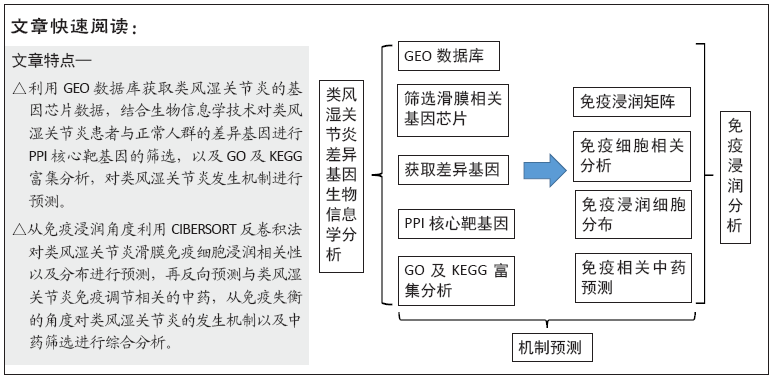
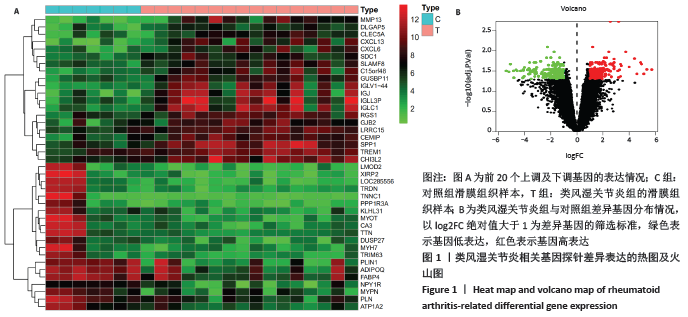
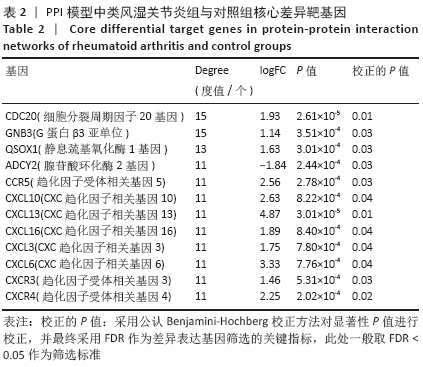
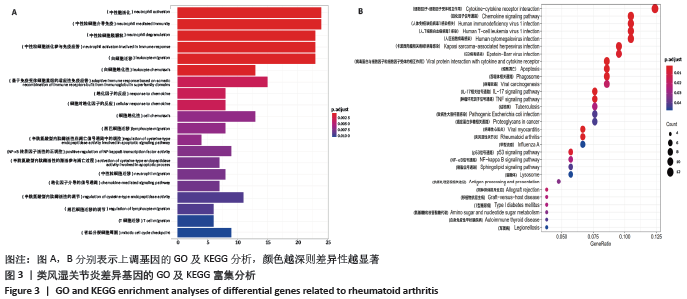
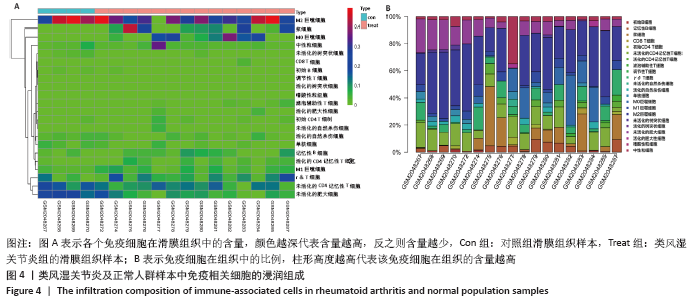
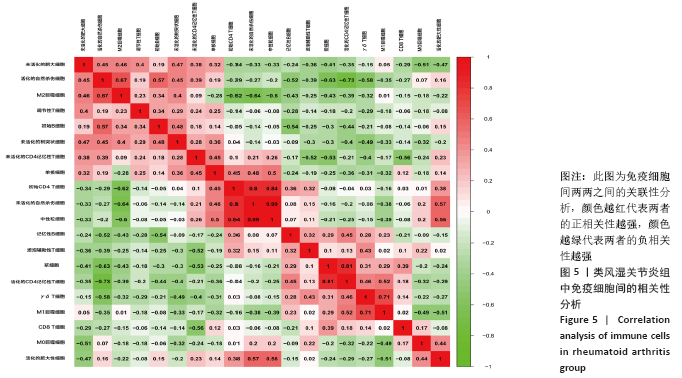
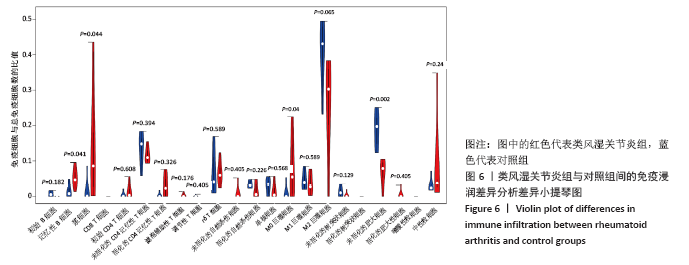
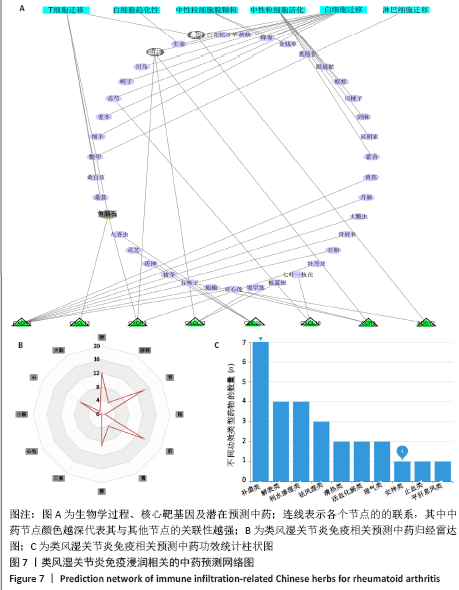
[1] FALCONER J, MURPHY AN, YOUNG SP, et al. Review: synovial cell metabolism and chronic inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70(7):984-999.
