中西医结合学报,2010,8(8):701-741.
[43] HUGH MACPHERSON,DOUGLAS G.ALTMAN,RICHARD HAMMERSCHLAG,等.针刺临床试验干预措施报告标准修订版:CONSORT声明的扩展[J].中国循证医学杂志,2010,10(10):1228-1239.
|