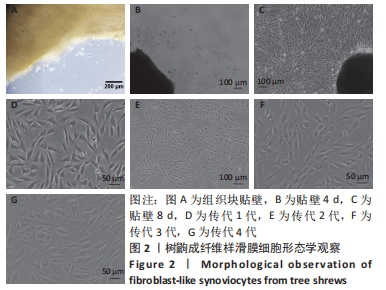
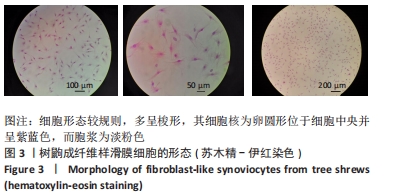
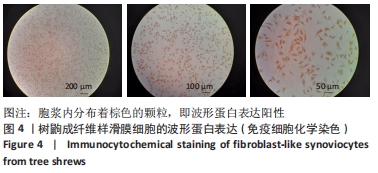
[1] SMOLEN JS, ALETAHA D, BARTON A, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:18001.
[2] DEL RMJ, VALIN Á, USATEGUL A, et al. Senescent synovial fibroblasts accumulate prematurely in rheumatoid arthritis tissue s and display an enhanced inflammatory phenotype. Immun Ageing. 2019;16:29.
[3] YUE T, FAN X, ZHANG Z, et al. Downregulation of lncRNA ITSN1-2 correlates with decreased disease risk and activity of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and reduces RA fibroblast-like synoviocytes proliferation and inflammation via inhibiting NOD2/RIP2 signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(8):4650.
[4] 奚正德,张冬青,张雁云,等.小鼠胶原诱导性关节炎的研究进展[J].自然杂志,2003,25(1):36-41.
[5] 仇海文,李卉,刘振州,等.Ⅱ型胶原诱导的关节炎大鼠滑膜成纤维细胞的培养、纯化和鉴定[J].南京师大学报(自然科学版),2017, 40(3):128-132.
[6] AZUSHIMA K, GURLEY SB, COFFMAN TM. Modelling diabetic nephropathy in mice. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018;14:48-56.
[7] ESTEVES PJ, ABRANTES J, BALDAUF HM, et al. The wide utility of rabbits as models of human diseases. Exp Mol Med. 2018;50:1-10.
[8] ZHAO Y , WANG J, KUANG D, et al. Susceptibility of tree shrew to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Sci Rep. 2020;10:16007.
[9] 薛丽香,张凤珠,孙瑞娟,等.我国疾病动物模型的研究现状和展望[J].中国科学:生命科学,2014,44(9):851-861.
[10] 徐林,张云,梁斌,等.实验动物树鼩和人类疾病的树鼩模型研究概述[J].动物学研究,2013,34(2):59-69.
[11] SACRE S, LO A, GREGORY B, et al. Oligodeoxynucleotide inhibition of Toll-like receptors 3, 7, 8, and 9 suppresses cytokine production in a human rheumatoid arthritis model. Eur J Immunol. 2016;46(3):772-781.
[12] 司徒镇强,吴军正.细胞培养[M].2版.西安:世界图书出版西安公司,2007:57-63.
[13] 王强,韩隆胤,魏赈权,等.断藤益母汤对类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞MEKK2及CIA小鼠关节炎的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2020,26(7):31-41.
[14] 邵玉宝,鲍兰馨,汪陶荣,等.丹皮酚通过调节中脑星形细胞神经营养因子的表达及细胞质/核易位抑制类风湿关节炎成纤维滑膜细胞炎症反应[J].中国药理学通报,2021,37(7):958-964.
[15] 刘琴,王丽平,陈芳,等.悬浮组织块法分离培养兔成纤维样滑膜细胞[J].中国免疫学杂志,2016,32(7):1009-1012.
[16] BRENTANO F, SCHORR O, GAY RE, et al. RNA released from necrotic synovial fluid cells activates rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts via Toll-like receptor 3. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:2656-2665
[17] PICCININI AM, WILLIAMS L, MCCANN FE, et al. Investigating the role of toll-like receptors in Models of Arthritis. Mol Biol (Clifton, NJ). 2016; 1390:351-381.