[2] MCINNES IB, SCHETT G. Pathogenetic insights from the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2017;389(10086):2328-2337.
[3] SHI YQ, QI WF, KONG CY. Drug screening and identification of key candidate genes and pathways of rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(2):986-996.
[4] AREND WP, FIRESTEIN GS. Pre-rheumatoid arthritis: predisposition and transition to clinical synovitis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8(10):573-586.
[5] COUTANT F, MIOSSEC P. Evolving concepts of the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis with focus on the early and late stages. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2020; 32(1):57-63.
[6] FANG Q, ZHOU C, NANDAKUMAR KS. Molecular and cellular pathways contributing to joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2020; 2020:3830212.
[7] ORR C, VIEIRA-SOUSA E, BOYLE DL, et al. Corrigendum: synovial tissue research: a state-of-the-art review. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;14(1):60.
[8] FANG Q, OU J, NANDAKUMAR KS. Autoantibodies as diagnostic markers and mediator of joint inflammation in arthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2019;2019: 6363086.
[9] YANG X, CHANG Y, WEI W. Emerging role of targeting macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis: Focus on polarization, metabolism and apoptosis. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(7): e12854.
[10] ROBERTS CA, DICKINSON AK, TAAMS LS. The Interplay Between Monocytes/Macrophages and CD4(+) T Cell Subsets in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol 2015;6:571.
[11] SMOLEN JS, LANDEWÉ R, BIJLSMA J, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(6):685-699.
[12] 逯卓卉,韦登明,张伊,等.组织工程方法修复类风湿性关节炎软骨缺损的研究进展[J].北京生物医学工程,2013,32(3):315-319.
[13] CHATZIDIONYSIOU K, SFIKAKIS PP. Low rates of remission with methotrexate monotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis: review of randomised controlled trials could point towards a paradigm shift. RMD Open. 2019;5(2):e000993.
[14] XING Q, FU L, YU Z, et al. Efficacy and safety of integrated traditional chinese medicine and western medicine on the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:4348709.
[15] 陈坤威,童亚林,姚咏明.组织工程支架材料对固有免疫反应的影响及调控效应[J]. 解放军医学杂志,2018,43(8):698-703.
[16] GUO X, JI J, FENG Z, et al. A network pharmacology approach to explore the potential targets underlying the effect of sinomenine on rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;80:106201.
[17] 池里群,周彬,高文远,等.治疗类风湿性关节炎常用药物的研究进展[J].中国中药杂志,2014,39(15):2851-2858.
[18] 王亚黎,刘健,叶文芳,等.中医药对类风湿关节炎患者免疫球蛋白影响的研究进展[J].风湿病与关节炎,2014,3(4):62-65.
[19] MOROZ LA, TALAKO ТМ, POTAPNEV MP, et al. Dichotomy of Local Th1- and Systemic Th2/Th3-Dependent Types of Immune Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2019;167(1):69-73.
[20] KOMATSU N, TAKAYANAGI H. Immune-bone interplay in the structural damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018;194(1):1-8.
[21] ALI HR, CHLON L, PHAROAH PD, et al. Patterns of immune infiltration in breast cancer and their clinical implications: a gene-expression-based retrospective study. PLoS Med. 2016;13(12):e1002194.
[22] XIONG Y, WANG K, ZHOU H, et al. Profiles of immune infiltration in colorectal cancer and their clinical significant: a gene expression-based study. Cancer Med. 2018;7(9):4496-4508.
[23] NEWMAN AM, LIU CL, GREEN MR, et al. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods. 2015;12(5):453-457.
[24] LU G, CHEN L, WU S, et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells and Relevant Therapeutic Strategy in Esophageal Cancer. Dis Markers. 2020; 2020:8974793.
[25] 古龙,周牮,彭建华,等.颅内动脉瘤的相关信号通路基因集富集及免疫浸润分析[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2020,26(7):178-185.
