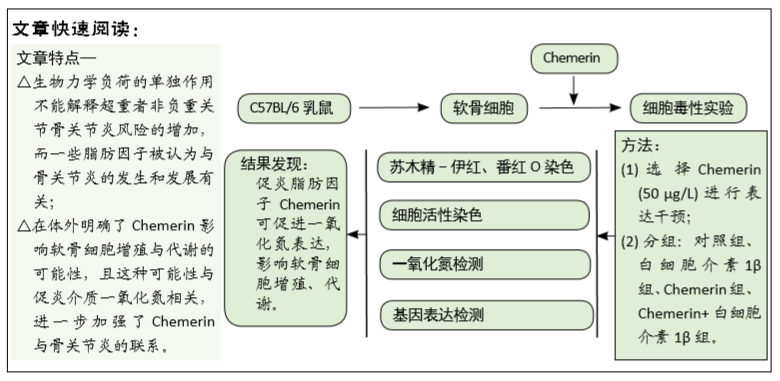
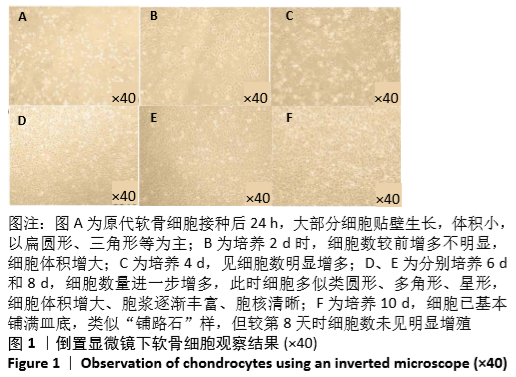
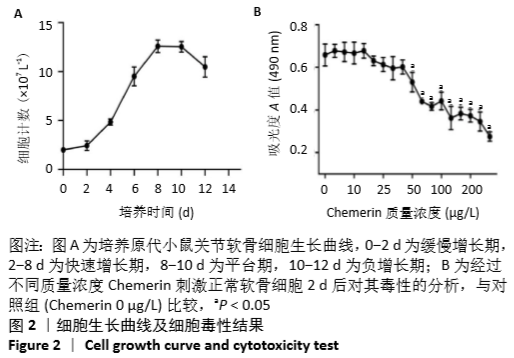
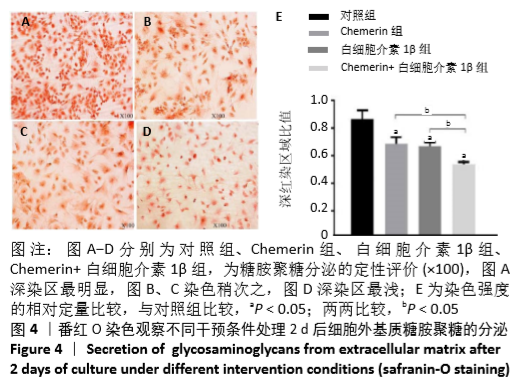
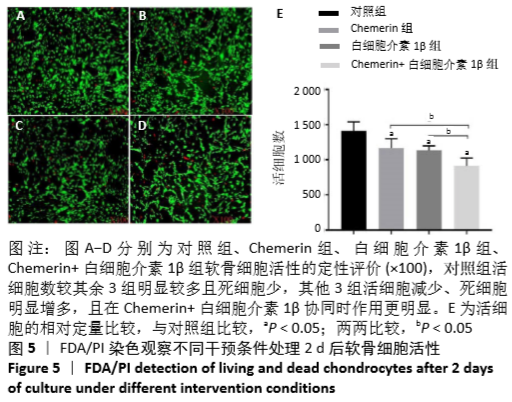
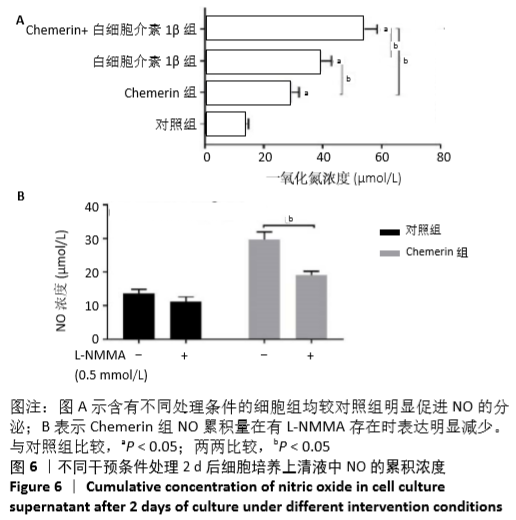
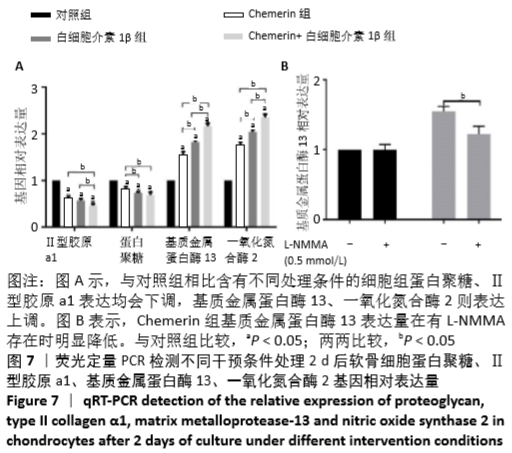
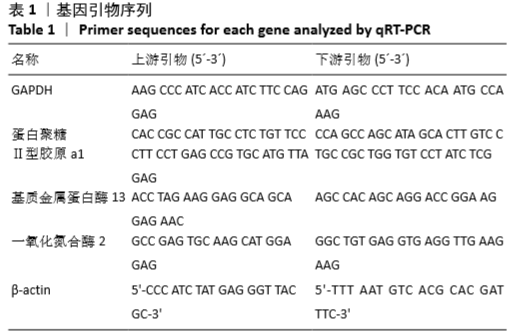
[1] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393:1745-1759.
[2] YOUM J, CHAN V, BELKORA J, et al. Impact of socioeconomic factors on informed decision making and treatment choice in patients with hip and knee OA.J Arthroplasty. 2015;30:171-175.
[3] HUNTER DJ, SCHOFIELD D, CALLANDER E. The individual and socioeconomic impact of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10(7):437-441.
[4] WANG T, HE C. Pro-inflammatory cytokines: The link between obesity and osteoarthritis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018;44:38-50.
[5] THIJSSEN E, VAN CAAM A, VAN DER KRAAN PM. Obesity and osteoarthritis, more than just wear and tear: pivotal roles for inflamed adipose tissue and dyslipidaemia in obesity-induced osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015;54(4):588-600.
[6] FRANCISCO V, PÉREZ T, PINO J, et al. Biomechanics, obesity, and osteoarthritis. The role of adipokines: When the levee breaks. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(2):594-604.
[7] SINGER SP, DAMMERER D, KRISMER M, et al. Maximum lifetime body mass index is the appropriate predictor of knee and hip osteoarthritis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018;138(1):99-103.
