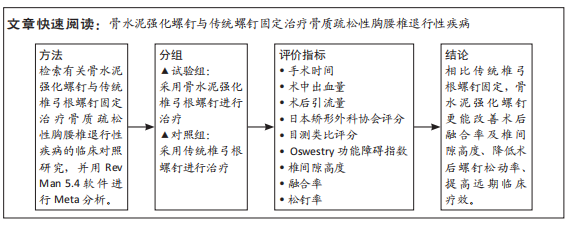
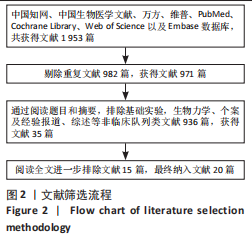
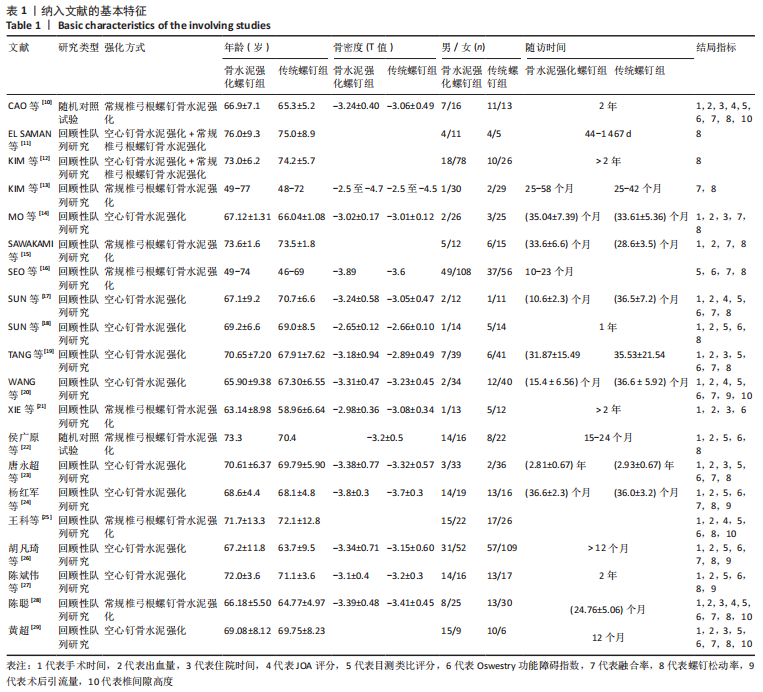
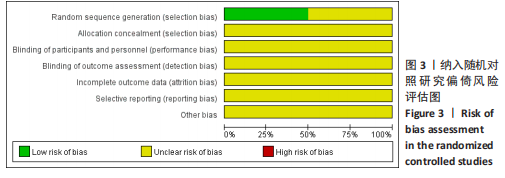
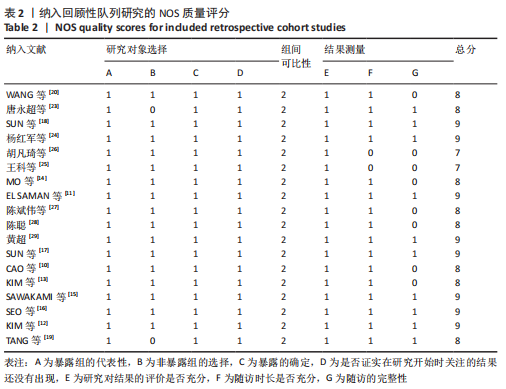
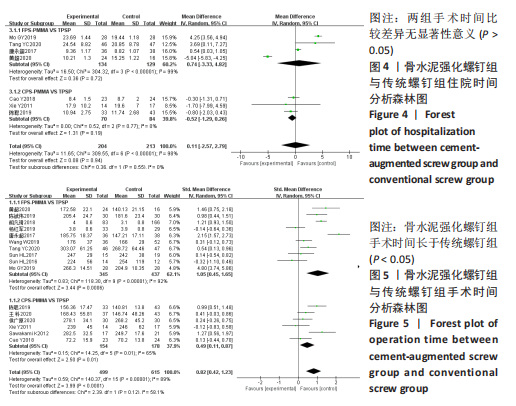
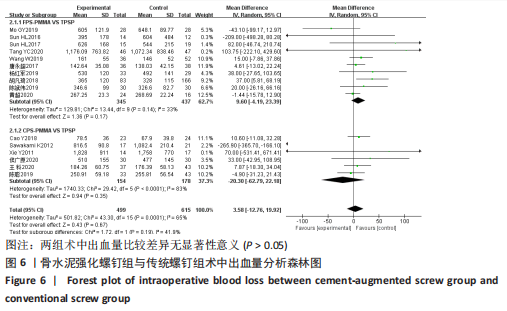
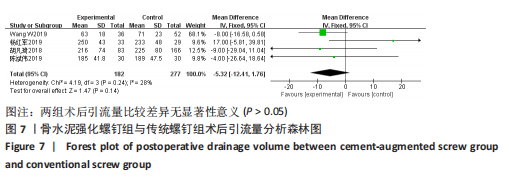
[1] TUOMAINEN I, PAKARINEN M, AALTO T, et al. Depression is associated with the long-term outcome of lumbar spinal stenosis surgery: a 10-year follow-up study. Spine J. 2018;18(3):458-463.
