中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (26): 4137-4144.doi: 10.12307/2021.111
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
蛋氨酸-胆碱缺乏饮食诱导代谢相关脂肪肝模型小鼠血清和肝脏胆汁酸谱的变化
杨海琳1,2,3,张定棋1,2,3,陈高峰1,2,3,张聪聪4,陈佳美1,2,3,王晓柠5,刘 伟1,2,3,刘 平1,2,3,5
- 上海中医药大学附属曙光医院,1肝病研究所,2上海市中医临床重点实验室,上海市 201203; 上海中医药大学,3肝肾疾病病证教育部重点实验室,4中药研究所,5交叉科学研究院,上海市 201203
Changes of serum and liver bile acid profiles in a mouse model of metabolic associated fatty liver disease induced by a methionine-choline-deficient diet
Yang Hailin1,2,3, Zhang Dingqi1,2,3, Chen Gaofeng1,2,3, Zhang Congcong4, Chen Jiamei1,2,3, Wang Xiaoning5, Liu Wei1,2,3, Liu Ping1,2,3,5
- 1Institute of Liver Diseases, 2Shanghai Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shuguang Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China; 3Liver and Kidney Diseases Key Laboratory of Ministry of Education, 4Institute of Chinese Materia Medica,5Institute of Interdisciplinary Science, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China
摘要:

文题释义:
蛋氨酸-胆碱缺乏饮食:是指蛋氨酸-胆碱缺乏饲料中通常具有高蔗糖含量(约40%)和中等脂肪含量(约10%),并且缺乏胆碱和蛋氨酸,长期喂养蛋氨酸-胆碱缺乏饲料可导致极低密度脂蛋白颗粒的产生受损与β-氧化损伤,继而导致代谢相关脂肪性肝病的发生。
代谢相关脂肪性肝病:曾用名非酒精性脂肪性肝病,全球患病率高达25%,至今在美国和欧盟尚无药物获批用于治疗该病。
背景:蛋氨酸-胆碱缺乏饮食模型是国际上被广泛使用的诱发代谢相关脂肪性肝病的动物模型,现有的相关研究数据中缺少该模型小鼠胆汁酸谱的动态变化,而胆汁酸的调节是干预肝脏脂质代谢的重要途径之一,因此有必要明晰该模型体内胆汁酸谱的变化。
目的:探讨蛋氨酸-胆碱缺乏饮食诱导的代谢相关脂肪性肝病小鼠模型血清及肝脏中胆汁酸谱的变化。
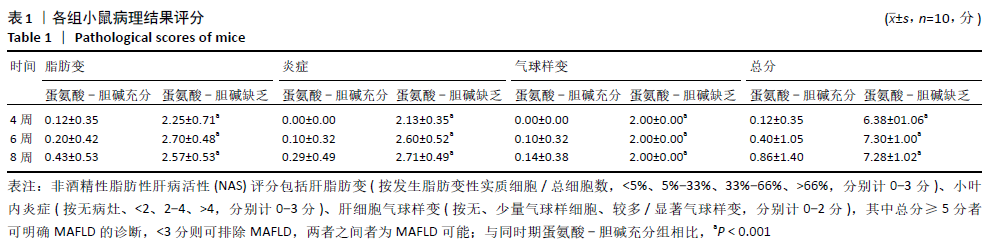
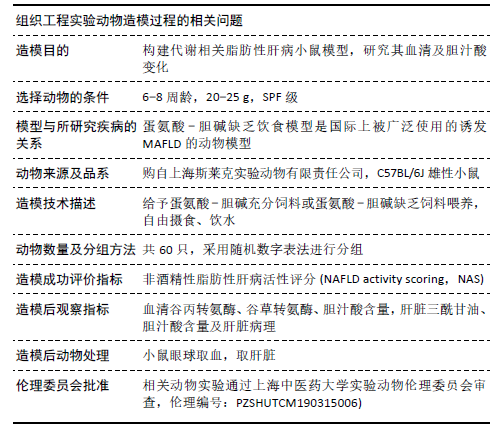
方法:将60只雄性C57/BL6J小鼠给予普通饲料适应性饲喂1周后随机分成2组,每组30只,其中一组为对照组给予蛋氨酸-胆碱充分饲料,另一组为模型组给予蛋氨酸-胆碱缺乏饲料喂养,自由摄食、饮水。分别于造模第4,6,8周末从两组中各随机抽取10只小鼠,收集小鼠血清和肝组织,检测各组小鼠血清谷丙转氨酶、谷草转氨酶活性及肝组织中三酰甘油含量,肝脏组织切片分别作苏木精-伊红、油红O和天狼猩红染色进行病理学评估,采用超高效液相串联质谱法对血清及肝脏中18种胆汁酸含量进行测定。