[8] REYES C, LEYLAND KM, PEAT G, et al. Association between overweight and obesity and risk of clinically diagnosed knee, hip, and hand osteoarthritis: a population-based cohort study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(8):1869-1875.
[9] LARRAÑAGA-VERA A, LAMUEDRA A, PÉREZ-BAOS S, et al. Increased synovial lipodystrophy induced by high fat diet aggravates synovitis in experimental osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):264.
[10] XIE C, CHEN Q. Adipokines: New Therapeutic Target for Osteoarthritis? Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2019;21(12):71.
[11] CHEN X, LU J, BAO J, et al. Adiponectin: a biomarker for rheumatoid arthritis?. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013;24(1):83-89.
[12] RUSCITTI P, DI BENEDETTO P, BERARDICURTI O, et al. Adipocytokines in rheumatoid arthritis: the hidden link between inflammation and cardiometabolic comorbidities. J Immunol Res. 2018;2018:8410182.
[13] YAN M, ZHANG J, YANG H, et al. The role of leptin in osteoarthritis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(14):e0257.
[14] STOJEK M. The role of chemerin in human disease. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2017;71:110-117.
[15] 宫计划, 徐昭.2型糖尿病患者血清脂肪细胞因子Chemerin表达水平及临床价值[J].中国医学创新,2018,15(27):22-25.
[16] KAUR J, MATTU HS, CHATHA K, et al. Chemerin in human cardiovascular disease. Vascul Pharmacol. 2018;110:1-6.
[17] HUANG K, DU G, LI L, et al. Association of chemerin levels in synovial fluid with the severity of knee osteoarthritis. Biomarkers. 2012;17(1):16-20.
[18] CIPOLLETTA C, JOUZEAU JY, GEGOUT-POTTIE P, et al. Modulation of IL-1-induced cartilage injury by NO synthase inhibitors: a comparative study with rat chondrocytes and cartilage entities. Br J Pharmacol. 1998;124(8): 1719-1727.
