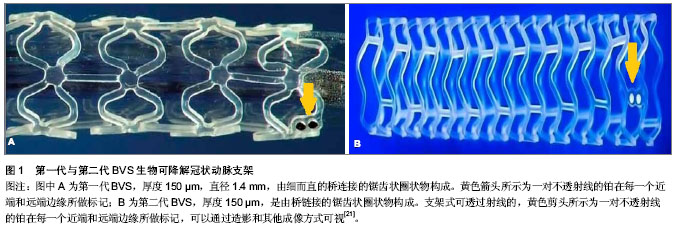
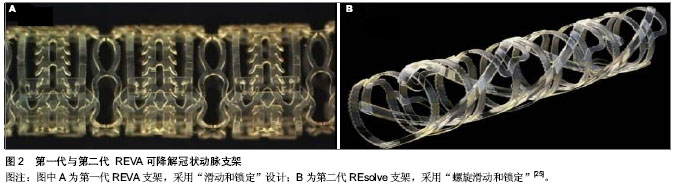
| [1] Schomig A,Kastrati A,Dirschinger J,et al.Coronary stenting plus platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa blockade compared with tissue plasminogen activator in acute myocardial infarction. Stent versus Thrombolysis for Occluded Coronary Arteries in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(6):385-391.[2] Stone GW,Grines CL,Cox DA,et al.Comparison of angioplasty with stenting, with or without abciximab, in acute myocardial infarction.N Engl J Med.2002;346(13):957-966.[3] Tamai H,Igaki K,Tsuji T,et al.A biodegradable poly-l-lacticacid coronary stent in the porcine coronary artery.J Interv Cardiol. 1999;12(6):443-449.[4] Daemen J,Wenaweser P,Tsuchida K,et al.Early and late coronary stent thrombosis of sirolimus-eluting and paclitaxel-eluting stents in routine clinical practice: data from a large two-institutional cohort study.Lancet.2007;369(9562): 667-678.[5] Kuchulakanti PK,Chu WW,Torguson R,et al.Correlates and long-term outcomes of angiographically proven stent thrombosis with sirolimus- and paclitaxel-eluting stents. Circulation.2006;113(8):1108-1113.[6] Cook S,Meier B.Have we been misled by the ESC DES firestorm? EuroIntervention. 2008;3(5):535-537.[7] Waksman R.Lessons learnt from preclinical studies of magnesium scaffolds (Biotronik’s DREAMS program). EuroPCR; Rotterdam, The Netherlands.2012.[8] Lincoff AM,Furst JG,Ellis SG,et al.Sustained local delivery of dexamethasone by a novel intravascular eluting stent to prevent restenosis in the porcine coronary injury model.J Am Coll Cardiol.1997;29(4):808-816.[9] Yamawaki T,Shimokawa H,Kozai T,et al.Intramural delivery of a specific tyrosine kinase inhibitor with biodegradable stent suppresses the restenotic changes of the coronary artery in pigs in vivo.J Am Coll Cardiol.1998;32(3):780-786.[10] Tamai H,Igaki K,Kyo E,et al.Initial and 6-month results of biodegradable poly-l-lactic acid coronary stents in humans.Circulation.2000;102(4):399-404.[11] Nishio S,Kosuga K,Igaki K,et al.Long-Term ( > 10 Years) Clinical outcomes of first-in-human biodegradable poly-l-lactic acid coronary stents igaki-tamai stents.Circulation. 2012; 125(19):2343-2352.[12] Onuma Y,Garg S,Okamura T,et al.Ten-year follow-up of the IGAKI-TAMAI stent. A posthumous tribute to the scientific work of Dr Hideo Tamai. Euro Intervention. 2009;5 Suppl F:F109-F111.[13] Onuma Y,Serruys PW,Perkins LE,et al.Intracoronary optical coherence tomography and histology at 1 month and 2, 3, and 4 years after implantation of everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffolds in a porcine coronary artery model: an attempt to decipher the human optical coherence tomography images in the ABSORB trial. Circulation. 2010; 122(22):2288-2300.[14] Ormiston JA,Serruys PW,Regar E,et al.A bioabsorbable everolimus-eluting coronary stent system for patients with single de-novo coronary artery lesions (ABSORB): a prospective open-label trial.Lancet.2008;371:899-907.[15] Serruys PW,Ormiston JA,Onuma Y,et al.A bioabsorbable everolimus-eluting coronary stent system (ABSORB): 2-year outcomes and results from multiple imaging methods. Lancet. 2009;373:897-910.[16] Tanimoto S,Bruining N,van Domburg RT,et al.Late stent recoil of the bioabsorbable everolimus-eluting coronary stent and its relationship with plaque morphology.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008; 52(20):1616-1620.