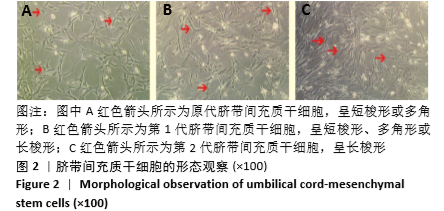
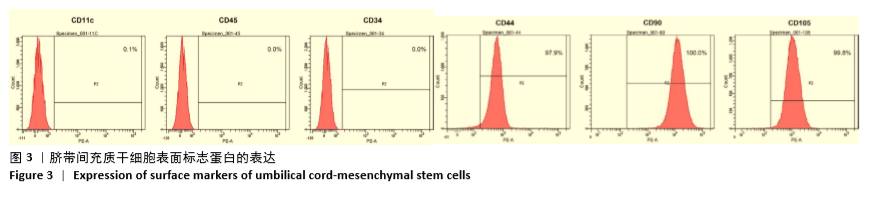
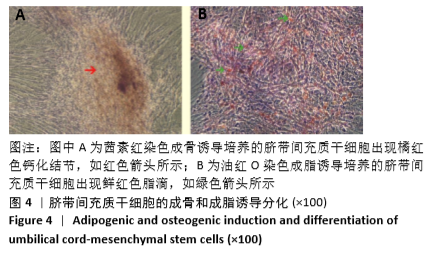
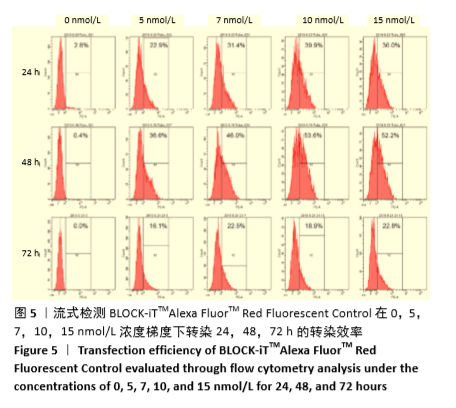
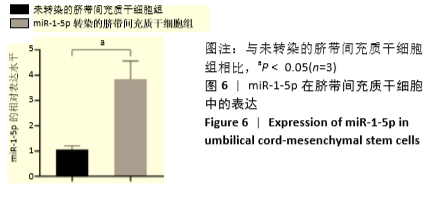
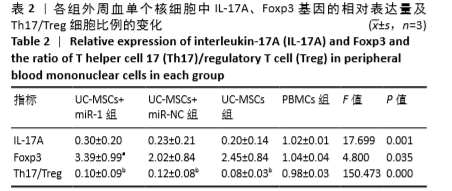
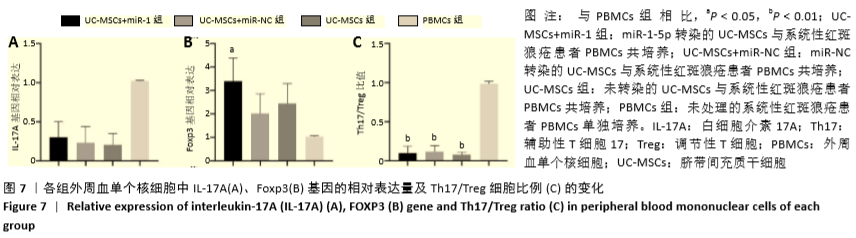
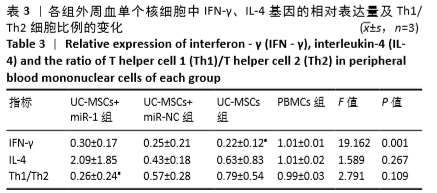
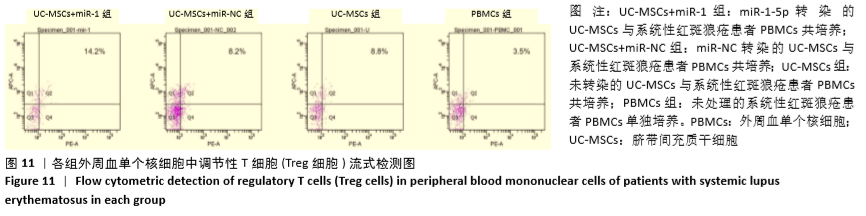
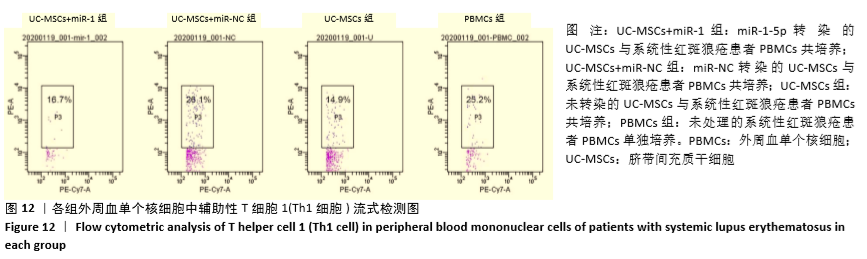
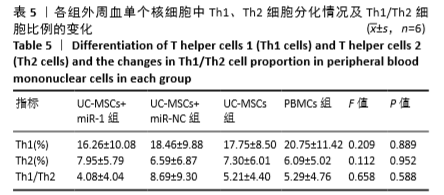
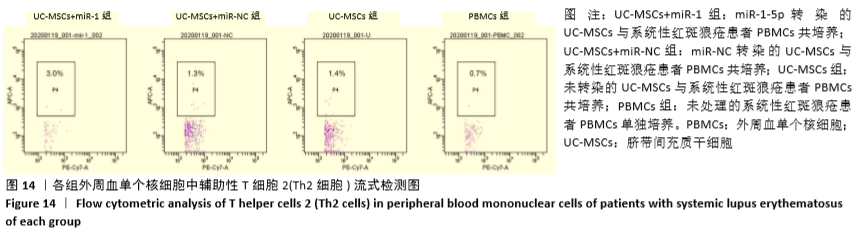
[1] HIDALGO Y, NÚÑEZ S, FUENZALIDA MJ, et al. Thymic B Cells Promote Germinal Center-Like Structures and the Expansion of Follicular Helper T Cells in Lupus-Prone Mice. Front Immunol. 2020;11:696.
[2] CHAN RW, LAI FM, LI EK, et al. Imbalance of Th1/Th2 transcription factors in patients with lupus nephritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006;45(8):951-957.
[3] CHEN M, CHEN X, WAN Q. Altered frequency of Th17 and Treg cells in new-onset systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Eur J Clin Invest. 2018;48(11):e13012.
[4] GUIMARÃES PM, SCAVUZZI BM, STADTLOBER NP, et al. Cytokines in systemic lupus erythematosus: far beyond Th1/Th2 dualism lupus: cytokine profiles. Immunol Cell Biol. 2017;95(9):824-831.
