[1] LANE FL, JACOBS S. Stem cells in gynecology. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2012;207(3):149-156.
[2] POLYKANDRIOTIS E, POPESCU LM, HORCH RE. Regenerative medicine: Then and now--an update of recent history into future possibilities. J Cell Mol Med. 2010;14(10):2350-2358.
[3] NI H, ZHAO Y, JI Y, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells contribute to cardiovascular remodeling. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(23):11756-11769.
[4] LELEK J, ZUBA-SURMA EK. Perspectives for Future Use of Extracellular Vesicles from Umbilical Cord- and Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells in Regenerative Therapies-Synthetic Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(3):799.
[5] SIMA Y, CHEN Y. MSC-based therapy in female pelvic floor disorders. Cell Biosci. 2020;10:104.
[6] GOOD MM, SOLOMON ER. Pelvic floor disorders. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2019;46(3):527-540.
[7] HASTINGS J, MACHEK M. Pelvic floor dysfunction in women. Curr Phys Med Rehabil Rep. 2020;8(2):64-75.
[8] 孟晓静,李旻,王少为.中老年女性盆底功能障碍性疾病的临床研究进展[J].中国老年保健医学,2021,19(2):94-97.
[9] ALVAREZ J, CVACH K, DWYER P. Complications in pelvic floor surgery. Minerva Ginecol. 2013;65(1):53-67.
[10] DURANDT C, DESSELS C, DA SILVA C, et al. The effect of early rounds of ex vivo expansion and cryopreservation on the adipogenic differentiation capacity of adipose-derived stromal/stem cells. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):15943.
[11] MELIEF SM, ZWAGINGA JJ, FIBBE WE, et al. Adipose tissue-derived multipotent stromal cells have a higher immunomodulatory capacity than their bone marrow-derived counterparts. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013;2(6):455-463.
[12] YU G, WU X, DIETRICH MA, et al. Yield and characterization of subcutaneous human adipose-derived stem cells by flow cytometric and adipogenic mrna analyzes. Cytotherapy. 2010; 12(4):538-546.
[13] 杨洋,肖云翔,金杰. 压力性尿失禁的干细胞治疗进展[J].中华泌尿外科杂志,2012,33(6):471-473.
[14] 单倩倩,陶丽,颜士杰.女性压力性尿失禁的发病机制及治疗进展[J].安徽医药,2013,17(3):364-367.
[15] 刘剑锋,阳莲,洪莉.水凝胶治疗盆底功能障碍性疾病的研究进展[J].医学研究杂志,2021,50(10):155-157,196.
[16] SONG K, LI L, YAN X, et al. Characterization of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells in vitro culture and in vivo differentiation in a temperature-sensitive chitosan/β- glycerophosphate/collagen hybrid hydrogel. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;70(Pt 1):231-240.
[17] 王琳琳,洪莉.可注射水凝胶治疗压力性尿失禁研究进展[J].中国实用妇科与产科杂志,2018,34(2):228-231.
[18] PU W, HAN Y, YANG M. Human decellularized adipose tissue hydrogels as a culture platform for human adipose-derived stem cell delivery. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2021;19:2280800020988141.
[19] KUMAR A, XU Y, YANG E, et al. Fidelity of long-term cryopreserved adipose-derived stem cells for differentiation into cells of ocular and other lineages. Exp Eye Res. 2019;189:107860.
[20] MIYAGI-SHIOHIRA C, KURIMA K, KOBAYASHI N, et al. Cryopreservation of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell Med. 2015;8(1-2):3-7.
[21] 金琦,彭程,王志平.脂肪来源干细胞在泌尿外科疾病中的研究进展[J].医学综述,2021,27(21):4204-4209.
[22] HARASYMIAK-KRZYŻANOWSKA I, NIEDOJADŁO A, KARWAT J, et al. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells show considerable promise for regenerative medicine applications. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2013;18(4):479-493.
[23] MAZINI L, ROCHETTE L, AMINE M, et al. Regenerative Capacity of Adipose Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs), Comparison with Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs). Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(10):2523.
[24] ARCHACKA K, BEM J, BRZOSKA E, et al. Beneficial Effect of IL-4 and SDF-1 on Myogenic Potential of Mouse and Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Stromal Cells. Cells. 2020;9(6):1479.
[25] TABATABAEI QOMI R, SHEYKHHASAN M. Adipose-derived stromal cell in regenerative medicine: A review. World J Stem Cells. 2017;9(8):107-117.
[26] DOMENIS R, CIFÙ A, QUAGLIA S, et al. Pro inflammatory stimuli enhance the immunosuppressive functions of adipose mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):13325.
[27] AL-GHADBAN S, BUNNELL BA. Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells: Immunomodulatory Effects and Therapeutic Potential. Physiology (Bethesda). 2020;35(2):125-133.
[28] SANDONÀ M, DI PIETRO L, ESPOSITO F, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Their Secretome: New Therapeutic Perspectives for Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:652970.
[29] ZHUANG G, WEN Y, BRIGGS M, et al. Secretomes of human pluripotent stem cell-derived smooth muscle cell progenitors upregulate extracellular matrix metabolism in the lower urinary tract and vagina. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):228.
[30] DINESCU S, DOBRANICI A, TECUCIANU R, et al. Exosomes as Part of the Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Secretome- Opening New Perspectives for Cell-Free Regenerative Applications. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1312:139-163.
[31] XING X, HAN S, CHENG G, et al. Proteomic Analysis of Exosomes from Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Tissue Injury. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:6094562.
[32] Mitchell R, Mellows B, Sheard J, et al. Secretome of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promotes skeletal muscle regeneration through synergistic action of extracellular vesicle cargo and soluble proteins. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):116.
[33] LIU X, WANG S, WU S, et al. Exosomes secreted by adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells regulate type I collagen metabolism in fibroblasts from women with stress urinary incontinence. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):159.
[34] 汪成合,陈忠.干细胞治疗女性压力性尿失禁的研究进展[J].临床泌尿外科杂志,2014,29(5):457-460.
[35] LIN G, WANG G, BANIE L, et al. Treatment of stress urinary incontinence with adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Cytotherapy. 2010;12(1):88-95.
[36] INOUE Y, FUJITA F, YAMAGUCHI I, et al. Improvement of Anal Function by Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Sheets. Dig Surg. 2018;35(1):64-69.
[37] KUISMANEN K, JUNTUNEN M, NARRA GIRISH N, et al. Functional Outcome of Human Adipose Stem Cell Injections in Rat Anal Sphincter Acute Injury Model. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2018;7(3):295-304.
[38] ZHAO W, ZHANG C, JIN C, et al. Periurethral injection of autologous adipose-derived stem cells with controlled-release nerve growth factor for the treatment of stress urinary incontinence in a rat model. Eur Urol. 2011;59(1):155-163.
[39] FU Q, SONG XF, LIAO GL, et al. Myoblasts differentiated from adipose-derived stem cells to treat stress urinary incontinence. Urology. 2010; 75(3):718-723.
[40] WU G, SONG Y, ZHENG X,et al. Adipose-derived stromal cell transplantation for treatment of stress urinary incontinence. Tissue Cell. 2011;43(4):246-253.
[41] 关立铭,李秀娟,陈亚萍,等.自体脂肪源性干细胞与成纤维细胞联合尿道周围注射治疗大鼠压力性尿失禁[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(14):2530-2533.
[42] 耿鹏,宋红娟,刘亚玲,等.脂肪源成体干细胞移植治疗压力性尿失禁的实验研究[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志(电子版),2015,5(3): 197-201.
[43] WANG Y, DUAN M, RAHMAN M, et al. Use of bioactive extracellular matrix fragments as a urethral bulking agent to treat stress urinary incontinence. Acta Biomater. 2020;117:156-166.
[44] GARCIA-ARRANZ M, ALONSO-GREGORIO S, FONTANA-PORTELLA P, et al. Two phase I/II clinical trials for the treatment of urinary incontinence with autologous mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020; 9(12):1500-1508.
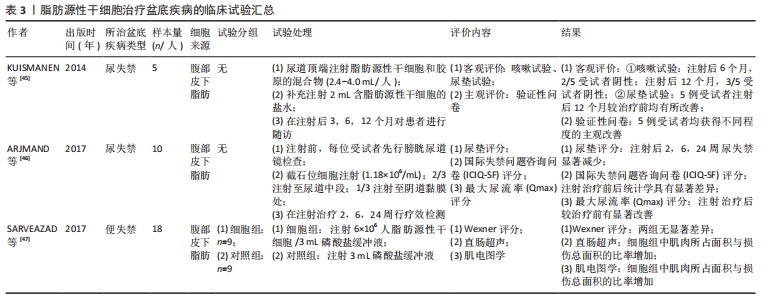
[45] KUISMANEN K, SARTONEVA R, HAIMI S, et al. Autologous adipose stem cells in treatment of female stress urinary incontinence: results of a pilot study. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014;3(8):936-941.
[46] ARJMAND B, SAFAVI M, HEIDARI R, et al. Concomitant Transurethral and Transvaginal-Periurethral Injection of Autologous Adipose Derived Stem Cells for Treatment of Female Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Phase One Clinical Trial. Acta Med Iran. 2017;55(6):368-374.
[47] SARVEAZAD A, NEWSTEAD GL, MIRZAEI R, et al. A new method for treating fecal incontinence by implanting stem cells derived from human adipose tissue: preliminary findings of a randomized double-blind clinical trial. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):40.
[48] 李露,洪莉.成体干细胞治疗压力性尿失禁的应用[J].现代妇产科进展,2019,28(5):385-387.
[49] 江长琴. 女性压力性尿失禁的治疗进展[J].国际泌尿系统杂志, 2021,41(4):753-755.
[50] DE LA GARZA-RODEA AS, VAN DER VELDE-VAN DIJKE I, BOERSMA H, et al. Myogenic properties of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from three different sources. Cell Transplant. 2012;21(1):153-173.
[51] 常悦,刘海峰,王建六. 组织工程及再生医学在盆底功能障碍性疾病中的应用进展[J].中华妇产科杂志,2015,50(6):470-472.
[52] MANODORO S, FRIGERIO M, BARBA M, et al. Stem Cells in Clinical Trials for Pelvic Floor Disorders: a Systematic Literature Review. Reprod Sci. 2022;29(6):1710-1720.
[53] 唐翔,朱兰.干细胞在妇科泌尿领域的应用[J].现代妇产科进展, 2017,26(10):788-790.
[54] HONG P, YANG H, WU Y, et al. The functions and clinical application potential of exosomes derived from adipose mesenchymal stem cells: a comprehensive review. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):242.
[55] SHUKLA L, YUAN Y, SHAYAN R, et al. Fat Therapeutics: The Clinical Capacity of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells and Exosomes for Human Disease and Tissue Regeneration. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:158.
|