[17] Tanimoto S,Serruys PW,Thuesen L,et al.Comparison of in vivo acute stent recoil between the bioabsorbable everolimus-eluting coronary stent and the everolimus-eluting cobalt chromium coronary stent: insights from the ABSORB and SPIRIT trials.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv.2007;70(4): 515-523.[18] Diletti R,Onuma Y,Farooq V,et al.6-month clinical outcomes following implantation of the bioresorbable everolimus-eluting vascular scaffold in vessels smaller or larger than 2.5 mm.J Am Coll Cardiol.2011;58(3):258-264.[19] Serruys PW,Onuma Y,Dudek D,et al.Evaluation of the second generation of a bioresorbable everolimus-eluting vascular scaffold for the treatment of de novo coronary artery stenosis: 12-month clinical and imaging outcomes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58(15):1578-1588.[20] Muramatsu T,Hector M,Christos V,et al.Incidence and Short-Term Clinical Outcomes of Small Side Branch Occlusion After Implantation of an Everolimus-Eluting Bioresorbable Vascular Scaffold.J Am Coll Cardiol.2013; 6(3):247-257.[21] Gogas BD,Farooq V,Onuma Y,et al.The ABSORB Bioresorbable Vascular Scaffold:An Evolution or Revolution in Interventional Cardiology?Hellenic J Cardiol.2012;53(4): 301-309.[22] Pollman MJ.Engineering a bioresorbable stent: REVA programme update. EuroIntervention.2009;5 Suppl F: F54-57.[23] Strandberg E,Zeltinger J,Schulz DG,et al.Late positive remodeling and late lumen gain contribute to vascular restoration by a non-drug eluting bioresorbable scaffold: a four-year intravascular ultrasound study in normal porcine coronary arteries. Circ Cardiovasc Interv.2012; 5(1):39-46.[24] Grube E. The Boston scientific and REVA technology. Euro PCR;Barcelona, Spain.2009.[25] Garg S,Serruys PW.Coronary stents: looking forward.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;56(10 Suppl):S43-78.[26] Jabara R,Chronos N,Robinson K.Novel bioabsorbable salicylate-based polymer as a drug-eluting stent coating. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv.2008;72(2):186-194.[27] Jabara R,Pendyala L,Geva S,et al.Novel fully bioabsorbable salicylate-based sirolimus-eluting stent.EuroIntervention. 2009; 5 Suppl F:F58-F64.[28] Jabara R.Poly-anhydride based on salicylic acid and adipic acid anhydride. EuroPCR;Barcelona, Spain.2009. [29] Yan J, Bhat VD. Elixir Medical’s bioresorbable drug eluting stent (BDES) programme: an overview.EuroIntervention.2009;5 Suppl F:F80-F82.[30] Verheye S. DESolve first in man study-preliminary results. EuroPCR; Rotterdam, The Netherlands.2012.[31] Verheye S. DESolve myolimus eluting bioresorbable coronary scaffold first in man trial- imaging and clinical results at 6 months.EuroPCR;Rotterdam,The Netherlands. 2012.[32] 沈雳,齐兵,吴轶喆,等.完全可降解聚乳酸西罗莫司洗脱支架在小型猪冠状动脉模型中的实验研究[J].中国介入心脏病学杂志, 2011,19(6):301-305. [33] Ghimire G,Spiro J,Kharbanda R,et al.Initial evidence for the return of coronary vasoreactivity following the absorption of bioabsorbable magnesium alloy coronary stents. EuroIntervention. 2009;4(4):481-484.[34] Waksman R. PROGRESS was made toward DREAM: magnesium Stent. EuroPCR; Rotterdam, The Netherlands. 2012.[35] Peuster M,Hesse C,Schloo T,et al.Long-term biocompatibility of a corrodible peripheral iron stent in the porcine descending aorta.Biomaterials.2006;27:4955-4962.[36] Waksman R,Pakala R,Baffour R,et al. Short-term effects of biocorrodible iron stents in porcine coronary arteries.J Interv Cardiol.2008;21:15-20.[37] 赵晓辉,尹扬光,方玉强,等.雌激素动员小鼠外周血内皮祖细胞修复损伤血管内皮[J]. 第三军医大学学报,2010,33(1): 94-97. |