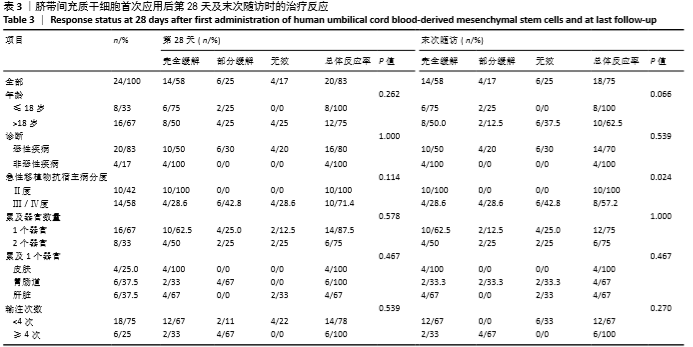
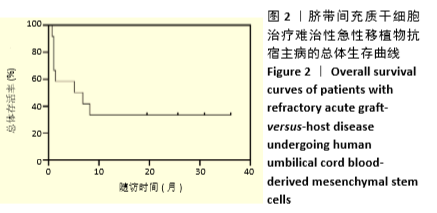
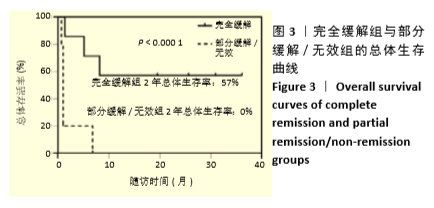
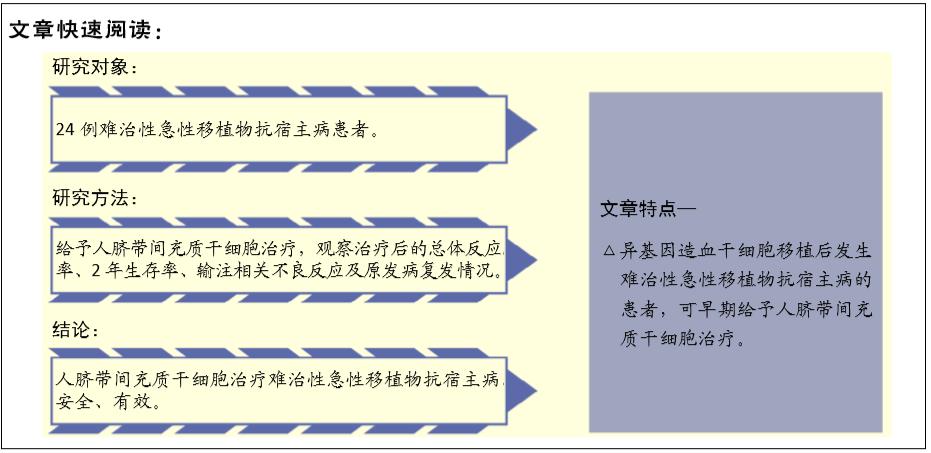
[1] 中华医学会血液学分会干细胞应用学组.中国异基因造血干细胞移植治疗血液系统疾病专家共识(Ⅲ)——急性移植物抗宿主病(2020年版)[J].中华血液学杂志,2020,41(7):529-536.
[2] MUNNEKE JM, SPRUIT MJ, CORNELISSEN AS, et al. The Potential of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells as Treatment for Severe Steroid-Refractory Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease: A Critical Review of the Literature. Transplantation. 2016;100(11):2309-2314.
[3] 许兰平,黄晓军.我如何治疗造血干细胞移植后急性移植物抗宿主病[J].中华血液学杂志,2017,38(8):649-655.
[4] PENACK O, MARCHETTI M, RUUTU T, et al. Prophylaxis and management of graft versus host disease after stem-cell transplantation for haematological malignancies: updated consensus recommendations of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7(2):e157-e167.
[5] RUUTU T, GRATWOHL A, DE WITTE T, et al. Prophylaxis and treatment of GVHD: EBMT-ELN working group recommendations for a standardized practice. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014;49(2):168-173.
[6] DEEG HJ. How I treat refractory acute GVHD. Blood. 2007;109(10): 4119-4126.
[7] DOTOLI GM, DE SANTIS GC, ORELLANA MD, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell infusion to treat steroid-refractory acute GvHD III/IV after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017;52(6):859-862.
[8] LE BLANC K, RASMUSSON I, SUNDBERG B, et al. Treatment of severe acute graft-versus-host disease with third party haploidentical mesenchymal stem cells. Lancet. 2004;363(9419):1439-1441.
[9] 巫丹,尹宇.人脐带间充质干细胞治疗不同疾病的研究进展[J].中国比较医学杂志,2020,30(8):125-130.
[10] 王佃亮.脐带间充质干细胞的临床应用[J].中国生物工程杂志,2020, 40(5):125-129.
