| [1]Park JC, Kim JM, Jung IH, et al.Isolation and characterization of human periodontal ligament (PDL) stem cells (PDLSCs) from the inflamed PDL tissue: in vitro and in vivo evaluations. J Clin Periodontol.2011;38(8):721-731.
[2]Lei M, Li K, Li B, et al.Mesenchymal stem cell characteristics of dental pulp and periodontal ligament stem cells after in vivo transplantation. Biomaterials. 2014;35(24):6332-6343.
[3]Jin ZL, Zhang YK, Sun HY, et al.Osteogenic-related gene expression profiles of human dental follicle cells induced by dexamethasone. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2008; 29(9): 1013-1020.
[4]Mostafa NZ, Uluda? H, Varkey M, et al.In vitro osteogenic induction of human gingival fibroblasts for bone regeneration. Open Dent J. 2011;5:139-145.
[5]Heggebö J, Haasters F, Polzer H, et al.Aged human mesenchymal stem cells: the duration of bone morphogenetic protein-2 stimulation determines induction or inhibition of osteogenic differentiation.Orthop Rev.2014;6(5242):65-70.
[6]Hirata K, Tsukazaki T, Kadowaki A, et al.Transplantation of skin fibroblasts expressing BMP-2 promotes bone repair more effectively than those expressing Runx2. Bone.2003;32(5): 502-512.
[7]Ivanovski S, Li H, Haase HR, et al. Expression of bone associated macromolecules by gingival and periodontal ligament fibroblasts. J Periodontal Res. 2001;36(3): 131-141.
[8]Myllylä RM, Haapasaari KM, Lehenkari P, et al.Bone morphogenetic proteins 4 and 2/7 induce osteogenic differentiation of mouse skin derived fibroblast and dermal papilla cells. Cell Tissue Res.2014;355(2):463-470.
[9]Khanna-Jain R, Agata H, Vuorinen A, et al.Addition of BMP-2 or BMP-6 to dexamethasone, ascorbic acid, and β-glycerophosphate may not enhance osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells. Growth Factors. 2010;28(6):437-446.
[10]Liu R, Ginn SL, Lek M, et al.Myoblast sensitivity and fibroblast insensitivity to osteogenic conversion by BMP-2 correlates with the expression of Bmpr-1a.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2009; 10:51.
[11]李颖,张文元,杨亚冬,等.人牙周膜细胞在矿化液作用下的增殖、成骨分化与相关基因表达[J].口腔医学研究,2014;1(30): 48-56.
[12]宋扬,金作林,宋镜明,等. BMP-2、bFGF和Dex联合应用对犬牙牙周膜细胞成骨分化能力的影响[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2012; 3(28):135-137.
[13]Anderson HC. Mechanism of mineral formation in bone. Lab Invest.1989;60(3):320-330.
[14]Miyahara T, Nemoto M, Tukamoto S, et al. Induction of metallothionein and stimulation of calcification by dexamethasone in cultured clonal osteogenic cells, MC3T3-E1. Toxicol Lett.1991;57(3):257-267.
[15]Cheng SL, Yang JW, Rifas L, et al. Differentiation of human bone marrow osteogenic stromal cells in vitro: induction of the osteoblast phenotype by dexamethasone. Endocrinology. 1994; 134(1):277-286.
[16]张维成.不同浓度地塞米松对骨髓基质细胞成脂、成骨分化的影响[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(29):98-100.
[17]Mikami Y, Lee M, Irie S, et al. Dexamethasone modulates osteogenesis and adipogenesis with regulation of osterix expression in rat calvaria-derived cells.J Cell Physiol.2011; 26(3):739-748.
[18]Turgeman G, Zilberman Y, Zhou S,et al. Systemically administered rhBMP-2 promotes MSC activity and reverses bone and cartilage loss in osteopenic mice. J Cell Biochem. 2002;86(3):461-474.
[19]Li R, Li X, Zhou M, et al. Quantitative determination of matrix Gla protein (MGP) and BMP-2 during the osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells. Arch Oral Biol. 2012;57(10):1408-1417.
[20]Nakashima K, Zhou X, Kunkel G, et al.The novel zinc finger-containing transcription factor osterix is required for osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Cell.2002; 108(1):17-29.