[19] JONASON JH, HOAK D, O’KEEFE RJ. Primary murine growth plate and articular chondrocyte isolation and cell culture. Methods Mol Biol. 2015; 1226:11-18.
[20] BUECHLER C, FEDER S, HABERL EM, et al. Chemerin Isoforms and Activity in Obesity. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(5):1128.
[21] MAKRILAKIS K, FRAGIADAKI K, SMITH J, et al. Interrelated reduction of chemerin and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 serum levels in rheumatoid arthritis after interleukin-6 receptor blockade. Clin Rheumatol. 2015;34(3):419-427.
[22] 段国庆,任春凤.血清chemerin含量与膝骨关节炎严重程度的相关性[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2015,9(1):63-66.
[23] ZHAO L, YAMAGUCHI Y, GE X, et al. Chemerin 156F, generated by chymase cleavage of prochemerin, is elevated in joint fluids of arthritis patients. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):132.
[24] EISINGER K, BAUER S, SCHÄFFLER A, et al. Chemerin induces CCL2 and TLR4 in synovial fibroblasts of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Exp Mol Pathol. 2012;92(1):90-96.
[25] BERG V, SVEINBJÖRNSSON B, BENDIKSEN S, et al. Human articular chondrocytes express ChemR23 and chemerin; ChemR23 promotes inflammatory signalling upon binding the ligand chemerin(21-157). Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(6):R228.
[26] MAN GS, MOLOGHIANU G. Osteoarthritis pathogenesis - a complex process that involves the entire joint. J Med Life. 2014;7(1):37-41.
[27] GUILAK F, NIMS RJ, DICKS A, et al. Osteoarthritis as a disease of the cartilage pericellular matrix. Matrix Biol. 2018;71-72:40-50.
[28] DERFOUL A, MIYOSHI AD, FREEMAN DE, et al. Glucosamine promotes chondrogenic phenotype in both chondrocytes and mesenchymal stem cells and inhibits MMP-13 expression and matrix degradation. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007;15(6):646-655.
[29] GROGAN SP, CHEN X, SOVANI S, et al. Influence of cartilage extracellular matrix molecules on cell phenotype and neocartilage formation. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20(1-2):264-274.
[30] YAN H, SU YX, LIN XY. In vitro culture and identification of IL-1beta induced degeneration of cartilage cells in New Zealand white rabbits knee joint. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2014;34(1):81-86.
[31] HALONEN KS, MONONEN ME, JURVELIN JS, et al. Importance of depth-wise distribution of collagen and proteoglycans in articular cartilage--a 3D finite element study of stresses and strains in human knee joint. J Biomech. 2013;46(6):1184-1192.
[32] CHUBINSKAYA S, KUETTNER KE, COLE AA. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases in normal and damaged articular cartilage from human knee and ankle joints. Lab Invest. 1999;79(12):1669-1677.
[33] RUAN G, XU J, WANG K, et al. Associations between knee structural measures, circulating inflammatory factors and MMP13 in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(8):1063-1069.
[34] LI Z, LIU B, ZHAO D, et al. Protective effects of Nebivolol against interleukin-1β (IL-1β)-induced type II collagen destruction mediated by matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP-13). Cell Stress Chaperones. 2017;22(6): 767-774.
[35] CHARLIER E, RELIC B, DEROYER C, et al. Insights on Molecular Mechanisms of Chondrocytes Death in Osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(12):2146.
[36] CHELESCHI S, FIORAVANTI A, DE PALMA A, et al. Methylsulfonylmethane and mobilee prevent negative effect of IL-1β in human chondrocyte cultures via NF-κB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;65:129-139.
[37] KALUNIAN KC. Current advances in therapies for osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2016;28(3):246-250.
[38] JENEI-LANZL Z, MEURER A, ZAUCKE F. Interleukin-1β signaling in osteoarthritis - chondrocytes in focus. Cell Signal. 2019;53:212-223.
[39] SANTORO A, CONDE J, SCOTECE M, et al. Choosing the right chondrocyte cell line: Focus on nitric oxide. J Orthop Res. 2015;33(12):1784-1788.
[40] LEONIDOU A, LEPETSOS P, MINTZAS M, et al. Inducible nitric oxide synthase as a target for osteoarthritis treatment. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018;22(4):299-318.
[41] SOROKIN A. Nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase pathways: a complex interplay in cellular signaling. Curr Med Chem. 2016;23(24):2559-2578. |