[18] CHOUDHARY N, BHATT LK, PRABHAVALKAR KS. Experimental animal models for rheumatoid arthritis. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2018;40(3):193-200.
[19] FISCHER BD, ADEYEMO A, O’LEARY ME, et al. Animal models of rheumatoid pain: experimental systems and insights. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;30;19(1):146.
[20] 黄英,陈哲,王玉,等.中药对类风湿关节炎成纤维滑膜细胞的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2017,35(8):2095-2097.
[21] 黄淑敏,钟森杰,廖晓倩,等.基于中西医临床病症特点的类风湿性关节炎动物模型分析[J].中国中药杂志,2021,46(19):5152-5158.
[22] LU T, PENG H, ZHONG L, et al. The Tree Shrew as a Model for Cancer Research. Front Oncol. 2021;11:653236.
[23] ROMER S, BENDER H, KNABE W, et al. Neural progenitors in the developing neocortex of the northern tree shrew (Tupaia belangeri) show a closer relationship to gyrencephalic primates than to lissencephalic rodents. Front Neuroanat. 2018;12:29.
[24] ZHANG J, LUO RC, MAN XY, et al. The anatomy of the skin of the Chinese tree shrew is very similar to that of human skin. Zool Res. 2020;41:208-212.
[25] 匡德宣,孙晓梅,代解杰,等.实验树齣主要内分泌器官的组织学观察[J].中国比较医学杂志, 2014,24(6):35-39.
[26] 王颖君,陈群,冷静,等.树鼩主要免疫器官组织学研究[J].广西中医药大学学报,2013,16(2):16-18.
[27] 周思齐,李皓桓.人成纤维样滑膜细胞原代培养的改良方法[J].广西医学,2019,41(2):212-215.
[28] EDWARDS JC. Fibrolast biology.Development and differentiation of synovial fibroblasts in arthritis. Arthritis Res.2000;2(5):344-347.
[29] HANS PK, MICHAEL BB. Building the synovium: cadherin-11 mediates fibroblast-like synoviocyte cell-to-cell adhesion. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(2):207-220.
[30] 肖楚吟,潘云峰,郭兴华,等.滑膜成纤维细胞的原代培养及生物特性[J].中国医学工程,2010,18(2):1-4.
[31] 刘琴,陈芳,朱以良,等.一种新的佐剂性关节炎兔成纤维样滑膜细胞分离培养法[J].第二军医大学学报,2019,40(7):793-797.
[32] 陈芳,刘琴,王丽平,等.改良组织块法分离培养兔成纤维样滑膜细胞[J].中国比较医学杂志,2016,26(4):75-78+85.
[33] ABDELWAHAB A, PALOSAARI S, ABDELWAHAB SA, et al. Differential synovial tissue expression of TLRs in seropositive and seronegative rheumatoid arthritis: A preliminary report. Autoimmun. 2021;54(1): 23-34.
[34] CHEN JQ, SZODORAY P, ZEHER M. Toll-Like Receptor Pathways in Autoimmune Diseases. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016;50(1):1-17.
[35] LEITE PA, BITOUN S, PAOLETTI A, et al. Characterization of Phenotypes and Functional Activities of Leukocytes From Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients by Mass Cytometry. Frontiers in Immunol. 2019;10:2384.
[36] TORIGOE, M, SAKATA K, ISHII A, et al. Hydroxychloroquine efficiently suppresses inflammatory responses of human class-switched memory B cells via Toll-like receptor 9 inhibition. Clin Immunol. 2018;195:1-7.
[37] NANKE Y, KOBASHIGAWA T, YAGO T, et al. RANK expression and osteoclastogenesis in human monocytes in peripheral blood from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Biomed Res Int. 2016:4874195.
[38] Kim KW, Kim BM, Won JY, et al. Toll-like receptor 7 regulates osteoclastogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. J Biochem. 2019;166(3): 259-270.
[39] GUIDUCCI C, GONG M, CEPIKA AM, et al. RNA recognition by human TLR8 can lead to autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med. 2013;210(13): 2903-2919.
[40] UGOLINI M, GERHARD J, BURKERT S, et al. Recognition of microbial viability via TLR8 drives TFH cell differentiation and vaccine responses. Nat Immunol. 2018;19(4):386-396.
|