[11] SCHOEMANS HM, LEE SJ, FERRARA JL, et al. EBMT-NIH-CIBMTR Task Force position statement on standardized terminology & guidance for graft-versus-host disease assessment. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2018;53(11):1401-1415.
[12] PRZEPIORKA D, WEISDORF D, MARTIN P, et al. 1994 Consensus Conference on Acute GVHD Grading. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995; 15(6):825-828.
[13] FORMAN SJ, NEGRIN RS, JOSEPH H, et al. Thomas’ Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: Stem Cell Transplantation.5th Ed. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. 2015:1012-1019.
[14] 王佃亮.脐带间充质干细胞制剂的质量管理及有效性和安全性[J].转化医学杂志,2020,9(2):65-69.
[15] HOLTAN SG, PASQUINI M, WEISDORF DJ. Acute graft-versus-host disease: a bench-to-bedside update. Blood. 2014;124(3):363-373.
[16] MARKEY KA, MACDONALD KP, HILL GR. The biology of graft-versus-host disease: experimental systems instructing clinical practice. Blood. 2014;124(3):354-362.
[17] 许兰平,韩婷婷.异基因造血干细胞移植术后移植物抗宿主病的研究进展[J].临床内科杂志,2011,28(11):725-728.
[18] 惠玉,周凡,张毅.MSC治疗aGVHD相关机制及临床应用研究进展[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2017,25(4):1245-1249.
[19] 刘茂兰,史明霞.间充质干细胞治疗急性移植物抗宿主病机制及应用进展[J].实用医学杂志,2019,35(11):1850-1853.
[20] WANG L, GU Z, ZHAO X, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Released from Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Prevent Life-Threatening Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease in a Mouse Model of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Stem Cells Dev. 2016;25(24):1874-1883.
[21] DENG Y, YI S, WANG G, et al. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells instruct dendritic cells to acquire tolerogenic phenotypes through the IL-6-mediated upregulation of SOCS1. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23(17):2080-2092.
[22] LIU Y, YIN Z, ZHANG R, et al. MSCs inhibit bone marrow-derived DC maturation and function through the release of TSG-6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;450(4):1409-1415.
[23] DAVIES LC, HELDRING N, KADRI N, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Secretion of Programmed Death-1 Ligands Regulates T Cell Mediated Immunosuppression. Stem Cells. 2017;35(3):766-776.
[24] GUO H, ZHAO N, GAO H, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Overexpressing Interleukin-35 Propagate Immunosuppressive Effects in Mice. Scand J Immunol. 2017;86(5):389-395.
[25] BOISSEL L, TUNCER HH, BETANCUR M, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells increase expansion of cord blood natural killer cells. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008;14(9):1031-1038.
[26] WILLIAMS AR, HARE JM. Mesenchymal stem cells: biology, pathophysiology, translational findings, and therapeutic implications for cardiac disease. Circ Res. 2011;109(8):923-940.
[27] LE BLANC K, FRASSONI F, BALL L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of steroid-resistant, severe, acute graft-versus-host disease: a phase II study. Lancet. 2008;371(9624):1579-1586.
[28] ZHAO K, LOU R, HUANG F, et al. Immunomodulation effects of mesenchymal stromal cells on acute graft-versus-host disease after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015;21(1):97-104.
[29] ZHAO K, LIU Q. The clinical application of mesenchymal stromal cells in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J Hematol Oncol. 2016; 9(1):46.
[30] MUROI K, MIYAMURA K, OKADA M, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (JR-031) for steroid-refractory grade III or IV acute graft-versus-host disease: a phase II/III study. Int J Hematol. 2016;103(2):243-250.
[31] ERBEY F, ATAY D, AKCAY A, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Treatment for Steroid Refractory Graft-versus-Host Disease in Children: A Pilot and First Study from Turkey. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:1641402.
[32] VON DALOWSKI F, KRAMER M, WERMKE M, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells for Treatment of Acute Steroid-Refractory Graft Versus Host Disease: Clinical Responses and Long-Term Outcome. Stem Cells. 2016;34(2):357-366.
[33] HASHMI S, AHMED M, MURAD MH, et al. Survival after mesenchymal stromal cell therapy in steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Haematol. 2016;3(1):e45-52.
[34] CHEN X, WANG C, YIN J, et al. Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Steroid-Refractory Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease following Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0136991.
[35] BADER P, KUÇI Z, BAKHTIAR S, et al. Effective treatment of steroid and therapy-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease with a novel mesenchymal stromal cell product (MSC-FFM). Bone Marrow Transplant. 2018;53(7):852-862.
[36] KURTZBERG J, PROCKOP S, TEIRA P, et al. Allogeneic human mesenchymal stem cell therapy (remestemcel-L, Prochymal) as a rescue agent for severe refractory acute graft-versus-host disease in pediatric patients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20(2):229-235.
|