[1] MOLL G, HOOGDUIJN MJ, ANKRUM JA. Editorial: Safety, Efficacy and Mechanisms of Action of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapies. Front Immunol. 2020;11:243.
[2] VADIVEL S, VINCENT P, SEKARAN S, et al. Inflammation in myocardial injury- Stem cells as potential immunomodulators for myocardial regeneration and restoration. Life Sci. 2020;250:117582.
[3] WANG W, WU RD, CHEN P, et al. Liraglutide combined with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation inhibits beta-cell apoptosis via mediating the ASK1/JNK/BAX pathway in rats with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020;36(2):e3212.
[4] CHEN Y, YU Q, HU Y, et al. Current Research and Use of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Therapy of Autoimmune Diseases. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;14(7):579-582.
[5] MAYILSAMY K, MARKOUTSA E, DAS M, et al. Treatment with shCCL20-CCR6 nanodendriplexes and human mesenchymal stem cell therapy improves pathology in mice with repeated traumatic brain injury. Nanomedicine. 2020;29:102247.
[6] BYDON M, DIETZ AB, GONCALVES S, et al. CELLTOP Clinical Trial: First Report From a Phase 1 Trial of Autologous Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of Paralysis Due to Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020;95(2):406-414.
[7] 单莎瑞,黄国志.干细胞抗衰老的理论研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(23):4347-4354.
[8] PATEL S, LEE KB. Probing stem cell behavior using nanoparticle-based approaches. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2015;7(6):759-778.
[9] VU H, ZHOU J, HUANG Y, et al. Development of a dual-wavelength fluorescent nanoprobe for in vivo and in vitro cell tracking consecutively. Bioorg Med Chem. 2019;27(9):1855-1862.
[10] KIRCHER MF, GAMBHIR SS, GRIMM J. Noninvasive cell-tracking methods. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011;8(11):677-688.
[11] WANG J, JOKERST JV. Stem Cell Imaging: Tools to Improve Cell Delivery and Viability. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:9240652.
[12] MAZZA M, LOZANO N, VIEIRA DB, et al. Liposome-Indocyanine Green Nanoprobes for Optical Labeling and Tracking of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Post-Transplantation In Vivo. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017;6(21): 1700374.
[13] 温清,刘人恺,王志勇.两亲性聚乙烯亚胺修饰量子点构建功能性光学探针用于干细胞治疗的示踪研究[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版),2015,44(1):28-31.
[14] CAO J, ZHU B, ZHENG K, et al. Recent Progress in NIR-II Contrast Agent for Biological Imaging. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;7:487.
[15] CHEN G,TIAN F,ZHANG Y, et al. Tracking of Transplanted Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Living Mice using Near-Infrared Ag2S Quantum Dots. Advanced Functional Materials. 2014;24(17):2481-2488.
[16] YANG Y, CHEN J, SHANG X, et al. Visualizing the Fate of Intra-Articular Injected Mesenchymal Stem Cells In Vivo in the Second Near-Infrared Window for the Effective Treatment of Supraspinatus Tendon Tears. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019;6(19):1901018.
[17] CHETTY SS, PRANEETHA S, GOVARTHANAN K, et al. Noninvasive Tracking and Regenerative Capabilities of Transplanted Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Labeled with I-III-IV Semiconducting Nanocrystals in Liver-Injured Living Mice. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(9):8763-8778.
[18] LI K, QIN W, DING D, et al. Photostable fluorescent organic dots with aggregation-induced emission (AIE dots) for noninvasive long-term cell tracing. Sci Rep. 2013;3:1150.
[19] YANG C, NI X, MAO D, et al. Seeing the fate and mechanism of stem cells in treatment of ionizing radiation-induced injury using highly near-infrared emissive AIE dots. Biomaterials. 2019;188:107-117.
[20] 杨磊,杨志,连锋.碳量子点作为生物相容性发光材料在再生医学方面的应用[J].材料导报,2019,33(S2):1-9.
[21] VENERANDO A, MAGRO M, BARATELLA D, et al. Biotechnological applications of nanostructured hybrids of polyamine carbon quantum dots and iron oxide nanoparticles. Amino Acids. 2020;52(2):301-311.
