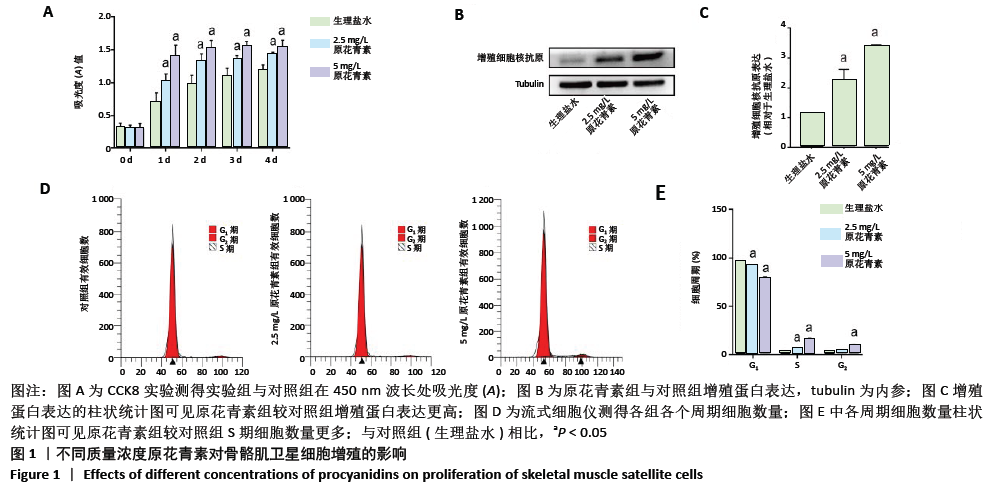
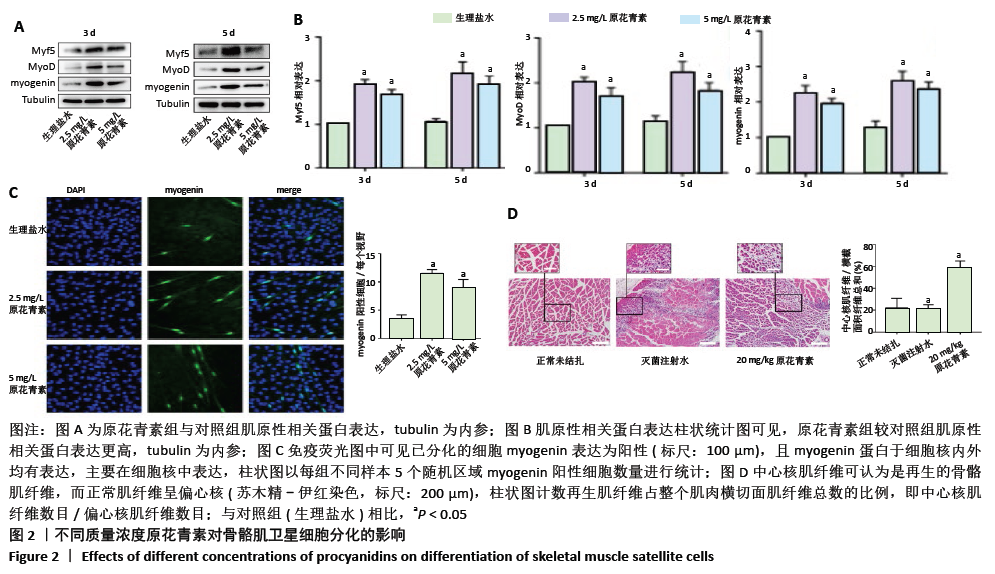
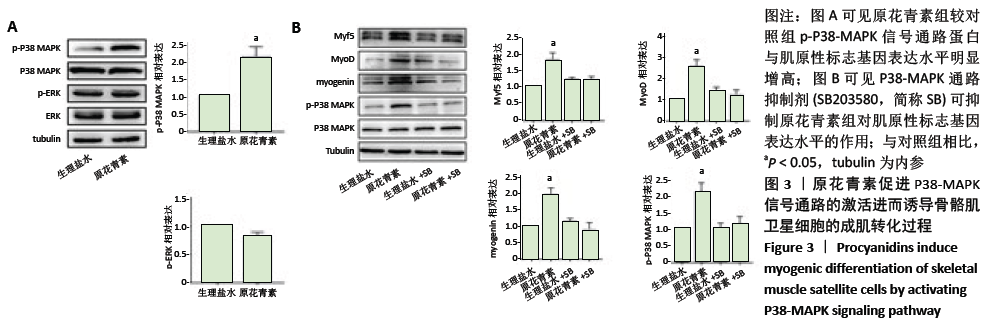
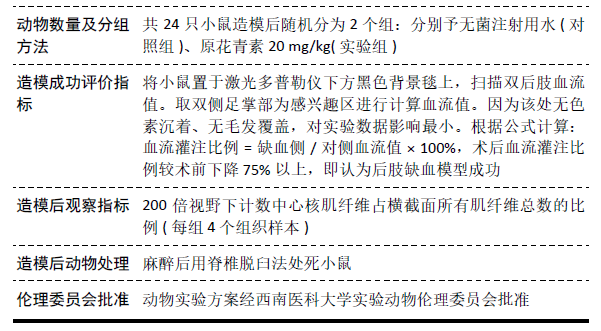
[1] WEITZ JI, BYRNE J, CLAGETT GP, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of chronic arterial insufficiency of the lower extremities: a critical review. Circulation. 1996;94(11):3026-3049.