[2] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.中国骨质疏松症流行病学调查及“健康骨骼”专项行动结果发布[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2019,12(4):317-318.
[3] YOUNG JJ, JENSEN RK, HARTVIGSEN J, et al. Prevalence of multimorbid degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis with knee or hip osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):177.
[4] MARIE-HARDY L, PASCAL-MOUSSELLARD H, BARNABA A, et al. Screw Loosening in Posterior Spine Fusion: Prevalence and Risk Factors. Global Spine J. 2020;10(5):598-602.
[5] TANDON V, FRANKE J, KALIDINDI KKV. Advancements in osteoporotic spine fixation. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020;11(5):778-785.
[6] SAKAURA H, IKEGAMI D, FUJIMORI T, et al. Early cephalad adjacent segment degeneration after posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a comparative study between cortical bone trajectory screw fixation and traditional trajectory screw fixation. J Neurosurg Spine. 2019;32(2):155-159.
[7] GAZZERI R, PANAGIOTOPOULOS K, GALARZA M, et al. Minimally invasive spinal fixation in an aging population with osteoporosis: clinical and radiological outcomes and safety of expandable screws versus fenestrated screws augmented with polymethylmethacrylate. Neurosurg Focus. 2020;49(2):E14.
[8] JANG SH, LEE JH, CHO JY, et al. The efficacy of hydroxyapatite for screw augmentation in osteoporotic patients. Neurol Med Chir. 2013; 53(12):875e881.
[9] HOPPE S, KEEL MJ. Pedicle screw augmentation in osteoporotic spine: indications, limitations and technical aspects. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2017;43(1):3-8.
[10] CAO Y, LIANG Y, WAN S, et al. Pedicle Screw with Cement Augmentation in Unilateral Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A 2-Year Follow-Up Study. World Neurosurg. 2018;118:e288-e295.
[11] EL SAMAN A, MEIER S, SANDER A, et al. Reduced loosening rate and loss of correction following posterior stabilization with or without PMMA augmentation of pedicle screws invertebral fractures in the elderly. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2013;39(5):455-460.
[12] KIM JH, AHN DK, SHIN WS, et al. Clinical Effects and Complications of Pedicle Screw Augmentation with Bone Cement: Comparison of Fenestrated Screw Augmentation and Vertebroplasty Augmentation. Clin Orthop Surg. 2020;12(2):194-199.
[13] KIM KH, LEE SH, LEE DY, et al. Anterior bone cement augmentation in anterior lumbar interbody fusion and percutaneous pedicle screw fixation in patients with osteoporosis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2010;12(5):525-532.
[14] MO GY, GUO HZ, GUO DQ, et al. Augmented pedicle trajectory applied on the osteoporotic spine with lumbar degenerative disease: mid-term outcome. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019; 14(1):170.
[15] SAWAKAMI K, YAMAZAKI A, ISHIKAWA S, et al. Polymethylmethacrylate augmentation of pedicle screws increases the initial fixation in osteoporotic spine patients. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012;25(2):E28-35.
[16] SEO JH, JU CI, KIM SW, et al. Clinical efficacy of bone cement augmented screw fixation for the severe osteoporotic spine. Korean J Spine. 2012;9(2):79-84.
[17] SUN HL, LI CD, YANG ZC, et al. Polymethylmethacrylate augmentation of bone cement-injectable cannulated pedicle screws for the treatment of degenerative lumbar diseases with osteoporosis. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016;48(6):1019-1025.
[18] SUN HL, LI CD, LI XW, et al. Polymethylmethacrylate augmentation of bone cement injectable cannulated pedicle screws was used to treat degenerative lumbar scoliosis with osteoporosis. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2017;49(2):256-261.
[19] TANG YC, GUO HZ, GUO DQ, et al. Effect and potential risks of using multilevel cement-augmented pedicle screw fixation in osteoporotic spine with lumbar degenerative disease. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020; 21(1):274.
[20] WANG W, LIU C, LI J, et al. Comparison of the fenestrated pedicle screw and conventional pedicle screw in minimally percutaneous fixation for the treatment of spondylolisthesis with osteoporotic spine. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2019;183:105377.