[22] YAN J, HOU S, YU Y, et al. The effect of surface charge on the cytotoxicity and uptake of carbon quantum dots in human umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;171:241-249.
[23] QIU J, LI D, MOU X, et al. Effects of Graphene Quantum Dots on the Self-Renewal and Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(6):702-710.
[24] OH EJ, LEE HW, KALIMUTHU S, et al. In vivo migration of mesenchymal stem cells to burn injury sites and their therapeutic effects in a living mouse model. J Control Release. 2018;279:79-88.
[25] YEH HW, KARMACH O, JI A, et al. Red-shifted luciferase-luciferin pairs for enhanced bioluminescence imaging. Nat Methods. 2017;14(10): 971-974.
[26] IWANO S, SUGIYAMA M, HAMA H, et al. Single-cell bioluminescence imaging of deep tissue in freely moving animals. Science. 2018;359 (6378):935-939.
[27] CAI WW, WANG LJ, LI SJ, et al. Effective tracking of bone mesenchymal stem cells in vivo by magnetic resonance imaging using melanin-based gadolinium3+ nanoparticles. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(1): 131-137.
[28] MOHSENI M, SHOJAEI S, MEHRAVI B, et al. Natural polymeric nanoparticles as a non-invasive probe for mesenchymal stem cell labelling. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2020;48(1):770-776.
[29] ROGOSNITZKY M, BRANCH S. Gadolinium-based contrast agent toxicity: a review of known and proposed mechanisms. Biometals. 2016;29(3):365-376.
[30] LIU SJ, WANG LJ, QIAO Y, et al. A promising magnetic resonance stem cell tracer based on natural biomaterials in a biological system: manganese(II) chelated to melanin nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:1749-1759.
[31] HAEDICKE IE, LOAI S, CHENG HM. An Efficient T 1 Contrast Agent for Labeling and Tracking Human Embryonic Stem Cells on MRI. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2019;2019:3475786.
[32] MOGHADDAM SE, HERNÁNDEZ-RIVERA M, ZAIBAQ NG, et al. A New High-Performance Gadonanotube-Polymer Hybrid Material for Stem Cell Labeling and Tracking by MRI. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2018; 2018:2853736.
[33] WANG LJ, YAN CP, CHEN D, et al. Efficacy Evaluation and Tracking of Bone Marrow Stromal Stem Cells in a Rat Model of Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:9105768.
[34] JIANG R, LIAO Y, YANG F, et al. SPIO nanoparticle-labeled bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit pulmonary EndoMT induced by SiO2. Exp Cell Res. 2019;383(1):111492.
[35] DEMIN AM, MEKHAEV AV, KANDARAKOV OF, et al. L-Lysine-modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles for magnetic cell labeling. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;190:110879.
[36] MISHRA SK, KHUSHU S, SINGH AK, et al. Homing and Tracking of Iron Oxide Labelled Mesenchymal Stem Cells After Infusion in Traumatic Brain Injury Mice: a Longitudinal In Vivo MRI Study. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2018;14(6):888-900.
[37] DUAN X, LU L, WANG Y, et al. The long-term fate of mesenchymal stem cells labeled with magnetic resonance imaging-visible polymersomes in cerebral ischemia. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:6705-6719.
[38] ZARE S, MEHRABANI D, JALLI R, et al. MRI-Tracking of Dental Pulp Stem Cells In Vitro and In Vivo Using Dextran-Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. J Clin Med. 2019;8(9):1418.
[39] HSU FT, WEI ZH, HSUAN YC, et al. MRI tracking of polyethylene glycol-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide-labelled placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells toward glioblastoma stem-like cells in a mouse model. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(sup3):S448-S459.
[40] ANDREAS K, GEORGIEVA R, LADWIG M, et al. Highly efficient magnetic stem cell labeling with citrate-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for MRI tracking. Biomaterials. 2012;33(18):4515-4525.
[41] LI L, JIANG W, LUO K, et al. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as MRI contrast agents for non-invasive stem cell labeling and tracking. Theranostics. 2013;3(8):595-615.
[42] AZEVEDO-PEREIRA RL, RANGEL B, TOVAR-MOLL F, et al. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as a tool to track mouse neural stem cells in vivo. Mol Biol Rep. 2019;46(1):191-198.