[2] FOWKES FG, RUDAN D, RUDAN I, et al. Comparison of global estimates of prevalence and risk factors for peripheral artery disease in 2000 and 2010: a systematic review and analysis. Lancet (London, England). 2013;382(9901):1329-1340.
[3] GRAY BH, CONTE MS, DAKE MD, et al. Atherosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease Symposium II: lower-extremity revascularization: state of the art. Circulation. 2008;118(25):2864-2872.
[4] LEJAY A, MEYER A, SCHLAGOWSKI AI, et al. Mitochondria: mitochondrial participation in ischemia-reperfusion injury in skeletal muscle. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014;50:101-105.
[5] BISCHOFF R, HEINTZ C. Enhancement of skeletal muscle regeneration. Dev Dyn. 1994;201(1):41-54.
[6] CHANG NC, RUDNICKI MA. Satellite cells: the architects of skeletal muscle. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2014;107:161-181.
[7] WANG YX, RUDNICKI MA. Satellite cells, the engines of muscle repair. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011;13(2):127-133.
[8] KUANG S, GILLESPIE MA, RUDNICKI MA. Niche regulation of muscle satellite cell self-renewal and differentiation. Cell Stem Cell. 2008; 2(1):22-31.
[9] KADI F, CHARIFI N, DENIS C, et al. The behaviour of satellite cells in response to exercise: what have we learned from human studies? Pflugers Arch. 2005;451(2):319-327.
[10] KIM AR, KIM KM, BYUN MR, et al. Catechins activate muscle stem cells by Myf5 induction and stimulate muscle regeneration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;489(2):142-148.
[11] RUDNICKI MA, SVHNEGELSBERG PN, STEAD RH, et al. MyoD or Myf-5 is required for the formation of skeletal muscle. Cell. 1993;75(7):1351-1359.
[12] CORNELISON DD, WOLD BJ. Single-cell analysis of regulatory gene expression in quiescent and activated mouse skeletal muscle satellite cells. Dev Biol. 1997;191(2):270-283.
[13] KUMAR R, DEEP G, WEMPE MF, et al. Procyanidin B2 3,3″-di-O-gallate inhibits endothelial cells growth and motility by targeting VEGFR2 and integrin signaling pathways. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2015;15(1):14-26.
[14] LEE TM, CHARNG MJ, TSENG CD, et al. A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of STA-2 (Green Tea Polyphenols) in Patients with Chronic Stable Angina. Acta Cardiologica Sinica. 2016;32(4):439-449.
[15] DAGLIA M. Polyphenols as antimicrobial agents. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2012;23(2):174-181.
[16] NAKAYAMA T. Suppression of hydroperoxide-induced cytotoxicity by polyphenols. Cancer Res. 1994;54(7 Suppl):1991s-1993s.
[17] CHANG WT, SHAO ZH, YIN JJ, et al. Comparative effects of flavonoids on oxidant scavenging and ischemia-reperfusion injury in cardiomyocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007;566(1-3):58-66.
[18] QUINTIERI AM, BALDINO N, FILICE E, et al. Malvidin, a red wine polyphenol, modulates mammalian myocardial and coronary performance and protects the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Nutr Biochem. 2013;24(7):1221-1231.
[19] MONTESANO A, LUZI L, SENESI P, et al. Resveratrol promotes myogenesis and hypertrophy in murine myoblasts. J Transl Med. 2013;11:310.
[20] DING Y, DAI X, JIANG Y, et al. Grape seed proanthocyanidin extracts alleviate oxidative stress and ER stress in skeletal muscle of low-dose streptozotocin- and high-carbohydrate/high-fat diet-induced diabetic rats. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013;57(2):365-369.
[21] 杜超, 何雪梅, 施森,等.原花青素对小鼠后肢缺血肌肉的作用及miR-133b的表达变化[J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2018, 34(5):108-116.
[22] TOGLIATTO G, TROMBETTA A, DENTELLI P, et al. Unacylated ghrelin promotes skeletal muscle regeneration following hindlimb ischemia via SOD-2-mediated miR-221/222 expression. J Am Heart Assoc. 2013; 2(6):e000376.