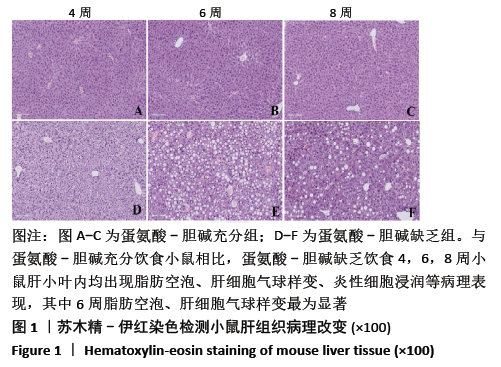
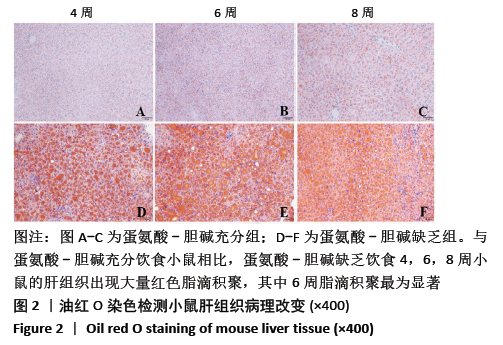
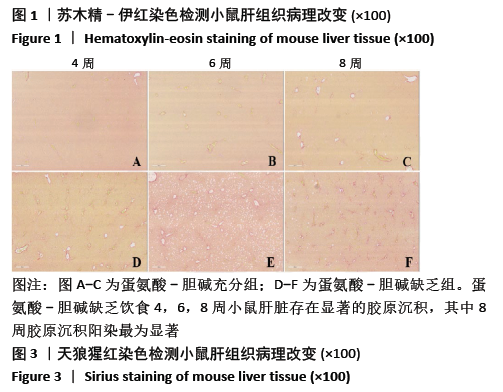
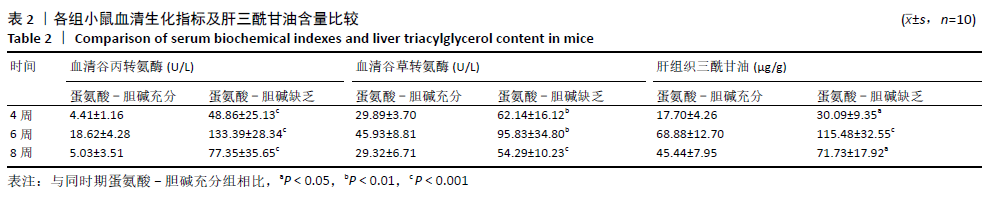
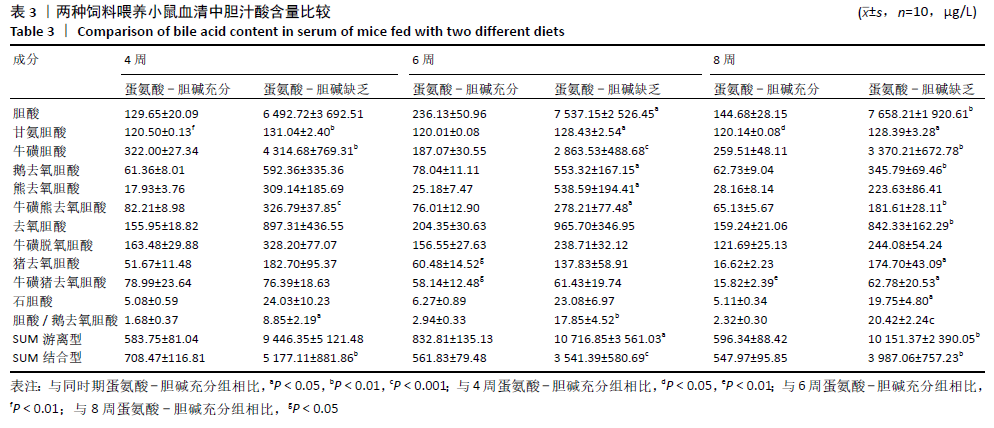
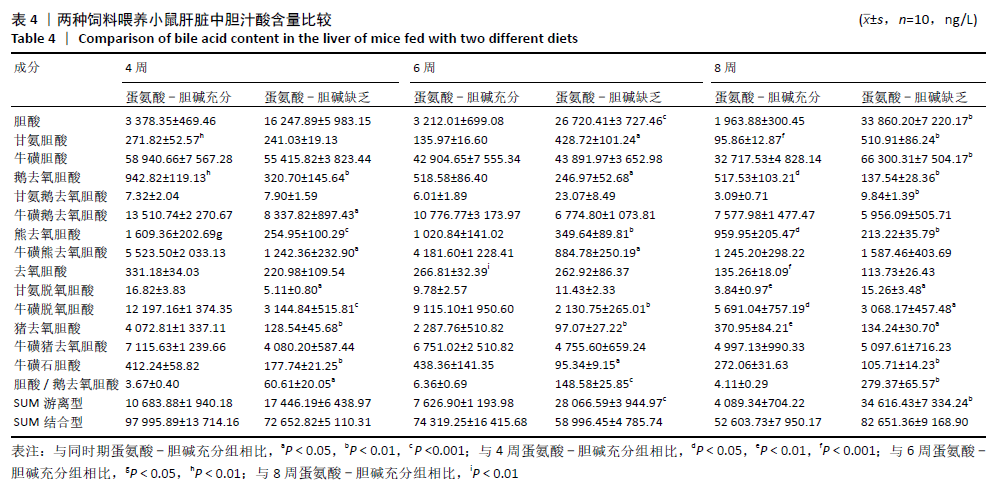
结果与结论:①不同造模时间动物样品检测结果发现,与同时期蛋氨酸-胆碱充分组相比,蛋氨酸-胆碱缺乏组小鼠血清谷丙转氨酶、谷草转氨酶活性及肝内三酰甘油含量显著升高(P < 0.05),蛋氨酸-胆碱缺乏组小鼠肝组织出现广泛肝细胞脂肪变性,窦周胶原纤维增加,非酒精性脂肪性肝病活性评分显著升高;②血清及肝脏胆汁酸谱检测结果发现,与同时期蛋氨酸-胆碱充分组相比,蛋氨酸-胆碱缺乏组小鼠血清中总游离型和总结合型胆汁酸以及除牛磺脱氧胆酸外的胆汁酸含量均呈上升趋势,胆酸/鹅去氧胆酸值显著升高;③与同期蛋氨酸-胆碱充分组相比,蛋氨酸-胆碱缺乏组肝脏中总游离型胆汁酸以及胆酸、甘氨胆酸、甘氨鹅去氧胆酸、牛磺胆酸含量呈上升趋势,鹅去氧胆酸、熊去氧胆酸、猪去氧胆酸、牛磺熊去氧胆酸、牛磺石胆酸、牛磺鹅去氧胆酸、牛磺脱氧胆酸含量呈下降趋势,甘氨脱氧胆酸含量随着造模时间延长呈先下降后上升趋势,脱氧胆酸、牛磺猪去氧胆酸含量基本不变,胆酸/鹅去氧胆酸值显著升高;④结果说明,蛋氨酸-胆碱缺乏饮食诱导的代谢相关脂肪性肝病小鼠模型血清与肝脏胆汁酸谱发生显著变化,尤其胆酸/鹅去氧胆酸比值的增高可能起到关键作用;提示蛋氨酸-胆碱缺乏模型引起代谢相关脂肪性肝病的进展与体内胆汁酸谱的变化及其毒性可能有密切关系。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1670-868X(杨海琳)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号:
