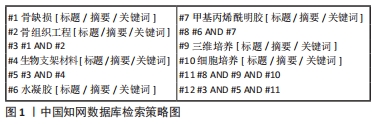
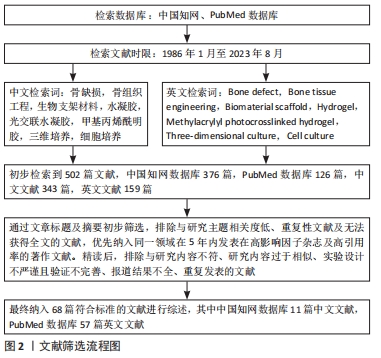
[1] SCHMITZ JP, HOLLINGER JO. The critical size defect as an experimental model for craniomandibulofacial nonunions. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986; (205):299-308.
[2] PERIC KZ, RIDER P, ALKILDANI S, et al. An introduction to bone tissue engineering. Int J Artif Organs. 2020;43(2):69-86.
[3] YUE K, TRUJILLO-DE SG, ALVAREZ MM, et al. Synthesis,properties,and biomedical applications of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2015;73:254-271.
[4] 林欢欢,刘肇兴,吴兴,等.明胶-甲基丙烯酰基水凝胶作为生物
材料在组织修复方面的应用进展[J].中国美容医学,2017,26(8):130-134.
[5] 陶金,宋雪,王璐瑶,等.3D细胞培养的研究进展和应用前景[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2022,43(18):1771-1775.
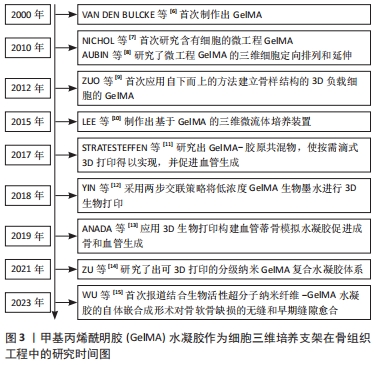
[6] VAN DEN BULCKE AI, BOGDANOV B, DE ROOZE N, et al. Structural and rheological properties of methacrylamide modified gelatin hydrogels. Biomacromolecules. 2000;1(1):31-38.
[7] NICHOL JW, KOSHY ST, BAE H, et al. Cell-laden microengineered gelatin methacrylate hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2010;31(21):5536-5544.
[8] AUBIN H, NICHOL JW, HUTSON CB, et al. Directed 3D cell alignment and elongation in microengineered hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2010;31(27): 6941-6951.
[9] ZUO Y, XIAO W, CHEN X, et al. Bottom-up approach to build osteon-like structure by cell-laden photocrosslinkable hydrogel. Chem Commun (Camb). 2012;48(26):3170-3172.
[10] LEE Y, LEE JM, BAE PK, et al. Photo-crosslinkable hydrogel-based 3D microfluidic culture device. Electrophoresis. 2015;36(7-8):994-1001.
[11] STRATESTEFFEN H, KOPF M, KREIMENDAHL F, et al. GelMA-collagen blends enable drop-on-demand 3D printablility and promote angiogenesis. Biofabrication. 2017;9(4):45002.
[12] YIN J, YAN M, WANG Y, et al. 3D bioprinting of low-concentration cell-laden gelatin methacrylate (GelMA) bioinks with a two-step cross-linking strategy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(8):6849-6857.
[13] ANADA T, PAN CC, STAHL AM, et al. Vascularized bone-mimetic hydrogel constructs by 3D bioprinting to promote osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(5):1096.
[14] ZU G, MEIJER M, MERGEL O, et al. 3D-printable hierarchical nanogel-GelMA composite hydrogel system. Polymers(Basel). 2021;13(15):2508.
[15] WU H, SHANG Y, SUN W, et al. Seamless and early gap healing of osteochondral defects by autologous mosaicplasty combined with bioactive supramolecular nanofiber-enabled gelatin methacryloyl (BSN-GelMA) hydrogel. Bioact Mater. 2023;19:88-102.
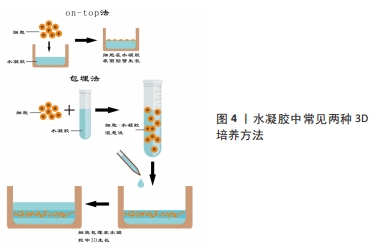
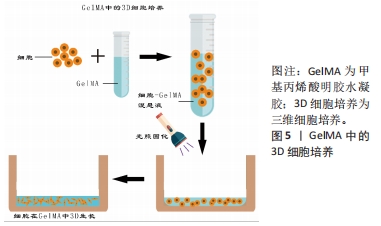
[16] TIBBITT MW, ANSETH KS. Hydrogels as extracellular matrix mimics for 3D cell culture. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2009;103(4):655-663.
[17] 卢晓琴,刘晓凤,钟浩,等.三维细胞培养技术及其应用进展[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2023,40(3):602-608.
[18] KOROLEVA A, DEIWICK A, EL-TAMER A, et al. In vitro development of human iPSC-derived functional neuronal networks on laser-fabricated 3D scaffolds. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(7):7839-7853.
[19] SUENAGA H, KAGAYA N, KAWADA M, et al. Phenotypic screening system using three-dimensional(3D)culture models for natural product screening. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2021;74(10):660-666.
[20] SCHAFER M, KHEYFETS VO, BARKER AJ, et al. Reduced shear stress and associated aortic deformation in the thoracic aorta of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Vasc Surg. 2018;68(1):246-253.
[21] KLOSS D, FISCHER M, ROTHERMEL A, et al. Drug testing on 3D in vitro tissues trapped on a microcavity chip. Lab Chip. 2008;8(6):879-884.
[22] 王晶波,陈晨,马妍,等.响应面法优化VitroGel体系上人源肝细胞三维培养条件的研究[J]. 卫生研究,2023,52(4):579-584.
[23] KAZI G, RAHMAN KA, FARAHAT M, et al. Fabrication of single gel with different mechanical stiffness using three-dimensional mold. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019;107(1):6-11.
[24] GATHANI KM, RAGHAVENDRA SS. Scaffolds in regenerative endodontics: a review. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2016;13(5):379-386.
[25] WU Y, TANG Z, MA S, et al. The promising application of hydrogel microneedles in medical application. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2023;75(8): 1011-1020.
[26] LA MANNA S, FLORIO D, DI NATALE C, et al. Modulation of hydrogel networks by metal ions. J Pept Sci. 2023;29(8):e3474.
[27] ARTHUR A, GRONTHOS S. Clinical application of bone marrow mesenchymal stem/stromal cells to repair skeletal tissue. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(24):9759.
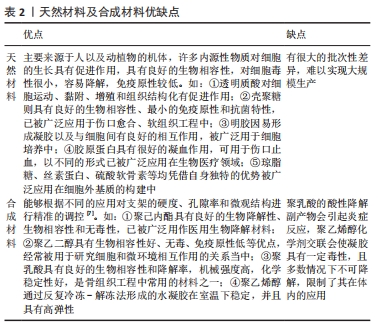
[28] CAO H, DUAN L, ZHANG Y, et al. Current hydrogel advances in physicochemical and biological response-driven biomedical application diversity. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):426.
[29] 房娜.可注射光交联HAMA-Hep/GelMA水凝胶的构建及其性质研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2022.
[30] LAI TC, YU J, TSAI WB. Gelatin methacrylate/carboxybetaine methacrylate hydrogels with tunable crosslinking for controlled drug release. J Mater Chem B. 2016;4(13):2304-2313.
[31] 张依蕾. GelMA/PEDOT: PSS导电水凝胶负载神经干细胞对改善脑缺血再灌注损伤的实验研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2022.
[32] KHODADADI YM, TAGHIZADEH A, TAGHIZADEH M, et al. Agarose-based biomaterials for advanced drug delivery. J Control Release. 2020;326: 523-543.
[33] CHEN S,WANG Y, LAI J, et al. Structure and properties of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) synthesized in different reaction systems. Biomacromolecules. 2023;24(6):2928-2941.
[34] 李媛媛,温瑜,李俊,等.GelMA复合水凝胶的制备与性能[J].太原理工大学学报,2021,52(5):842-848.
[35] 顾恒,连芩,王慧超,等.GelMA复合凝胶的挤出式3D打印工艺及其性能研究[J].机械工程学报,2020,56(1):196-204.
[36] XU H, CASILLAS J, KRISHNAMOORTHY S, et al. Effects of Irgacure 2959 and lithium phenyl-2,4,6-trimethylbenzoylphosphinate on cell viability, physical properties,and microstructure in 3D bioprinting of vascular-like constructs. Biomed Mater. 2020;15(5):55021.
[37] KURIAN AG, SINGH RK, PATEL KD, et al. Multifunctional GelMA platforms with nanomaterials for advanced tissue therapeutics. Bioact Mater. 2022;8: 267-295.
[38] WU Y, XIANG Y, FANG J, et al. The influence of the stiffness of GelMA substrate on the outgrowth of PC12 cells. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(1): BSR20181748.
[39] MCBETH C, LAUER J, OTTERSBACH M, et al. 3D bioprinting of GelMA scaffolds triggers mineral deposition by primary human osteoblasts. Biofabrication. 2017;9(1):15009.
[40] CELIKKIN N, MASTROGIACOMO S, JAROSZEWICZ J, et al. Gelatin methacrylate scaffold for bone tissue engineering: the influence of polymer concentration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(1):201-209.
[41] SHANG L, LIU Z, MA B, et al. Dimethyloxallyl glycine/nanosilicates-loaded osteogenic/angiogenic difunctional fibrous structure for functional periodontal tissue regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(4):1175-1188.
[42] 赵杰.具有BMP-2及VEGF缓释功能的组织工程骨膜的构建及其性能研究[D].苏州:苏州大学,2020.
[43] REHMAN S, AUGUSTINE R,ZAHID AA, et al. Reduced graphene oxide incorporated GelMA hydrogel promotes angiogenesis for wound healing applications. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:9603-9617.
[44] ZUO Y, XIAO W, CHEN X, et al. Bottom-up approach to build osteon-like structure by cell-laden photocrosslinkable hydrogel. Chem Commun (Camb). 2012;48(26):3170-3172.
[45] LIU Y, CHAN-PARK MB. A biomimetic hydrogel based on methacrylated dextran-graft-lysine and gelatin for 3D smooth muscle cell culture. Biomaterials. 2010;31(6):1158-1170.
[46] LOESSNER D, MEINERT C, KAEMMERER E, et al. Functionalization,preparation and use of cell-laden gelatin methacryloyl-based hydrogels as modular tissue culture platforms. Nat Protoc. 2016;11(4):727-746.
[47] SUN M, SUN X, WANG Z, et al. Synthesis and properties of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels and their recent applications in load-bearing tissue. Polymers (Basel). 2018;10(11):1290.
[48] 李明欣,李军,王文朝,等.载细胞多孔甲基丙烯酸酐化明胶三维支架及对细胞行为的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(16):2532-2539.
[49] JIA W, GUNGOR-OZKERIM PS, ZHANG YS, et al. Direct 3D bioprinting of perfusable vascular constructs using a blend bioink. Biomaterials. 2016; 106:58-68.
[50] MELCHELS FP, FEIJEN J, GRIJPMA DW. A review on stereolithography and its applications in biomedical engineering. Biomaterials. 2010;31(24): 6121-6130.
[51] 汤勇,罗科宇,陈玥琦,等.层粘连蛋白α4链功能肽修饰脱钙骨基质支架诱导H型血管及骨生成促进骨缺损修复的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(12):1594-1601.
[52] KANG Y, MOCHIZUKI N, KHADEMHOSSEINI A, et al. Engineering a vascularized collagen-beta-tricalcium phosphate graft using an electrochemical approach. Acta Biomater. 2015;11:449-458.
[53] SHANJANI Y, PAN CC, ELOMAA L, et al. A novel bioprinting method and system for forming hybrid tissue engineering constructs. Biofabrication. 2015;7(4):45008.
[54] JIANG G, LI S, YU K, et al. A 3D-printed PRP-GelMA hydrogel promotes osteochondral regeneration through M2 macrophage polarization in a rabbit model. Acta Biomater. 2021;128:150-162.
[55] GAO J, LI M, CHENG J, et al. 3D-printed GelMA/PEGDA/F127DA scaffolds for bone regeneration. J Funct Biomater. 2023;14(2):96.
[56] DUA R, RAMASWAMY S. Relative survivability of human osteoblasts is enhanced by 39 degrees C and ascorbic acid after exposure to photopolymerization ingredients. Cytotechnology. 2013;65(4):587-596.
[57] GOTO R, NISHIDA E, KOBAYASHI S, et al. Gelatin methacryloyl-riboflavin (GelMA-RF) hydrogels for bone regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1635.
[58] LI H, FAN XL, WANG YN, et al. Extracellular vesicles from human urine-derived stem cells ameliorate particulate polyethylene-induced osteolysis. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021;16:7479-7494.
[59] LU W, ZENG M, LIU W, et al. Human urine-derived stem cell exosomes delivered via injectable GelMA templated hydrogel accelerate bone regeneration. Mater Today Bio. 2023;19:100569.
[60] PABLOS JL, JIMENEZ-HOLGUIN J, SALCEDO SS, et al. New photocrosslinked 3D foamed scaffolds based on GelMA copolymers: potential application in bone tissue engineering. Gels. 2023;9(5):403.
[61] NIMGAMPALLE M, CHAKRAVARTHY H, SHARMA S, et al. Neurotransmitter systems in the etiology of major neurological disorders: emerging insights and therapeutic implications. Ageing Res Rev. 2023;89:101994.
[62] KANG MS, PARK R, JO HJ, et al. Stem cells by tuna-bone-derived hydroxyapatite composites withspontaneous osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal green tea polyphenol-reduced graphene oxide. Cells. 2023;12(11):1448.
[63] ZHANG X, ZHANG H, ZHANG Y, et al. 3D printed reduced graphene oxide-GelMA hybrid hydrogel scaffolds for potential neuralized bone regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2023;11(6):1288-1301.
[64] LATOURTE A, KLOPPENBURG M, RICHETTE P. Emerging pharmaceutical therapies for osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(12):673-688.
[65] HODGKINSON T, KELLY DC, CURTIN CM, et al. Mechanosignalling in cartilage: an emerging target for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(2):67-84.
[66] PENG Z, SUN H, BUNPETCH V, et al. The regulation of cartilage extracellular matrix homeostasis in joint cartilage degeneration and regeneration. Biomaterials. 2021;268:120555.
[67] FENG K, YU Y, CHEN Z, et al. Injectable hypoxia-preconditioned cartilage progenitor cells-laden GelMA microspheres system for enhanced osteoarthritis treatment. Mater Today Bio. 2023;20:100637.
[68] BEN M G, AVEIC S, WACHENDOERFER M, et al. 3D printable gelatin methacryloyl (gelma)-dextran aqueous two-phase system with tunable pores structure and size enables physiological behavior of embedded cells in vitro. Small. 2023;19(44):e2208089. |