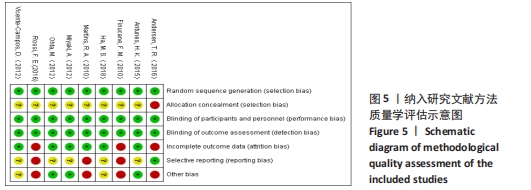
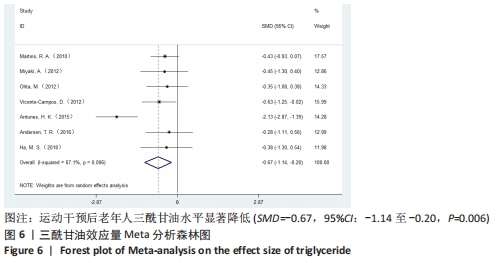
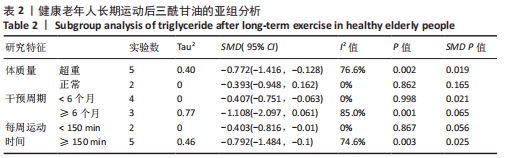
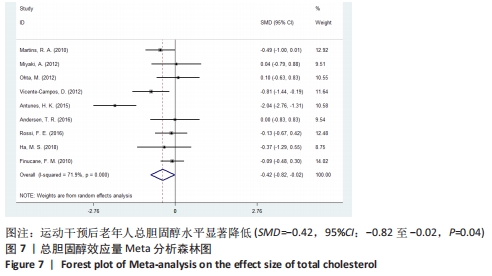
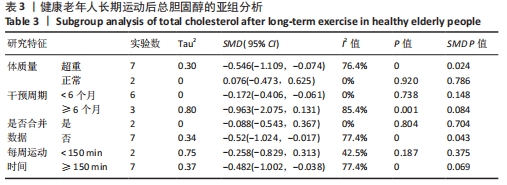
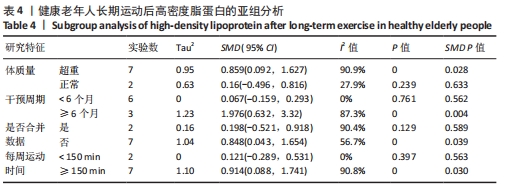
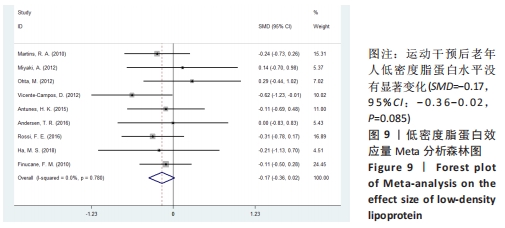
[1] 中国心血管健康与疾病报告编写组.中国心血管健康与疾病报告2020概要[J].中国循环杂志,2021,36(6):521-545.
[2] 蔡芳.有氧运动对老年慢性病患者健康管理效果的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2019, 39(19):4762-4765.
[3] 王保平.老年人体育锻炼现状及其对老年人心血管功能指标的影响[J].中国老年学杂志, 2020,40(5):1005-1007.
[4] PEKAS EJ, SHIN J, SON WM ,et al. Habitual Combined Exercise Protects against Age-Associated Decline in Vascular Function and Lipid Profiles in Elderly Postmenopausal Women. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020; 17(11):3893.
[5] ALBARRATI AM, ALGHAMDI M SM, NAZER RI ,et al. Effectiveness of Low to Moderate Physical Exercise Training on the Level of Low-Density Lipoproteins: A Systematic Review. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:5982980.
[6] MURPHY MH, MURTAGH EM, BOREHAM CA, et al. The effect of a worksite based walking programme on cardiovascular risk in previously sedentary civil servants. BMC Public Health. 2006;6:136.
[7] MIYAKI A, MAEDA S, CHOI Y ,et al. Habitual aerobic exercise increases plasma pentraxin 3 levels in middle-aged and elderly women. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2012;37(5):907-911.
[8] 诸骏仁.中国成人血脂异常防治指南(2016年修订版)[J].中国循环杂志,2016,31(10): 937-953.
[9] STONE NJ, ROBINSON JG, LICHTENSTEIN AH, et al. 2013 ACC/AHA guideline on the treatment of blood cholesterol to reduce atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(25 Pt B): 2889-2934.
[10] CATAPANO AL, REINER Z, DE BACKER G ,et al. ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias The Task Force for the management of dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS). Atherosclerosis. 2011;217(1):3-46.
[11] ROSSI FE, FORTALEZA AC, NEVES LM ,et al. Combined Training (Aerobic Plus Strength) Potentiates a Reduction in Body Fat but Demonstrates No Difference on the Lipid Profile in Postmenopausal Women When Compared With Aerobic Training With a Similar Training Load. J Strength Cond Re. 2016;30(1): 226-234.
[12] FINUCANE FM, SHARP SJ, PURSLOW LR, et al. The effects of aerobic exercise on metabolic risk, insulin sensitivity and intrahepatic lipid in healthy older people from the Hertfordshire Cohort Study: a randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia. 2010;53(4):624-631.
[13] MARTINS RA, VERISSIMO MT, COELHO E SILVA MJ, et al. Effects of aerobic and strength-based training on metabolic health indicators in older adults. Lipids Health Dis. 2010;9:76.
[14] ANDERSEN TR, SCHMIDT JF, PEDERSEN MT, et al. The Effects of 52 Weeks of Soccer or Resistance Training on Body Composition and Muscle Function in +65-Year-Old Healthy Males--A Randomized Controlled Trial. PLoS One. 2016;11(2):e0148236.