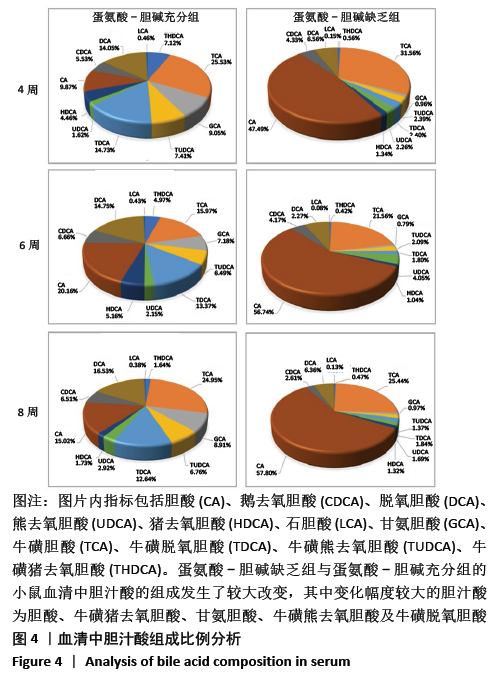
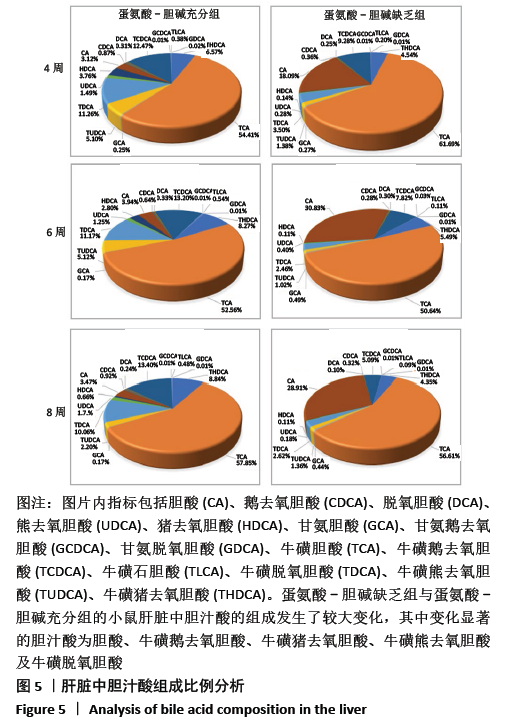
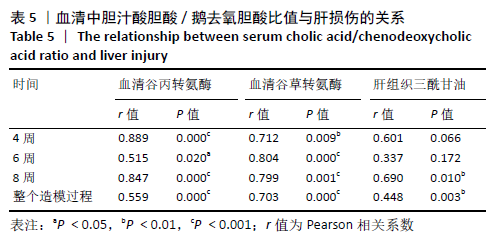
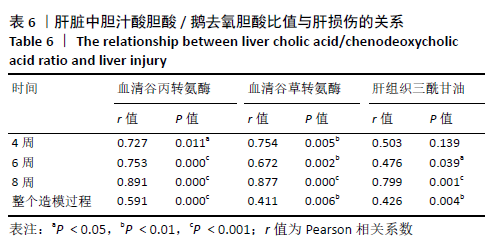
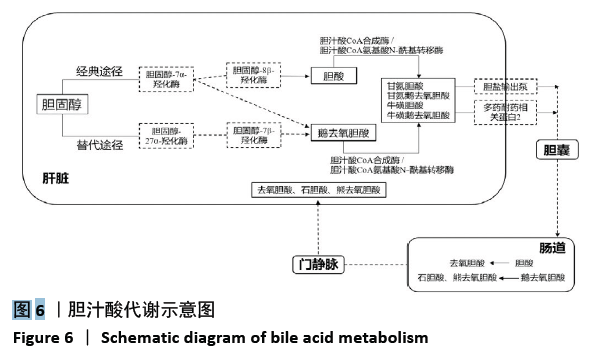 机体内胆汁酸的种类较多,不同类型的胆汁酸具有不同的亲水性和毒性,对脂质吸收、代谢和排泄的影响也不相同[20]。结合型胆汁酸极性较大,在体内结构较稳定,在盐或酸环境中不易沉淀[21-22]。而游离性胆汁酸在胆汁代谢异常时容易积聚,且实验证明胆汁酸的毒性与其亲疏水性有关,疏水性胆汁酸有一定的细胞毒作用,其机制可能与胆汁酸的去污作用、细胞能量代谢和氧自由基作用有关[23-24]。一般来说,胆汁酸的疏水性越大,其本身的毒性越强。在肝细胞中,胆汁酸的积累导致线粒体损伤,最终导致细胞凋亡或坏死,同时也导致氧化应激[25]。胆固醇除了代谢成胆汁酸以外,还有另一条重要的排泄途径,即随着胆汁一起从胆囊进入肠道,然后排出体外,组成胆汁的胆汁酸的亲水性越大,越有利于胆固醇在胆汁中的溶解和排泄[26]。此次研究结果显示,与蛋氨酸-胆碱充分组相比,4,6,8 周的蛋氨酸-胆碱缺乏组小鼠血清中总游离型和总结合型胆汁酸含量均呈上升趋势,且随着造模时间延长总游离型胆汁酸含量增长更为显著;肝脏中总游离型胆汁酸含量呈上升趋势,总结合型胆汁酸含量虽呈先上升后下降趋势,但整体含量变化不大。