中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (33): 5257-5264.doi: 10.12307/2024.073
• 骨与关节生物力学 bone and joint biomechanics • 上一篇 下一篇
动力位下早期脊髓型颈椎病患者脊髓致压特点的有限元分析
李承蔚1,张翼升1,李智斐2,钟远鸣2,蒙纪文1,梁钦秋1,陈华龙3
- 1广西中医药大学研究生学院,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530000;2广西中医药大学第一附属医院,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530000;3玉林市中西医结合骨伤医院,广西壮族自治区西林市 537000
Finite element analysis of characteristics of spinal cord compression in patients with early cervical spondylotic myelopathy under dynamic position
Li Chengwei1, Zhang Yisheng1, Li Zhifei2, Zhong Yuanming2, Meng Jiwen1, Liang Qinqiu1, Chen Hualong3
- 1Graduate School of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3Yulin Orthopedic Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Xilin 537000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
脊髓型颈椎病:是导致中老年人功能障碍的重要原因,这是一种呈进行性恶化的疾病,它由椎骨、椎间盘、小关节和相关韧带的退行性变化逐渐引起,这些变化通过直接压迫脊髓或周围血管而导致脊髓型颈椎病的发病。早期脊髓型颈椎病患者:目前尚未有早期脊髓型颈椎病的业内统一专家诊断共识,此次研究基于前期研究基础,将具有脊髓型颈椎病的症状、体征,常规中立位MRI未见明显异常或仅见肥厚的黄韧带压迫硬膜囊,但颈椎动态核磁共振成像(dMRI)发现脊髓受压的患者定义为“早期脊髓型颈椎病患者”。
颈椎有限元生物力学:通过有限元计算机仿真模拟技术将人体的结构通过CT平扫数据进行模拟建立3D立体模型,再通过建立人体生理或 其他受力环境,将模型置于建立的力学环境中进行受力分析得到数据,分析数据的意义进而指导临床工作。
背景:脊髓型颈椎病是导致中老年人功能障碍的进行性加重疾病,早期诊断困难,近年来临床上有学者发现动态磁共振成像(dMRI)技术可更早期发现动力位下的脊髓受压,但其具体生物力学机制亟待阐明。
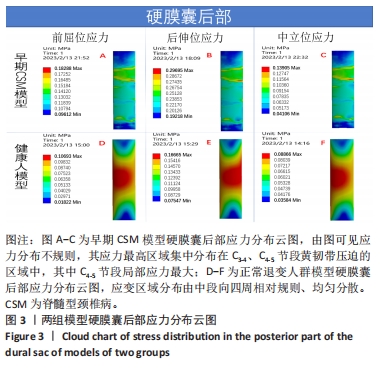