[26] LAN YY, WANG YQ, LIU Y. CCR5 silencing reduces inflammatory response, inhibits viability, and promotes apoptosis of synovial cells in rat models of rheumatoid arthritis through the MAPK signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(10): 18748-18762.
[27] GUO Q, ZHENG K, FAN D, et al. Wu-Tou Decoction in rheumatoid arthritis: integrating network pharmacology and in vivo pharmacological evaluation. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:230.
[28] LEE JH, KIM B, JIN WJ, et al. Pathogenic roles of CXCL10 signaling through CXCR3 and TLR4 in macrophages and T cells: relevance for arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):163.
[29] ARMAS-GONZÁLEZ E, DOMÍNGUEZ-LUIS MJ, DÍAZ-MARTÍN A, et al. Role of CXCL13 and CCL20 in the recruitment of B cells to inflammatory foci in chronic arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):114.
[30] PANDYA JM, LUNDELL AC, ANDERSSON K, et al. Blood chemokine profile in untreated early rheumatoid arthritis: CXCL10 as a disease activity marker. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):20.
[31] MIYABE Y, LIAN J, MIYABE C, et al. Chemokines in rheumatic diseases: pathogenic role and therapeutic implications. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15(12):731-746.
[32] TSUJIMURA S, ADACHI T, SAITO K, et al. Relevance of P-glycoprotein on CXCR4+ B cells to organ manifestation in highly active rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2018;28(2):276-286.
[33] COSTANTINO AB, ACOSTA C, ONETTI L, et al. Follicular helper T cells in peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Reumatol Clin. 2017;13(6):338-343.
[34] ZHOU LF, ZENG W, SUN LC, et al. IKKε aggravates inflammatory response via activation of NF-κB in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018; 22(7):2126-2133.
[35] LIU YR, YAN X, YU HX, et al. NLRC5 promotes cell proliferation via regulating the NF-κB signaling pathway in Rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Immunol. 2017;91:24-34.
[36] ONISHI RM, PARK SJ, HANEL W, et al. SEF/IL-17R (SEFIR) is not enough: an extended SEFIR domain is required for IL-17RA-mediated signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(43):32751-32759.
[37] 郭江燕,高梓珊,姜姝姝,等.IL-17和NF-κB通路与类风湿性关节炎的相关性研究[J].长春中医药大学学报,2015,31(1):192-194.
[38] 董甜甜,王金龄,李世刚,等.肥大细胞在小鼠佐剂性关节炎疼痛中的作用及其机制研究[J].中国病理生理杂志,2020,36(4):693-699.
[39] OKAMURA Y, MISHIMA S, KASHIWAKURA JI, et al. The dual regulation of substance P-mediated inflammation via human synovial mast cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Allergol Int. 2017;66S:S9-9S20.
[40] KUNG CC, DAI SP, CHIANG H, et al. Temporal expression patterns of distinct cytokines and M1/M2 macrophage polarization regulate rheumatoid arthritis progression. Mol Biol Rep. 2020;47(5):3423-3437.
[41] 阮静瑶,陈必成,张喜乐,等.巨噬细胞M1/M2极化的信号通路研究进展[J].免疫学杂志,2015,31(10):911-917.
[42] 王艳霞.类风湿性关节炎滑膜淋巴细胞CD3、CD4、CD8的表达及意义[D].天津:天津医科大学,2012:1-60.
[43] 田杰祥,陶永明,王钢,等.中医药治疗类风湿关节炎滑膜炎的机理研究进展[J].中医药学报,2019,47(3):122-124.
[44] 张佳琪.基于焦树德教授治疗类风湿关节炎辨证分型的用药规律探讨[J].风湿病与关节炎,2017,6(12):33-37.
[45] 卜祥伟,张红红,张建萍,等.基于数据挖掘探讨孟凤仙教授治疗类风湿关节炎用药规律[J].中华中医药学刊,2018,36(7):1573-1576.
[46] 蔡辉,陆乐,赵智明.“以毒攻毒”在类风湿关节炎治疗中的运用[J].中医学报,2015,30(11):1664-1666.
[47] NIU X, HE Z, LI W, et al. Immunomodulatory Activity of the Glycoprotein Isolated from the Chinese Yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb). Phytother Res. 2017;31(10): 1557-1563.
[48] JEONG JW, LEE HH, LEE KW, et al. Mori folium inhibits interleukin-1β-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinases and inflammatory mediators by suppressing the activation of NF-κB and p38 MAPK in SW1353 human chondrocytes. Int J Mol Med. 2016;37(2):452-460.
[49] 侯瑞宏,廖森泰,刘凡,等.桑叶多糖对小鼠免疫调节作用的影响[J].食品科学,2011,32(13):280-283.
[50] 赵婷,高昂,巩江,等.鱼脑石药学研究概况[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2011, 13(9):82-84.
[51] 匡红,解葵,孙晨,等.512例类风湿关节炎患者血清5种微量元素含量分析[J].国际检验医学杂志,2013,34(10):1214-1215,1218.
[52] 吴文英,张如峰,马凤英,等.不同药物治疗对类风湿关节炎患者血清铜、硒及锌水平的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2015,35(6):1555-1556.
|