除此之外,作者对小鼠胆汁酸的组成进行分析发现,与蛋氨酸-胆碱充分组相比,4,6,8 周的蛋氨酸-胆碱缺乏组小鼠血清和肝脏中疏水性游离型胆汁酸的总占比增大,亲水性结合型胆汁酸的总占比减小,其中小鼠血清中游离型胆汁酸的总占比大于结合型胆汁酸。可能导致胆汁酸毒性增强,进而引起肝细胞损伤,并且胆固醇在胆汁中的溶解和排泄受到抑制,基于此,作者推测该模型可能存在一条通过影响胆汁酸代谢进而引起MAFLD的致病途径。
机体内胆汁酸的种类较多,不同类型的胆汁酸具有不同的亲水性和毒性,对脂质吸收、代谢和排泄的影响也不相同[20]。结合型胆汁酸极性较大,在体内结构较稳定,在盐或酸环境中不易沉淀[21-22]。而游离性胆汁酸在胆汁代谢异常时容易积聚,且实验证明胆汁酸的毒性与其亲疏水性有关,疏水性胆汁酸有一定的细胞毒作用,其机制可能与胆汁酸的去污作用、细胞能量代谢和氧自由基作用有关[23-24]。一般来说,胆汁酸的疏水性越大,其本身的毒性越强。在肝细胞中,胆汁酸的积累导致线粒体损伤,最终导致细胞凋亡或坏死,同时也导致氧化应激[25]。胆固醇除了代谢成胆汁酸以外,还有另一条重要的排泄途径,即随着胆汁一起从胆囊进入肠道,然后排出体外,组成胆汁的胆汁酸的亲水性越大,越有利于胆固醇在胆汁中的溶解和排泄[26]。此次研究结果显示,与蛋氨酸-胆碱充分组相比,4,6,8 周的蛋氨酸-胆碱缺乏组小鼠血清中总游离型和总结合型胆汁酸含量均呈上升趋势,且随着造模时间延长总游离型胆汁酸含量增长更为显著;肝脏中总游离型胆汁酸含量呈上升趋势,总结合型胆汁酸含量虽呈先上升后下降趋势,但整体含量变化不大。除此之外,作者对小鼠胆汁酸的组成进行分析发现,与蛋氨酸-胆碱充分组相比,4,6,8 周的蛋氨酸-胆碱缺乏组小鼠血清和肝脏中疏水性游离型胆汁酸的总占比增大,亲水性结合型胆汁酸的总占比减小,其中小鼠血清中游离型胆汁酸的总占比大于结合型胆汁酸。可能导致胆汁酸毒性增强,进而引起肝细胞损伤,并且胆固醇在胆汁中的溶解和排泄受到抑制,基于此,作者推测该模型可能存在一条通过影响胆汁酸代谢进而引起MAFLD的致病途径。