[5] TALAAT RM, MOHAMED SF, BASSYOUNI IH, et al. Th1/Th2/Th17/Treg cytokine imbalance in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients: Correlation with disease activity. Cytokine. 2015;72(2):146-153.
[6] ÁLVAREZ-RODRÍGUEZ L, MARTÍNEZ-TABOADA V, CALVO-ALÉN J, et al. Altered Th17/Treg Ratio in Peripheral Blood of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus but Not Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Front Immunol. 2019;10:391.
[7] MARTINO DJ, BOSCO A, MCKENNA KL, et al. T-cell activation genes differentially expressed at birth in CD4+ T-cells from children who develop IgE food allergy. Allergy. 2012;67(2):191-200.
[8] DOLFF S, BIJL M, HUITEMA MG, et al. Disturbed Th1, Th2, Th17 and T(reg) balance in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol. 2011; 141(2):197-204.
[9] LA CAVA A. Tregs in SLE: an Update. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2018;20(2):6.
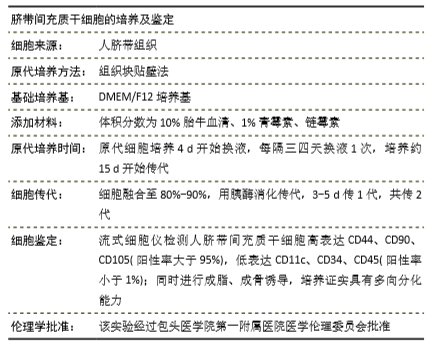
[10] EL OMAR R, BEROUD J, STOLTZ JF, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: the new gold standard for mesenchymal stem cell-based therapies? Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2014;20(5):523-544.
