中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (31): 4939-4944.doi: 10.12307/2021.133
• 骨髓干细胞 bone marrow stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
过表达miR-378a可影响骨髓间充质干细胞膜片成骨及成血管分化的能力
李 君1,左新慧1,刘小元1,张 凯1,韩祥祯1,何惠宇 1,2
- 1新疆医科大学第一附属医院(附属口腔医院)口腔修复科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054;2新疆维吾尔自治区口腔医学研究所,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054
Effect of over expression of miR-378a on osteogenic and vascular differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell sheet
Li Jun1, Zuo Xinhui1, Liu Xiaoyuan1, Zhang Kai1, Han Xiangzhen1, He Huiyu1, 2
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, The First Affiliated Hospital (Affiliated Stomatological Hospital) of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Institute of Stomatology, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
miR-378a:为miR-378a-3p和miR-378a-5p的总称,是含有1个茎环结构的非编码小RNA分子,可通过与靶基因3'UTR不完全的碱基互补配在细胞增殖、分化、凋亡和侵袭等过程中发挥重要调控作用,是目前再生医学研究的热点。
细胞膜片技术:该技术可有效保存干细胞周围的细胞外基质及包含各种生物和机械特性的完整细胞-细胞连接,可以在移植期间提高细胞存活率并减少细胞损失,已成为组织工程中基于支架材料的有效传递种子细胞的主流方法。
背景:近年来利用微小RNA(miRNA)调节干细胞的功能和分化是再生医学的一个极具吸引力的治疗模式,因此将miRNA负载于干细胞膜片增强其成骨及成血管相关性能,对骨缺损的修复研发一种新型修复材料具有重要意义。
目的:探讨过表达miR-378a基因对骨髓间充质干细胞膜片成骨及成血管分化能力的影响。