[15] ANTUNES HK, DE MELLO MT, DE AQUINO LEMOS V, et al. Aerobic physical exercise improved the cognitive function of elderly males but did not modify their blood homocysteine levels. Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra. 2015;5(1):13-24.
[16] VICENTE-CAMPOS D, MORA J, CASTRO-PINERO J, et al. Impact of a physical activity program on cerebral vasoreactivity in sedentary elderly people. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2012;52(5): 537-544.
[17] OHTA M, HIRAO N, MORI Y, et al. Effects of bench step exercise on arterial stiffness in post-menopausal women: contribution of IGF-1 bioactivity and nitric oxide production. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2012;22(1):36-41.
[18] HA MS, KIM JH, KIM YS ,et al. Effects of aquarobic exercise and burdock intake on serum blood lipids and vascular elasticity in Korean elderly women. Exp Gerontol. 2018; 101:63-68.
[19] LEON AS, SANCHEZ OA. Response of blood lipids to exercise training alone or combined with dietary intervention. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2001;33:S502-515.
[20] KELLEY GA, KELLEY KS, ROBERTS S, et al. Combined effects of aerobic exercise and diet on lipids and lipoproteins in overweight and obese adults: a meta-analysis. J Obes. 2012;2012:985902.
[21] KELLEY GA, KELLEY KS, ROBERTS S, et al. Comparison of aerobic exercise, diet or both on lipids and lipoproteins in adults: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Nutr. 2012;31(2):156-167.
[22] IGARASHI Y, AKAZAWA N, MAEDA S. Effects of Aerobic Exercise Alone on Lipids in Healthy East Asians: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2019;26(5):488-503.
[23] 苏杭.我国运动减肥相关研究可视化分析及其高频关键词结果的Meta分析[D].武汉:武汉体育学院,2020.
[24] 汪毅.55-65岁静坐少动女性运动干预的时效性研究[D].北京:北京体育大学,2016.
[25] 张培珍.血脂异常的中老年人调脂运动处方的研究[D].北京:北京体育大学,2004.
[26] NELSON ME, REJESKI WJ, BLAIR SN, et al. Physical activity and public health in older adults: recommendation from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007; 39(8):1435-1445.
[27] KODAMA S, TANAKA S, SAITO K, et al. Effect of aerobic exercise training on serum levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol: a meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167(10):999-1008.
[28] IGARASHI Y, AKAZAWA N, MAEDA S. Regular aerobic exercise and blood pressure in East Asians: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2018; 40(4):378-389.
[29] KUHLE CL, STEFFEN MW, ANDERSON PJ, et al. Effect of exercise on anthropometric measures and serum lipids in older individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2014;4(6):e005283.
[30] 袁空军.中国人群1990—2019年高低密度脂蛋白胆固醇归因疾病负担趋势分析[J].中国循证医学杂志,2022,22(4):444-449.
[31] MUSCELLA A, STEFANO E, MARSIGLIANTE S. The effects of exercise training on lipid metabolism and coronary heart disease. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020;319(1): H76-H88.
[32] 赵少平.中等强度有氧运动对高血脂患者血脂水平影响的元分析——基于随机对照试验的证据[J].武汉体育学院学报,2022, 56(3):79-85.
[33] O’DONOVAN G, OWEN A, BIRD SR, et al. Changes in cardiorespiratory fitness and coronary heart disease risk factors following 24 wk of moderate- or high-intensity exercise of equal energy cost. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2005;98(5):1619-1625.
[34] GOLDBERG AC, HOPKINS PN, TOTH PP, et al. Familial hypercholesterolemia: screening, diagnosis and management of pediatric and adult patients: clinical guidance from the National Lipid Association Expert Panel on Familial Hypercholesterolemia. J Clin Lipidol. 2011;5(3):133-140.
[35] DAVIDSON MH, BALLANTYNE CM, JACOBSON TA ,et al. Clinical utility of inflammatory markers and advanced lipoprotein testing: advice from an expert panel of lipid specialists. J Clin Lipidol. 2011;5(5):338-367.
[36] 刘广彬.低密度脂蛋白亚型与冠状动脉病变程度的关系[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2019, 27(12):1053-1057.
[37] SARZYNSKI MA, BURTON J, RANKINEN T, et al. The effects of exercise on the lipoprotein subclass profile: A meta-analysis of 10 interventions. Atherosclerosis. 2015;243(2): 364-372.
[38] VARADY KA, ST-PIERRE AC, LAMARCHE B, et al. Effect of plant sterols and endurance training on LDL particle size and distribution in previously sedentary hypercholesterolemic adults. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2005;59(4):518-525.
[39] ELOSUA R, MOLINA L, FITO M, et al. Response of oxidative stress biomarkers to a 16-week aerobic physical activity program, and to acute physical activity, in healthy young men and women. Atherosclerosis. 2003;167(2):327-334.
[40] YANG N, LIN M, WANG BG, et al. Low level of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol is related with increased hemorrhagic transformation after acute ischemic cerebral infarction. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016;20(4):673-678.
[41] MA C, GUROL ME, HUANG Z, et al. Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and risk of intracerebral hemorrhage: A prospective study. Neurology. 2019;93(5):e445-e457.
[42] JOHANNESEN C DL, LANGSTED A, MORTENSEN MB, et al. Association between low density lipoprotein and all cause and cause specific mortality in Denmark: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2020;371:m4266.
[43] WU B, YU Z, TONG T, et al. Evaluation of small dense low-density lipoprotein concentration for predicting the risk of acute coronary syndrome in Chinese population. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020;34(3):e23085.
|