[21] XIE Y, FU Q, CHEN ZQ, et al. Comparison between two pedicle screw augmentation instrumentations in adult degenerative scoliosis with osteoporosis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12:286.
[22] 侯广原,张继学,张志军,等.骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗伴骨质疏松腰椎退行性疾病的1年随访[J].中国组织工程研究, 2021,25(6):878-883.
[23] 唐永超,梁德,陈博来,等.骨水泥钉道强化与否治疗伴骨质疏松的单节段腰椎退行性疾病的临床对照研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2017,27(12):1092-1098.
[24] 杨红军,苏高建,冯智海,等.新型骨水泥椎弓根螺钉内固定系统治疗重度骨质疏松腰椎退变性疾病的临床研究[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2019,8(9):703-708.
[25] 王科,路琪,陆锡平.骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗骨质疏松伴腰椎退行性疾病效果及影响因素分析[J].河北医学,2020, 26(8):1246-1251.
[26] 胡凡琦,胡文浩,张昊,等.骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉技术治疗合并骨质疏松脊柱疾病的疗效观察[J].解放军医学院学报,2018,39(6):470-476.
[27] 陈斌伟,廖壮文,黄帅,等.可注射骨水泥椎弓根钉内固定术治疗伴骨质疏松的多节段腰椎管狭窄症的疗效[J].实用医学杂志, 2019,35(24):3793-3797.
[28] 陈聪.骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉治疗骨质疏松性腰椎退变疾病的疗效观察[D].扬州:扬州大学,2019.
[29] 黄超.骨水泥螺钉治疗老年腰椎滑脱患者疗效分析[D].长沙:湖南师范大学,2020.
[30] CHIN DK, PARK JY, YOON YS, et al. Prevalence of osteoporosis in patients requiring spine surgery: incidence and significance of osteoporosis in spine disease. Osteoporos Int. 2007;18(9):1219-1224.
[31] 高明暄,周胜虎,邓晓文,等.骨质疏松对椎弓根螺钉稳定性影响的实验研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2013,19(1):39-42.
[32] WEISER L, SEHMISCH S, LEHMANN W, et al. Techniques to increase pedicle screw stability in osteoporotic vertebrae. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2019;31(4):284-292.
[33] ZHUANG XM, YU BS, ZHENG ZM, et al. Effect of the degree of osteoporosis on the biomechanical anchoring strength of the sacral pedicle screws: an in vitro comparison betweenunaugmented bicortical screws and polymethylmethacrylate aug-mented unicortical screws. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010; 35(19):E925-E931.
[34] MCCOY S, TUNDO F, CHIDAMBARAM S, et al. Clinical considerations for spinal surgery in the osteoporotic patient: A comprehensive review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2019;180:40-47.
[35] LEHMAN RA JR, KANG DG, WAGNER SC. Management of osteoporosis in spine surgery. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23(4):253-263.
[36] ERDEM MN, KARACA S, SARı S, et al. Application of cement on strategic vertebrae in the treatment of the osteoporotic spine. Spine J. 2017;17(3):328-337.
[37] GIRARDO M, CINNELLA P, GARGIULO G, et al. Surgical treatment of osteo-porotic thoraco -lumbar compressive fractures: the use of pediclescrew with augmentation PMMA. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(Suppl 4):546-551.
[38] SHI S, ZHOU Z, NI HJ, et al. Does anxiety influence the prognosis of percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy in the treatment of lumbar disc herniation? A preliminary propensity score matching analysis. Int Orthop. 2020;44(11):2357-2363.
[39] WANG Y, YANG L, LI C, et al. The Biomechanical Properties of Cement-Augmented Pedicle Screws for Osteoporotic Spines. Global Spine J. 2022;12(2):323-332.
[40] JANSSEN I, RYANG YM, GEMPT J, et al. Risk of cement leakage and pulmonary embolism by bone cement-augmented pedicle screw fixation of the thoracolumbar spine. Spine J. 2017;17(6):837-844.
[41] EHRESMAN J, PENNINGTON Z, ELSAMADICY AA, et al. Fenestrated pedicle screws for thoracolumbar instrumentation in patients with poor bone quality: Case series and systematic review of the literature. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2021;206:106675.
[42] CHEN LH, TAI CL, LEE DM, et al. Pullout strength of pedicle screws with cement augmentation in severe osteoporosis: a comparative study between cannulated screws with cement injection and solid screws with cement pre-filling. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12:33.
[43] 郭海威,谢家豪,林燕平,等.骨水泥强化空心侧孔与常规椎弓根螺钉内固定修复骨质疏松椎体效果及安全性Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(30):4891-4899. |