[43] 马思雨,王鹏,杨玉志,等.磁性纳米颗粒标记间充质干细胞及对其功能的调控[J].中国材料进展,2019,38(6):559-566.
[44] CORES J, CARANASOS TG, CHENG K. Magnetically Targeted Stem Cell Delivery for Regenerative Medicine. J Funct Biomater. 2015;6(3): 526-546.
[45] GU L, LI X, JIANG J, et al. Stem cell tracking using effective self-assembled peptide-modified superparamagnetic nanoparticles. Nanoscale. 2018;10(34):15967-15979.
[46] SHELAT R, BHATT LK, KHANNA A, et al. A comprehensive toxicity evaluation of novel amino acid-modified magnetic ferrofluids for magnetic resonance imaging. Amino Acids. 2019;51(6):929-943.
[47] MARKIDES H, NEWELL KJ, RUDORF H, et al. Ex vivo MRI cell tracking of autologous mesenchymal stromal cells in an ovine osteochondral defect model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):25.
[48] MUHAMMAD G, JABLONSKA A, ROSE L, et al. Effect of MRI tags: SPIO nanoparticles and 19F nanoemulsion on various populations of mouse mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2015;75(2): 144-159.
[49] HU S, ZHOU Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Enhanced bone regeneration and visual monitoring via superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle scaffold in rats. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(4):e2085-e2098.
[50] HEQUET E, HENOUMONT C, MULLER RN, et al. Fluorinated MRI contrast agents and their versatile applications in the biomedical field. Future Med Chem. 2019;11(10):1157-1175.
[51] RIZZO S, PETRELLA F, ZUCCA I, et al. In vitro labelling and detection of mesenchymal stromal cells: a comparison between magnetic resonance imaging of iron-labelled cells and magnetic resonance spectroscopy of fluorine-labelled cells. Eur Radiol Exp. 2017;1(1):6.
[52] VU-QUANG H, VINDING MS, XIA D, et al. Chitosan-coated poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) perfluorooctyl bromide nanoparticles for cell labeling in (19)F magnetic resonance imaging. Carbohydr Polym. 2016;136: 936-944.
[53] QUANG HV, CHANG CC, SONG P, et al. Caveolae-mediated mesenchymal stem cell labelling by PSS-coated PLGA PFOB nano-contrast agent for MRI. Theranostics. 2018;8(10):2657-2671.
[54] MOONSHI SS, ZHANG C, PENG H, et al. A unique 19F MRI agent for the tracking of non phagocytic cells in vivo. Nanoscale. 2018;10(17): 8226-8239.
[55] CAO M, MAO J, DUAN X, et al. In vivo tracking of the tropism of mesenchymal stem cells to malignant gliomas using reporter gene-based MR imaging. Int J Cancer. 2018;142(5):1033-1046.
[56] HUANG X, XUE Y, WU J, et al. MRI Tracking of SPIO- and Fth1-Labeled Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Transplantation for Treatment of Stroke. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2019;2019:5184105.
[57] PEREIRA SM, MOSS D, WILLIAMS SR, et al. Overexpression of the MRI Reporter Genes Ferritin and Transferrin Receptor Affect Iron Homeostasis and Produce Limited Contrast in Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(7):15481-15496.
[58] SRIVASTAVA AK, BULTE JW. Seeing stem cells at work in vivo. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2014;10(1):127-144.
[59] CHO IK, MORAN SP, PAUDYAL R, et al. Longitudinal monitoring of stem cell grafts in vivo using magnetic resonance imaging with inducible maga as a genetic reporter. Theranostics. 2014;4(10):972-989.
[60] PEREIRA SM, WILLIAMS SR, MURRAY P, et al. MS-1 magA: Revisiting Its Efficacy as a Reporter Gene for MRI. Mol Imaging. 2016;15: 1536012116641533.
[61] KERANS FFA, LUNGARO L, AZFER A, et al. The Potential of Intrinsically Magnetic Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Tissue Engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(10):3159.
[62] SOOD V, MITTAL BR, BHANSALI A, et al. Biodistribution of 18F-FDG-Labeled Autologous Bone Marrow-Derived Stem Cells in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Exploring Targeted and Intravenous Routes of Delivery. Clin Nucl Med. 2015;40(9):697-700.