[11] WANG D, HUANG S, YUAN X, et al. The regulation of the Treg/Th17 balance by mesenchymal stem cells in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell Mol Immunol. 2017;14(5):423-431.
[12] ZHANG J, ZHOU S, ZHOU Y, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor gene-modified adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate radiation induced liver damage in a rat model. PLoS One. 2014;9(12):e114670.
[13] XU WL, ONG HS, ZHU Y, et al. In Situ Release of VEGF Enhances Osteogenesis in 3D Porous Scaffolds Engineered with Osterix-Modified Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017;23(9-10):445-457.
[14] FOROUZANFAR F, AMIN B, GHORBANI A, et al. New approach for the treatment of neuropathic pain: Fibroblast growth factor 1 gene-transfected adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Eur J Pain. 2018;22(2):295-310.
[15] XIAO C, NEMAZEE D, GONZALEZ-MARTIN A. MicroRNA control of B cell tolerance, autoimmunity and cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020;64:102-107.
[16] WU Y, PU N, SU W, et al. Downregulation of miR-1 in colorectal cancer promotes radioresistance and aggressive phenotypes. J Cancer. 2020;11(16):4832-4840.
[17] TOWNLEY-TILSON WH, CALLIS TE, WANG D. MicroRNAs 1, 133, and 206: critical factors of skeletal and cardiac muscle development, function, and disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010;42(8):1252-1255.
[18] KURA B, KALOCAYOVA B, DEVAUX Y, et al. Potential Clinical Implications of miR-1 and miR-21 in Heart Disease and Cardioprotection. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(3):700.
[19] HAN C, ZHOU Y, AN Q, et al. MicroRNA-1 (miR-1) inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation and migration by targeting MET. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(9):6715-6723.
[20] NASSER MW, DATTA J, NUOVO G, et al. Down-regulation of micro-RNA-1 (miR-1) in lung cancer. Suppression of tumorigenic property of lung cancer cells and their sensitization to doxorubicin-induced apoptosis by miR-1. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(33):12945.
[21] DATTA J, KUTAY H, NASSER MW, et al. Methylation mediated silencing of MicroRNA-1 gene and its role in hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2008;68(13):5049-5058.
[22] YOSHINO H, CHIYOMARU T, ENOKIDA H, et al. The tumour-suppressive function of miR-1 and miR-133a targeting TAGLN2 in bladder cancer. Br J Cancer. 2011; 104(5):808-818.
[23] LIU C, WANG J, ZHANG X. The involvement of MiR-1-clathrin pathway in the regulation of phagocytosis. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e98747.
[24] TIAN M, ZHOU Y, JIA H, et al. The Clinical Significance of Changes in the Expression Levels of MicroRNA-1 and Inflammatory Factors in the Peripheral Blood of Children with Acute-Stage Asthma. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:7632487.
[25] ZILAHI E, ADAMECZ Z, BODOKI L, et al. Dysregulated expression profile of myomiRs in the skeletal muscle of patients with polymyositis. EJIFCC. 2019;30(2): 237-245.
[26] NAVARRO QUIROZ E, NAVARRO QUIROZ R, PACHECO LUGO L, et al. Integrated analysis of microRNA regulation and its interaction with mechanisms of epigenetic regulation in the etiology of systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS One. 2019;14(6):e0218116.
[27] MORADIAN TEHRANI R, VERDI J, NOUREDDINI M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: A new platform for targeting suicide genes in cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2018; 233(5):3831-3845.
[28] Zhang Y, Xia Y, Ni S, et al. Transplantation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviates pneumonitis of MRL/lpr mice. J Thorac Dis. 2014;6(2):109-117.
[29] Gu Z, Akiyama K, Ma X, et al. Transplantation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviates lupus nephritis in MRL/lpr mice. Lupus. 2010;19(13):1502-1514.