[23] HELLINGMAN AA, BASTIAANSEN AJ, DE VRIES MR, et al. Variations in surgical procedures for hind limb ischaemia mouse models result in differences in collateral formation. Eur JVasc Endovasc Surg. 2010; 40(6):796-803.
[24] LIMBOURG A, KORFF T, NAPP LC, et al. Evaluation of postnatal arteriogenesis and angiogenesis in a mouse model of hind-limb ischemia. Nat Protoc. 2009;4(12):1737-1746.
[25] ZHAI L, WU R, HAN W, et al. miR-127 enhances myogenic cell differentiation by targeting S1PR3. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(3):e2707.
[26] CRIQUI MH, ABOYANS V. Epidemiology of peripheral artery disease. Circ Res. 2015;116(9):1509-1526.
[27] TEDESCO FS, DELLAVALLE A, DIAZ-MANERA J, et al. Repairing skeletal muscle: regenerative potential of skeletal muscle stem cells. J Clin Invest. 2010;120(1):11-19.
[28] TROY A, CADWALLADER AB, FEDOROV Y, et al. Coordination of satellite cell activation and self-renewal by Par-complex-dependent asymmetric activation of p38α/β MAPK. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;11(4):541-553.
[29] ZAMMIT PS, GOLDING JP, NAGATA Y, et al. Muscle satellite cells adopt divergent fates: a mechanism for self-renewal? J Cell Biol. 2004;166(3): 347-357.
[30] SABOURIN LA, GIRGIS-GABARDO A, SEALE P, et al. Reduced differentiation potential of primary MyoD-/- myogenic cells derived from adult skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1999;144(4):631-643.
[31] CHARGE SB, RUDNICKI MA. Cellular and molecular regulation of muscle regeneration. Physiol Rev. 2004;84(1):209-238.
[32] POUSSARD S, PIRES-ALVES A, DIALLO R, et al. A natural antioxidant pine bark extract, Oligopin®, regulates the stress chaperone HSPB1 in human skeletal muscle cells: a proteomics approach. Phytother Res. 2013;27(10):1529-1535.
[33] ZHANG YP, LIU SY, SUN QY, et al. Proanthocyanidin B2 attenuates high-glucose-induced neurotoxicity of dorsal root ganglion neurons through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(9): 1628-1636.
[34] GAO M, ZHAO Z, LV P, et al. Quantitative combination of natural anti-oxidants prevents metabolic syndrome by reducing oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2015;6:206-217.
[35] LI P, WANG J, LU S, et al. Protective effect of hawthorn leaf procyanidins on cardiomyocytes of neonatal rats subjected to simulated ischemia-reperfusion injury. Zhongguo Zhong yao za zhi. 2009;34(1):96-99.
[36] MORENO-LUNA R, MUNOZ-HERNANDEZ R, MIRANDA ML, et al. Olive oil polyphenols decrease blood pressure and improve endothelial function in young women with mild hypertension. Am JHypertens. 2012;25(12):1299-1304.
[37] KONG X, GUAN J, GONG S, et al. Neuroprotective Effects of Grape Seed Procyanidin Extract on Ischemia-Reperfusion Brain Injury. Chin Med Sci J. 2017;32(2):92-99.
[38] KRUGER MJ, SMITH C. Postcontusion polyphenol treatment alters inflammation and muscle regeneration. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2012; 44(5):872-880.
[39] ZACCAGNINIG, MARTELLI F, MAGENTA A, et al. p66(ShcA) and oxidative stress modulate myogenic differentiation and skeletal muscle regeneration after hind limb ischemia. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(43): 31453-31459.
[40] COLETTI D, TEODORI L, LIN Z, et al. Restoration versus reconstruction: cellular mechanisms of skin, nerve and muscle regeneration compared. Regen Med Res. 2013;1(1):4.
[41] YIN H, PRICE F, RUDNICKI MA. Satellite cells and the muscle stem cell niche. Physiol Rev. 2013;93(1):23-67.
[42] COUFFINHAL T, SILVER M, ZHENG LP, et al. Mouse model of angiogenesis. Am JPathol. 1998;152(6):1667-1679.
[43] PERDIGUERO E, SOUSA-VICTOR P, RUIZ-BONILLA V, et al. p38/MKP-1-regulated AKT coordinates macrophage transitions and resolution of inflammation during tissue repair. J Cell Biol. 2011;195(2):307-322.
[44] DUMONT NA, BENTZINGER CF, SINCENNES MC, et al. Satellite Cells and Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Compr Physiol. 2015;5(3):1027-1059.
[45] RIUZZI F, SORCI G, SAHGEDDU R, et al. HMGB1-RAGE regulates muscle satellite cell homeostasis through p38-MAPK- and myogenin-dependent repression of Pax7 transcription. J Cell Sci. 2012;125(Pt 6): 1440-1454.
|