[21]Enomoto H, Furuichi T, Zanma A,et al.Runx2 deficiency in chondrocytes causes adipogenic changes in vitro.J Cell Sci.2004;117(Pt 3):417-425.
[22]Komori T, Yagi H, Nomura S, et al. Targeted disruption of Cbfa1 results in a complete lack of bone formation owing to maturational arrest of osteoblasts. Cell. 1997;89(5):755-764.
[23]Seki K, Fujimori T, Savagner P, et al.Mouse Snail family transcription repressors regulate chondrocyte, extracellular matrix, type II collagen, and aggrecan. J Biol Chem.2003; 278(43):41862-41870.
[24]Jeon EJ, Lee KY, Choi NS, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 stimulates Runx2 acetylation. J Biol Chem. 2006; 281(24):16502-16511. |
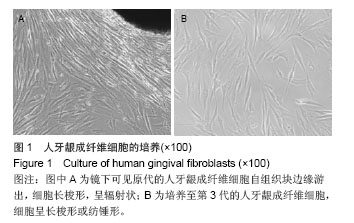
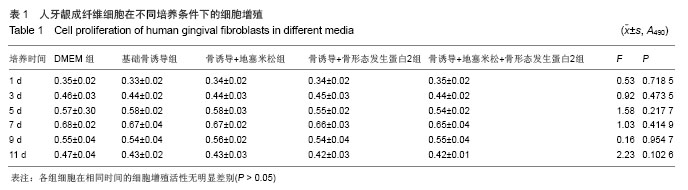
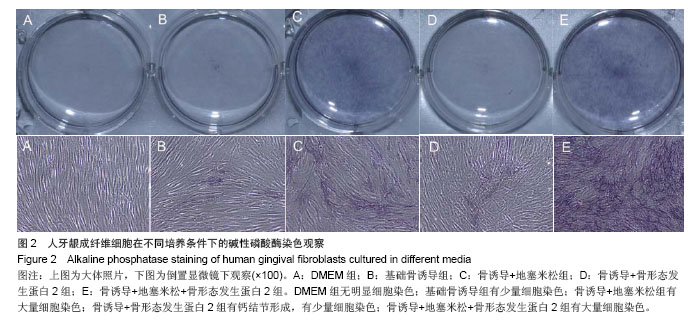
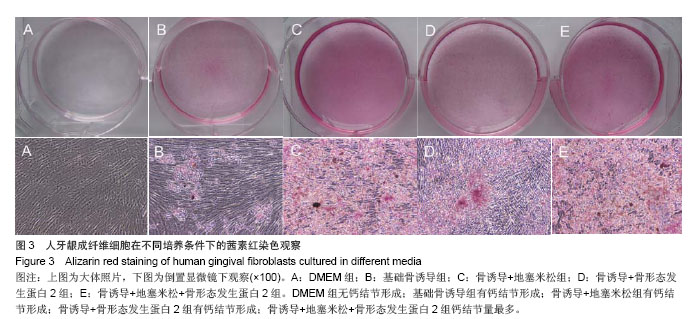
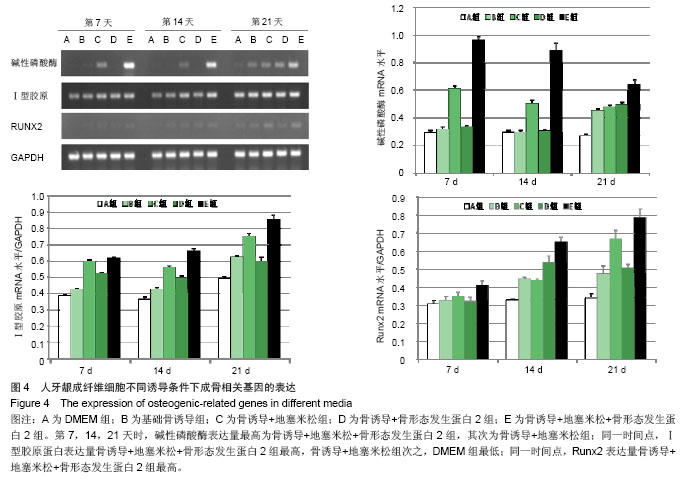
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)