[30] 蔡心珍,倪军,李邹,等.脐带间充质干细胞对MRL/lpr小鼠免疫炎性易栓状态的调节作用[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2015,23(6):1697-1701.
[31] KOT M, BAJ-KRZYWORZEKA M, SZATANEK R, et al. The Importance of HLA Assessment in “Off-the-Shelf” Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Based-Therapies. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(22):5680.
[32] ZHAO S, WEHNER R, BORNHÄUSER M, et al. Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stromal cells and their therapeutic consequences for immune-mediated disorders. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(5):607-614.
[33] ZHOU T, LI HY, LIAO C, et al. Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:6518508.
[34] WANG D, LI J, ZHANG Y, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in active and refractory systemic lupus erythematosus: a multicenter clinical study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(2):R79.
[35] GU F, WANG D, ZHANG H, et al. Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for lupus nephritis patients refractory to conventional therapy. Clin Rheumatol. 2014;33(11):1611-1619.
[36] LI X, WANG D, LIANG J, et al. Mesenchymal SCT ameliorates refractory cytopenia in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013; 48(4):544-550.
[37] ZHOU C, ZHAO X, DUAN S. The role of miR-543 in human cancerous and noncancerous diseases. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(1):15-26.
[38] CHEN JQ, PAPP G, SZODORAY P, et al. The role of microRNAs in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 2016;15(12):1171-1180.
[39] LIU D, ZHANG N, ZHANG X, et al. MiR-410 Down-Regulates the Expression of Interleukin-10 by Targeting STAT3 in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;39(1):303-315.
[40] LI D, LI X, DUAN M, et al. MiR-153-3p induces immune dysregulation by inhibiting PELI1 expression in umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmunity. 2020;53(4):201-209.
[41] CHEN JF, MANDEL EM, THOMSON JM, et al. The role of microRNA-1 and microRNA-133 in skeletal muscle proliferation and differentiation. Nat Genet. 2006;38(2):228-233.
[42] DUAN L, XIONG X, LIU Y, et al. miRNA-1: functional roles and dysregulation in heart disease. Mol Biosyst. 2014;10(11):2775-2782.
[43] PARKES JE, DAY PJ, CHINOY H, et al. The role of microRNAs in the idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015;27(6):608-615.
[44] LI D, GUO B, WU H, et al. Interleukin-17 in systemic lupus erythematosus: A comprehensive review. Autoimmunity. 2015;48(6):353-361.
[45] VALENCIA X, YARBORO C, ILLEI G, et al. Deficient CD4+CD25high T regulatory cell function in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 2007;178(4):2579-2588.
[46] 孙雯,俞建,时毓民,等.中药槐耳调节哮喘缓解期儿童外周血单个核细胞Th1/Th2平衡的基因及蛋白水平研究[J].中华中医药杂志,2009,24(7):915-917.
[47] DE LA VARGA MARTÍNEZ R, RODRÍGUEZ-BAYONA B, AÑEZ GA, et al. Clinical relevance of circulating anti-ENA and anti-dsDNA secreting cells from SLE patients and their dependence on STAT-3 activation. Eur J Immunol. 2017;47(7):1211-1219.
[48] EGWUAGU CE. STAT3 in CD4+ T helper cell differentiation and inflammatory diseases. Cytokine. 2009;47(3):149-156.
[49] ALUNNO A, PADJEN I, FANOURIAKIS A, et al. Pathogenic and Therapeutic Relevance of JAK/STAT Signaling in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Integration of Distinct Inflammatory Pathways and the Prospect of Their Inhibition with an Oral Agent. Cells. 2019;8(8):898.
[50] LUO X, ZHANG L, LI M, et al. The role of miR-125b in T lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2013;31(2): 263-271.
[51] ZUO H, WENG K, LUO M, et al. A MicroRNA-1-Mediated Inhibition of the NF-κB Pathway by the JAK-STAT Pathway in the Invertebrate Litopenaeus vannamei. J Immunol. 2020;204(11):2918-2930.
[52] LI L, MA X, ZHAO YF, et al. MiR-1-3p facilitates Th17 differentiation associating with multiple sclerosis via targeting ETS1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020; 24(12):6881-6892.
|