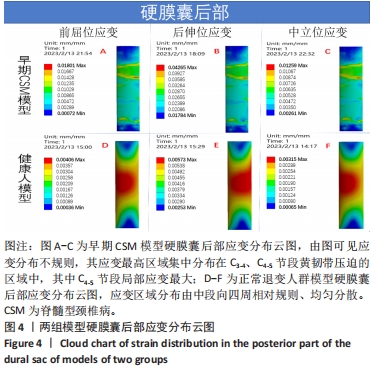
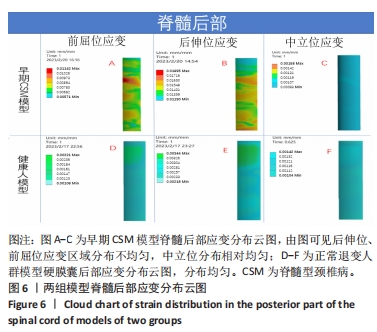
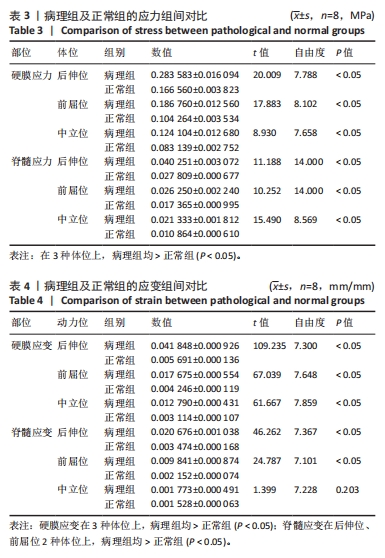
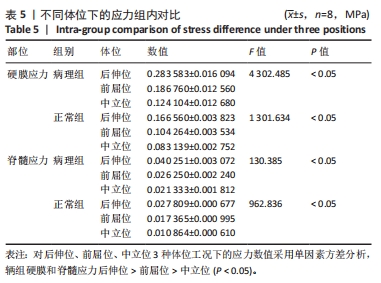
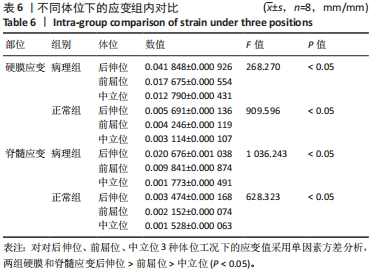
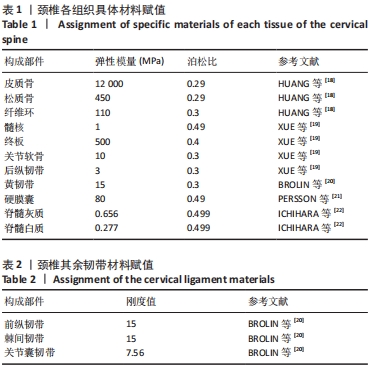
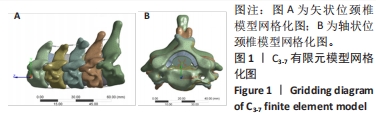
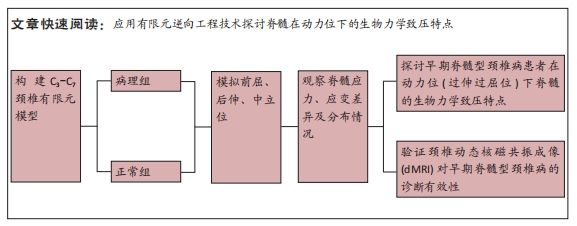
目的:探讨早期脊髓型颈椎病患者在动力位(过伸过屈位)下脊髓的生物力学致压特点,验证颈椎dMRI对早期脊髓型颈椎病诊断的有效性。方法:回顾性分析2022年1-6月在广西中医药大学第一附属医院骨科就诊并拍摄过颈段dMRI患者的病历资料,共纳入16例,分为2组,病理组为8例以黄韧带肥厚为主要征象的早期脊髓型颈椎病患者,男5例,女3例;正常组为8例正常退变人群,男4例,女4例。所有患者均已拍摄颈椎CT平扫、MRI平扫、dMRI平扫。此次研究分为以下3个部分实验进行阐述:①采集两组受试者dMRI图像的DCOM数据,并采集其颈椎CT、中立位MRI图像DCOM数据了解两组受试者在中立位下的骨质及软组织情况;②基于MRI及CT平扫的图像DCOM数据,使用逆向工程软件分别建模正常退变人群、脊髓型颈椎病早期患者的下颈椎(C3-7)三维有限元模型,分析脊髓、硬膜后部的等效应力、等效弹性应变数值,观察应力、应变分布情况;③得出应力、应变数据后进行组间数据对比,分析出早期脊髓型颈椎病在动力位下脊髓致压的力学特点,验证dMRI对早期脊髓型颈椎病诊断的有效性。
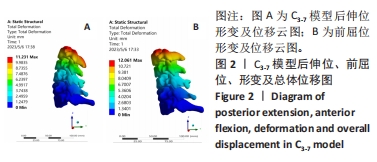
结果与结论:①两组受试者下颈椎(C3-7)模型在模拟后伸、前屈、中立位时,其脊髓后部的应力、应变数值从大到小依次为后伸位>前屈位>中立位(P < 0.05),应变数值从大到小依次为后伸位>前屈位>中立位(P < 0.05);②与正常退变人群模型比较,病理组模型在前屈、后伸2种自由度下,其脊髓的等效应力、应变均较正常组模型增大(P < 0.05),且脊髓后部应力、应变分布区域不规则;③在中立位下,两组模型脊髓的应变数值无明显差异(P > 0.05),应变分布区域均匀规则;④提示在颈椎后伸位状态下,以黄韧带肥厚为主要征象的早期脊髓型颈椎病患者硬膜囊和脊髓后部均受压变形,脊髓的受压形变程度明显大于前屈位和中立位;中立位状态下,早期脊髓型颈椎病患者硬膜受压变形,脊髓无明显形变征象;此次研究从生物力学的角度验证了dMRI对早期脊髓型颈椎病诊断的有效性。
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-6509-3874 (李承蔚)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: