[1] EINHORN TA, GERSTENFELD LC. Fracture healing: mechanisms and interventions. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(1):45-54.
[2] VAN GRIENSVEN M. Preclinical testing of drug delivery systems to bone. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;94:151-164.
[3] 涂振兴,王斌,卢爱东,等.单平面截骨骨搬移联合髓内钉治疗胫骨骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(12):1849-1853.
[4] FüRMETZ J, SOO C, BEHRENDT W, et al. Bone Transport for Limb Reconstruction Following Severe Tibial Fractures. Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2016;8(1):63-84.
[5] EL-ALFY B, EL-MOWAFI H, EL-MOGHAZY N. Distraction osteogenesis in management of composite bone and soft tissue defects. Int Orthop. 2010;34(1):115-118.
[6] 涂振兴,王斌,方均,等.胫骨骨搬移对接点愈合的影响因素分析[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2021,14(6):496-500.
[7] PALEY D, MAAR DC. Ilizarov bone transport treatment for tibial defects. J Orthop Trauma. 2000;14(2):76-85.
[8] ROBINSON PM, PAPANNA M, YOUNIS F, et al. Arthroscopic debridement of docking site in Ilizarov bone transport. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2010; 92(5):437-438.
[9] 柴明祥, 臧建成, 吴天昊,等.胫骨骨搬运后对合端不愈合的原因与治疗[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2013,15(10):840-844.
[10] KOCAOGLU M, ERALP L, RASHID HU, et al. Reconstruction of segmental bone defects due to chronic osteomyelitis with use of an external fixator and an intramedullary nail. J Bone Joint Surg. 2006;88(10): 2137-2145.
[11] PENG J, MIN L, XIANG Z, et al. Ilizarov bone transport combined with antibiotic cement spacer for infected tibial nonunion. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(6):10058-10065.
[12] TRESLEY J, SCHOENLEBER SJ, SINGER AD, et al. “Ilizarov” external fixation: what the radiologist needs to know. Skeletal Radiol. 2015; 44(2):179-195.
[13] LIU Y, YUSHAN M, LIU Z, et al. Complications of bone transport technique using the Ilizarov method in the lower extremity: a retrospective analysis of 282 consecutive cases over 10 years. BioMed Central. 2020;(1):119-115.
[14] MORA R, PEDROTTI L, BERTANI B, et al. Prevention of complications of epidermato-fascio-osteoplasty in the treatment of tibial infected nonunions with bone and soft tissue loss. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006; 8(6):158-165.
[15] DROR P. Bone transport: The Ilizarov treatment for bone defects. Techn Orthop. 1989;4(3):80-93.
[16] MORA R, MACCABRUNI A, BERTANI B, et al. Revision of 120 tibial infected non-unions with bone and soft tissue loss treated with epidermato-fascial osteoplasty according to Umiarov. Injury. 2014; 45(2):383-387.
[17] GIOTAKIS N, NARAYAN B, NAYAGAM S. Distraction osteogenesis and nonunion of the docking site: is there an ideal treatment option? Injury. 2007;38 Suppl 1:S100-107.
[18] CHARALAMBOUS CP, WILKES RA. Bone grafting of the un-united docking site in bone transport: description of a percutaneous approach. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2008;90(7):613.
[19] LOVISETTI G, SALA F. Clinical strategies at the docking site of distraction osteogenesis: are open procedures superior to the simple compression of Ilizarov? Injury. 2013;44 Suppl 1:S58-62.
[20] YIN P, ZHANG L, ZHANG L, et al. Ilizarov bone transport for the treatment of fibular osteomyelitis: a report of five cases. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:242.
[21] 梁斌,张锴.骨搬移并发症对接点不愈合的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(8):1275-1280.
[22] EL-ROSASY MA. Acute Shortening and Re-lengthening to Bridge Bone Defects. Bone Joint J. 2015;20(4):175-180.
[23] AKTUGLU K, EROL K, VAHABI A. Ilizarov bone transport and treatment of critical-sized tibial bone defects: a narrative review. J Orthop Traumatol. 2019;20(1):22.
[24] 刘亦杨,沈立锋,张春,等.骨搬移技术治疗下肢长骨干慢性骨髓炎伴骨缺损术后骨性愈合不良的原因分析及对策[J].中国骨伤, 2018,31(6):556-561.
[25] MAGADUM MP, BASAVARAJ YADAV CM, PHANEESHA MS, et al. Acute compression and lengthening by the Ilizarov technique for infected nonunion of the tibia with large bone defects. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2006;14(3):273-279.
[26] HATZOKOS I, STAVRIDIS SI, IOSIFIDOU E, et al. Autologous bone marrow grafting combined with demineralized bone matrix improves consolidation of docking site after distraction osteogenesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(7):671-678.
[27] LOWENBERG DW, FEIBEL RJ, LOUIE KW, et al. Combined muscle flap and Ilizarov reconstruction for bone and soft tissue defects. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(332):37-51.
[28] MOGHADDAM MH, VAHEDI E. Effect of decortications on union rate of tibial plating. Orthopedics. 2015;38(3):e213-216.
[29] TALL M, BONKOUNGOU D, SAWADOGO M, et al. Treatment of nonunion in neglected long bone shaft fractures by osteoperiosteal decortication. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100(6 Suppl):S299-303.
[30] 陶大为,王志刚,张锴.骨皮质剥脱与其他固定方式联用修复骨不连:是否需植骨及内置物的处理 [J].中国组织工程研究,2015,31(5): 256-261.
[31] KARARGYRIS O, POLYZOIS VD, KARABINAS P, et al. Papineau debridement, Ilizarov bone transport, and negative-pressure wound closure for septic bone defects of the tibia. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014;24(6):1013-1017.
[32] SOMANCHI BV, KHAN S. Vacuum-assisted wound closure (VAC) with simultaneous bone transport in the leg: a technical note. Acta Orthop Belg. 2008;74(4):538-541.
[33] PALEY D. Problems, obstacles, and complications of limb lengthening by the Ilizarov technique. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;(250):81-104. |
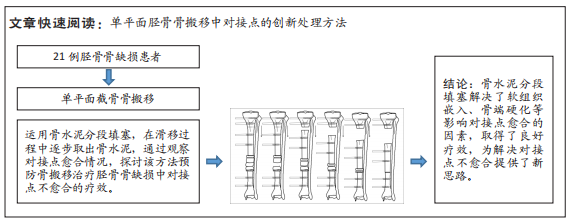
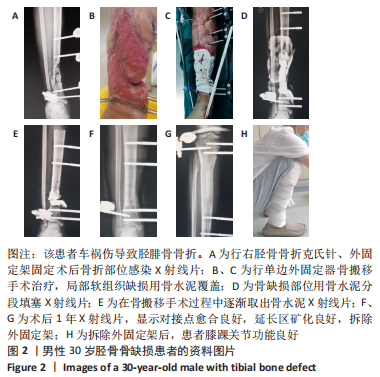
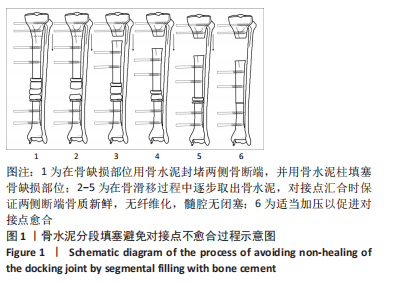
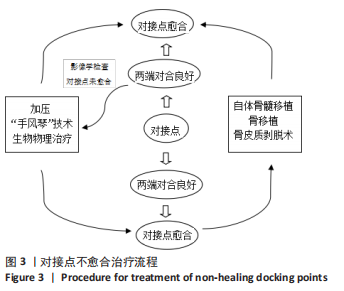 那么,对接点不愈合又该如何预防呢?目前预防对接点不愈合的方法主要有:①短缩延长术:延长术后先直接使对接点汇合并加压后再行肢体延长[17];②快速短缩法,术后先以2.0-3.0 mm/d的速度快速短缩,直至对接点对接后再适当加压后再行肢体延长[17];其他方法还包括联合使用髓内钉或负压吸引等[3,31-32]。然而这些方法同样存在不同的不足之处,比如短缩延长术和快速短缩法有时会出现血管危象等棘手问题,髓内钉可能增加髓内感染风险等问题。
那么,对接点不愈合又该如何预防呢?目前预防对接点不愈合的方法主要有:①短缩延长术:延长术后先直接使对接点汇合并加压后再行肢体延长[17];②快速短缩法,术后先以2.0-3.0 mm/d的速度快速短缩,直至对接点对接后再适当加压后再行肢体延长[17];其他方法还包括联合使用髓内钉或负压吸引等[3,31-32]。然而这些方法同样存在不同的不足之处,比如短缩延长术和快速短缩法有时会出现血管危象等棘手问题,髓内钉可能增加髓内感染风险等问题。