[63] DUDHIA J, BECERRA P, VALDÉS MA, et al. In Vivo Imaging and Tracking of Technetium-99m Labeled Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Equine Tendinopathy. J Vis Exp. 2015;(106):e52748.
[64] PARK BN, LIM TS, YOON JK, et al. In vivo tracking of intravenously injected mesenchymal stem cells in an Alzheimer’s animal model. Cell Transplant. 2018;27(8):1203-1209.
[65] CEN P, CHEN J, HU C, et al. Noninvasive in-vivo tracing and imaging of transplanted stem cells for liver regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):143.
[66] BANSAL A, PANDEY MK, DEMIRHAN YE, et al. Novel (89)Zr cell labeling approach for PET-based cell trafficking studies. EJNMMI Res. 2015;5:19.
[67] MUÑOZ-ÁLVAREZ KA, ALTOMONTE J, LAITINEN I, et al. PET imaging of oncolytic VSV expressing the mutant HSV-1 thymidine kinase transgene in a preclinical HCC rat model. Mol Ther. 2015;23(4):728-736.
[68] SCHÖNITZER V, HAASTERS F, KÄSBAUER S, et al. In vivo mesenchymal stem cell tracking with PET using the dopamine type 2 receptor and 18F-fallypride. J Nucl Med. 2014;55(8):1342-1347.
[69] WOLFS E, HOLVOET B, GIJSBERS R, et al. Optimization of multimodal imaging of mesenchymal stem cells using the human sodium iodide symporter for PET and Cerenkov luminescence imaging. PLoS One. 2014;9(4):e94833.
[70] PEI Z, ZENG J, SONG Y, et al. In vivo imaging to monitor differentiation and therapeutic effects of transplanted mesenchymal stem cells in myocardial infarction. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):6296.
[71] CHEN F, JOKERST JV. Stem Cell Tracking with Nanoparticle-Based Ultrasound Contrast Agents. Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2126:141-153.
[72] FOROUTAN F, JOKERST JV, GAMBHIR SS, et al. Sol-gel synthesis and electrospraying of biodegradable (P2O5)55-(CaO)30-(Na2O)15 glass nanospheres as a transient contrast agent for ultrasound stem cell imaging. ACS Nano. 2015;9(2):1868-1877.
[73] BHATTACHARYA K, SACCHETTI C, EL-SAYED R, et al. Enzymatic ‘stripping’ and degradation of PEGylated carbon nanotubes. Nanoscale. 2014;6(24):14686-14690.
[74] BOUCHÉ M, HSU JC, DONG YC, et al. Recent Advances in Molecular Imaging with Gold Nanoparticles. Bioconjug Chem. 2020;31(2): 303-314.
[75] KIM T, LEMASTER JE, CHEN F, et al. Photoacoustic Imaging of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Labeled with Prussian Blue-Poly(l-lysine) Nanocomplexes. ACS Nano. 2017;11(9):9022-9032.
[76] DHADA KS, HERNANDEZ DS, SUGGS LJ. In Vivo Photoacoustic Tracking of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Viability. ACS Nano. 2019;13(7):7791-7799.
[77] LAFFEY MK, KUBELICK KP, DONNELLY EM, et al. Effects of Freezing on Mesenchymal Stem Cells Labeled with Gold Nanoparticles. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2020;26(1):1-10.
[78] PAYSEN H, LOEWA N, STACH A, et al. Cellular uptake of magnetic nanoparticles imaged and quantified by magnetic particle imaging. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):1922.
[79] ZHENG B, VON SEE MP, YU E, et al. Quantitative Magnetic Particle Imaging Monitors the Transplantation, Biodistribution, and Clearance of Stem Cells In Vivo. Theranostics. 2016;6(3):291-301.
[80] SONG G, CHEN M, ZHANG Y, et al. Janus Iron Oxides @ Semiconducting Polymer Nanoparticle Tracer for Cell Tracking by Magnetic Particle Imaging. Nano Lett. 2018;18(1):182-189.
[81] WANG Q, MA X, LIAO H, et al. Artificially Engineered Cubic Iron Oxide Nanoparticle as a High-Performance Magnetic Particle Imaging Tracer for Stem Cell Tracking. ACS Nano. 2020;14(2):2053-2062.
[82] 胡越,彭焘,黄明声,等.多模态成像对间充质干细胞移植后活体示踪的应用研究[J].中国医学影像技术,2019,35(11):1622-1626.
[83] KUBELICK KP, EMELIANOV SY. Prussian blue nanocubes as a multimodal contrast agent for image-guided stem cell therapy of the spinal cord. Photoacoustics. 2020;18:100166.
[84] MASTHOFF M, BUCHHOLZ R, BEUKER A, et al. Introducing Specificity to Iron Oxide Nanoparticle Imaging by Combining 57Fe-Based MRI and Mass Spectrometry. Nano Lett. 2019;19(11):7908-7917.
[85] LIU M, WANG Y, LI M, et al. Using tyrosinase as a tri-modality reporter gene to monitor transplanted stem cells in acute myocardial infarction. Exp Mol Med. 2018;50(4):54.
[86] NOMBELA-ARRIETA C, RITZ J, SILBERSTEIN LE. The elusive nature and function of mesenchymal stem cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011;12(2): 126-131.
[87] GU J, HUANG L, ZHANG C, et al. Therapeutic evidence of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for cerebral palsy: a randomized, controlled trial. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):43.
[88] MATHIASEN AB, QAYYUM AA, JØRGENSEN E, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cell treatment in patients with ischaemic heart failure: final 4-year follow-up of the MSC-HF trial. Eur J Heart Fail. 2020;22(5):884-892.
[89] EDMUNDSON M, THANH NT, SONG B. Nanoparticles based stem cell tracking in regenerative medicine. Theranostics. 2013;3(8):573-582.
[90] BERKOWITZ AL, MILLER MB, MIR SA, et al. Glioproliferative Lesion of the Spinal Cord as a Complication of “Stem-Cell Tourism”. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(2):196-198.
[91] WANG Y, XU C, OW H. Commercial nanoparticles for stem cell labeling and tracking. Theranostics. 2013;3(8):544-560.
[92] PETERSON KM, FRANCHI F, OLTHOFF M, et al. Pathway-specific reporter genes to study stem cell biology. Stem Cells. 2020;38(6):808-814.
|
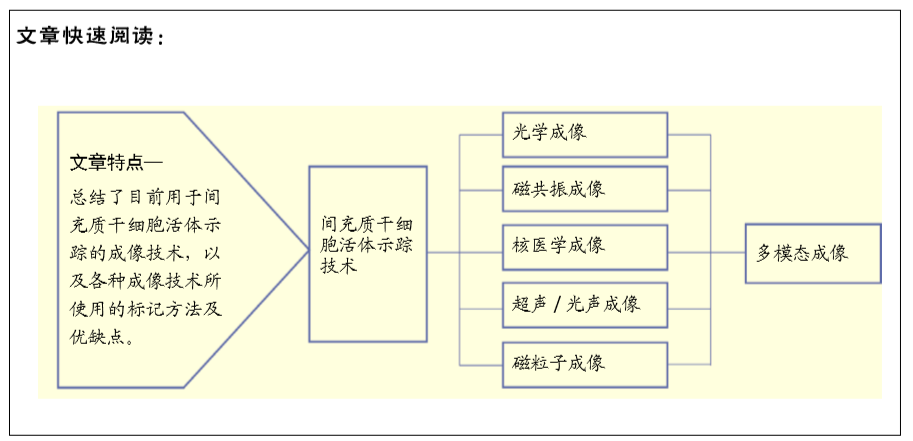

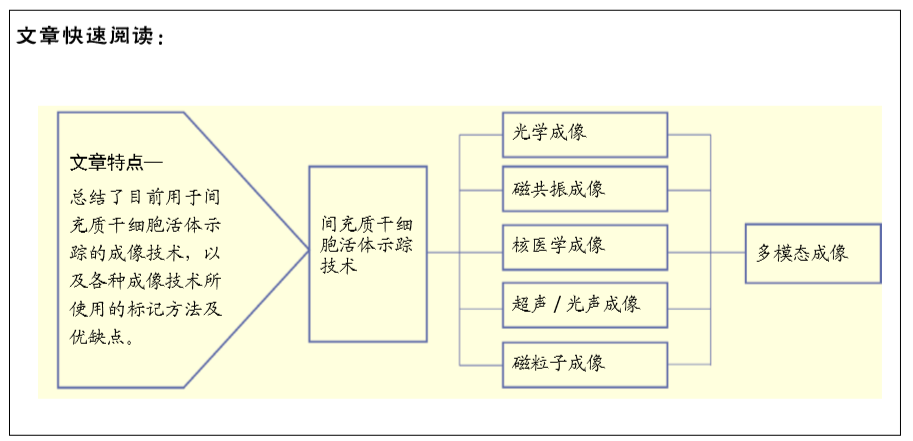
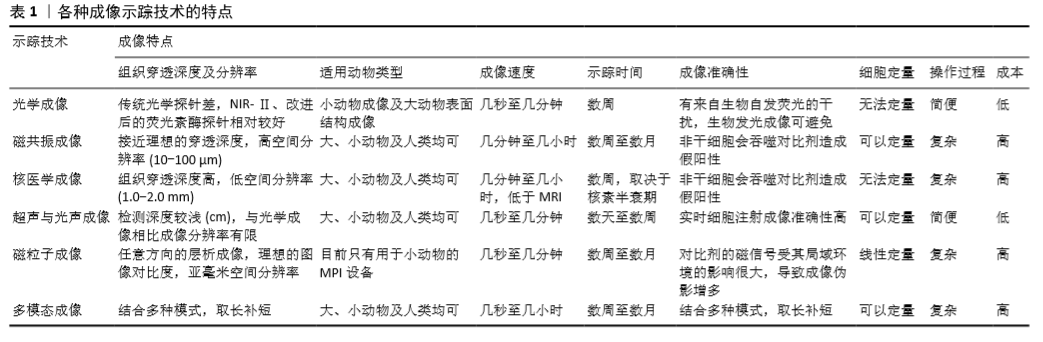 干细胞移植后在生物体内的存活率与死亡或清除时间也是影响治疗效果的主要因素之一,而报告基因的表达往往与细胞的活性直接相关。近年来,基于纳米颗粒的细胞示踪探针在各种成像技术中的开发和应用,以及高时空分辨成像技术及新影像设备的快速发展,对于小动物活体成像,采用NIR-Ⅱ荧光成像结合生物发光成像技术可以同时提供细胞分布及存活情况的信息,对于大动物和人类成像,采用多模态成像技术可以满足不同需求,超声/光声与MRI结合可以实时引导干细胞注射,同时对移植后的细胞分布进行追踪;基于报告基因的PET成像技术与MRI结合成像可以提供细胞存活与否和体内分布的信息,目前已生产了联合这两种技术的成像设备。目前对于干细胞移植后的体内长期高灵敏度监测仍是一大难点,并且区分细胞的存活状态、分化与否也至关重要,干细胞途径特异性报告基因有望解决这一问题[92]。因此,对于现代甚至未来的疾病治疗,特别是干细胞治疗和免疫治疗,结合多模式技术和集成智能探针的活体细胞示踪将具有巨大的潜力。
干细胞移植后在生物体内的存活率与死亡或清除时间也是影响治疗效果的主要因素之一,而报告基因的表达往往与细胞的活性直接相关。近年来,基于纳米颗粒的细胞示踪探针在各种成像技术中的开发和应用,以及高时空分辨成像技术及新影像设备的快速发展,对于小动物活体成像,采用NIR-Ⅱ荧光成像结合生物发光成像技术可以同时提供细胞分布及存活情况的信息,对于大动物和人类成像,采用多模态成像技术可以满足不同需求,超声/光声与MRI结合可以实时引导干细胞注射,同时对移植后的细胞分布进行追踪;基于报告基因的PET成像技术与MRI结合成像可以提供细胞存活与否和体内分布的信息,目前已生产了联合这两种技术的成像设备。目前对于干细胞移植后的体内长期高灵敏度监测仍是一大难点,并且区分细胞的存活状态、分化与否也至关重要,干细胞途径特异性报告基因有望解决这一问题[92]。因此,对于现代甚至未来的疾病治疗,特别是干细胞治疗和免疫治疗,结合多模式技术和集成智能探针的活体细胞示踪将具有巨大的潜力。