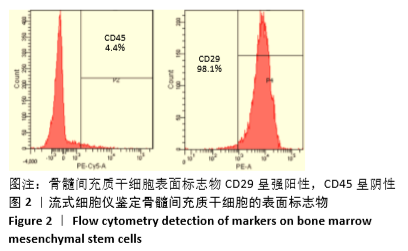
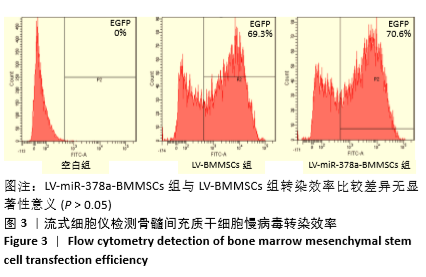
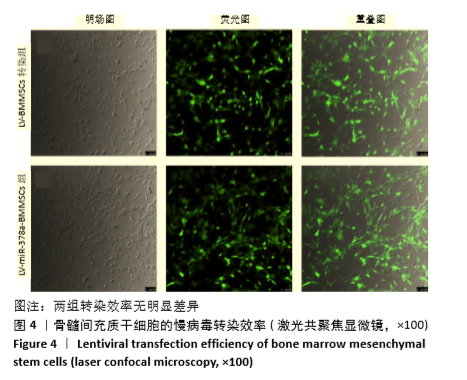
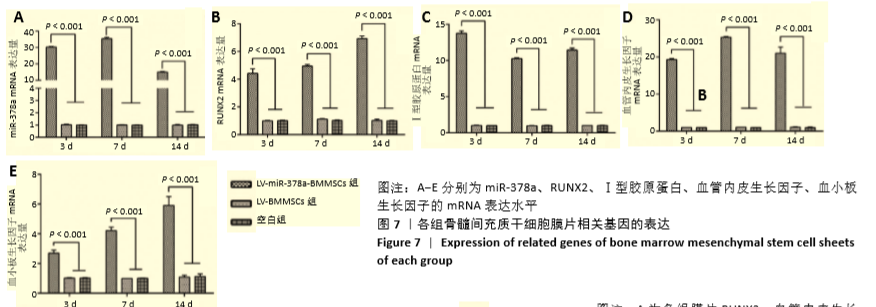
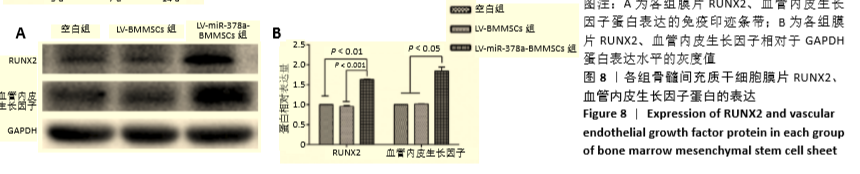
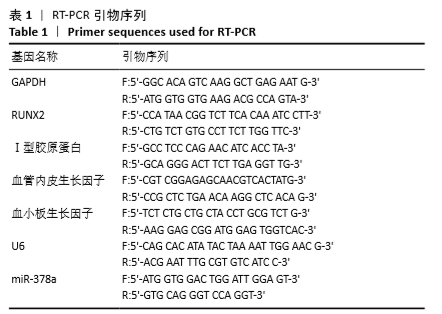
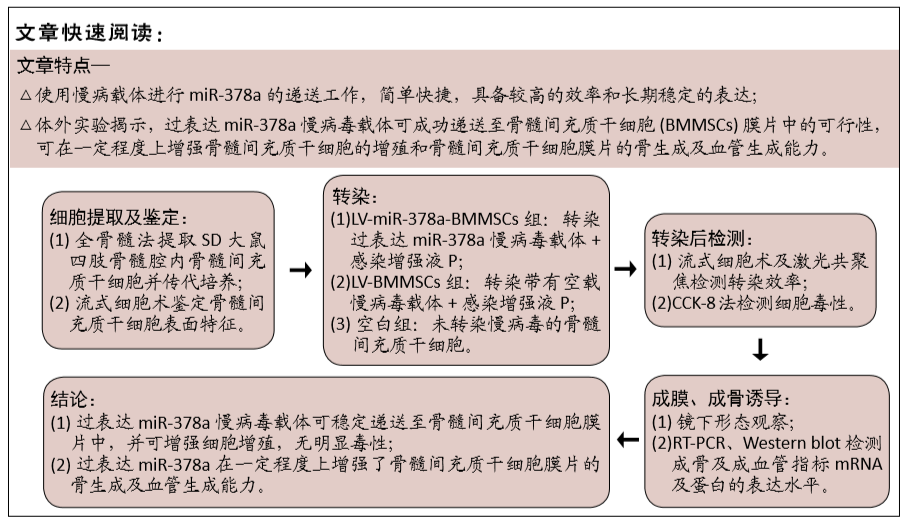
方法:分离培养SD大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞,选用合适滴度的miR-378a慢病毒载体、阴性对照病毒分别感染骨髓间充质干细胞,依次记为LV-miR-378a-BMMSCs组、LV-BMMSCs组,以未转染病毒载体的细胞为空白组。将3组细胞分别接种于6孔板内,加入膜片诱导液培养6 d,镜下观察膜片形态。膜片形成后更换为成骨诱导液培养,培养3,7,14 d时,采用RT-PCR检测miR-378a、成骨基因RUNX2、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白及成血管基因血管内皮生长因子、血小板生长因子mRNA的表达;培养14 d时,采用Western blot法检测RUNX2、血管内皮生长因子蛋白表达。
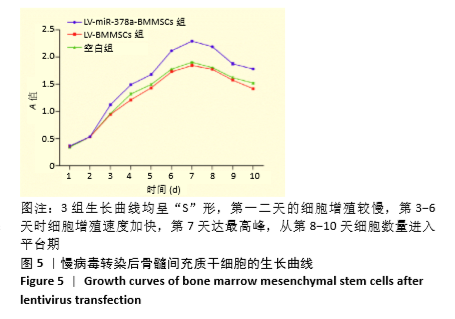
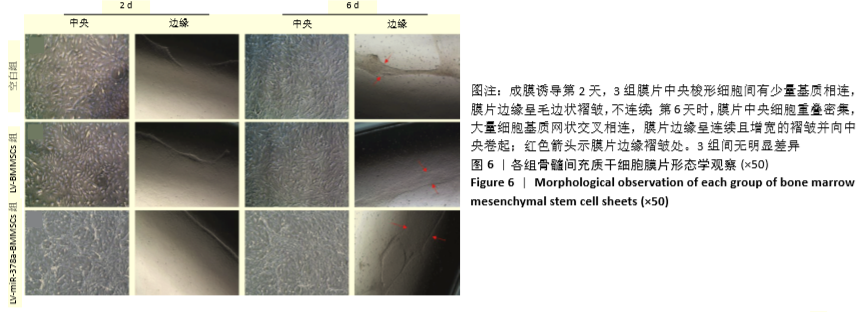
结果与结论:①成膜诱导第2天,LV-miR-378a-BMMSCs组、LV-BMMSCs组镜下均可见膜片中央梭形细胞间有少量基质相连,膜片边缘呈毛边状褶皱,不连续;第6天时,膜片中央细胞重叠密集,大量细胞基质网状交叉相连,膜片边缘呈连续且增宽的褶皱并向中央卷起,与空白组形态变化无明显差异;②LV-miR-378a-BMMSCs组各时间点的miR-378a、RUNX2、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、血管内皮生长因子、血小板生长因子的mRNA表达均高于LV-BMMSCs组、空白组(P < 0.001),RUNX2、血管内皮生长因子蛋白表达均高于LV-BMMSCs组(P < 0.001)、空白组(P < 0.01);③结果表明,过表达miR-378a基因可促进骨髓间充质干细胞膜片的体外成骨与成血管能力。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9244-1310(李君)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: