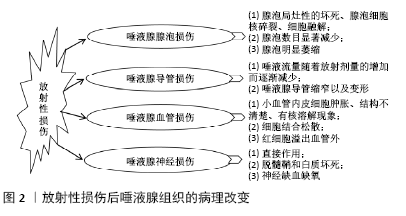
[1] DU Y, DU S, LIU L, et al. Radiation-Induced Bystander Effect can be Transmitted Through Exosomes Using miRNAs as Effector Molecules.Radiat Res. 2020;194(1): 89-100.
[2] WIDEL M. Radiation induced bystander effect: from in vitro studies toclinical application.Int J Med Phys Clin Eng Radiat Oncol.2016;5(1):1-17.
[3] LANGENDIJK JA, DOORNAERT P, VERDONCK-DELEEUW IM, et al. Impact of late treatment-related toxicity on quality of life among patients with head and neck cancer treated with radiotherapy.J. Clin. Oncol. 2008;26:3770-3776.
[4] DIRIX P, NUYTS S. Evidence-based organ-sparing radiotherapy in head and neck cancer.Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:85-91.
[5] CHOI J, KIM SH, KOH YW, et al. Tumor Stage-Related Role of Radiotherapy in Patients with an External Auditory Canal and Middle Ear Carcinoma.Cancer Res Treat. 2017;49(1):178-184.
[6] MOLONEY JN, COTTER TG.ROS signalling in the biology of cancer.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018;80:50-64.
[7] BORREGO-SOTO G, ORTIZ-LÓPEZ R, ROJAS-MARTÍNEZ A. Ionizing radiation-induced DNA injury and damage detection in patients with breast cancer. Genet Mol Biol. 2015;38(4):420-432.
[8] VON ZGLINICKI T. Oxidative stress shortens telomeres.Trends Biochem Sci. 2002; 27(7):339-44.
[9] HUBENAK J, ZHANG Q, BRANCH CD, et al.Mechanisms of injury to normal tissue after radiotherapy: a review.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014;133(1):49e-56e.
[10] CAMPISI J. Aging, cellular senescence, and cancer.Annu Rev Physiol. 2013;75: 685-705.
[11] 陈犹白,柴密,乌兰哈斯,等.放射性损伤:类型、症状和机制[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2017,12(3):203-206.
[12] MARZI S, FARNETI A, VIDIRI A, et al. Radiation-induced parotid changes in oropharyngeal cancer patients: the role of early functional imaging and patient-/treatment-related factors.Radiat Oncol. 2018;13(1):189.
[13] STEPHENS LC, SCHULTHEISS TE, PRICE RE, et al. Radiation apoptosis of serous acinar cells of salivary and lacrimal glands.Cancer. 1991;67(6):1539-1543.
[14] WADA A, UCHIDA N, YOKOKAWA M, et al. Radiation-induced xerostomia: objective evaluation of salivary gland injury using MR sialography.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009;30(1):53-58.
[15] 刘学奎,曾宗渊,张书旭,等.兔颌下腺移位术防治放疗后口干燥症[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志,2005,25(5):445-446.
[16] ZHOU S, QIAN J J, XU L, et al. The quantitative evaluation of early radiation-induced changes in the salivary glands using MRI.Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017;97:492-495.
[17] 陈希.基于磁共振弥散加权成像的唾液腺放射性损伤剂量-效应相关性研究[J].中国医学创新,2017,14(35):45-48.
[18] 李碧霞,陈倩怡,戴振晖,等.放射性口干症动物模型建立及颌下腺放射性组织损伤的生物学效应[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(32):5164-5169.
[19] GRUNDMANN O, MITCHELL GC, LIMESAND KH. Sensitivity of salivary glands to radiation: from animal models to therapies.J Dent Res. 2009;88(10):894-903.
[20] EMMERSON E, KNOX SM. Salivary gland stem cells: A review of development, regeneration and cancer.Genesis.2018;56: e23211.
[21] 颜兴,武鸿毅,许诺,等.放疗对小型猪腮腺颌下腺舌下腺微血管损伤影响的实验研究[J].口腔医学研究,2017,33(1):15-18.
[22] Cotrim AP, Sowers A, Mitchell JB, et al. Prevention of irradiation-induced salivary hypofunction by microvessel protection in mouse salivary glands.Mol Ther. 2007;15(12):2101-2106.
[23] 陈晨. 海带多糖调节P38MAPK通路保护放射诱导损伤的下颌下腺血管[D].南宁:广西医科大学,2018.
[24] LIN YS, JEN YM, LIN JC. Radiation-related cranial nerve palsy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Cancer. 2002;95:404-409.
[25] MOLONEY EC, BRUNNER M, ALEXANDER AJ, et al. Quantifying fibrosis in head and neck cancer treatment: An overview.Head Neck. 2015;37(8):1225-1231.
[26] JOHANSSON S, SVENSSON H, LARSSON LG, et al. Brachial plexopathy after postoperative radiotherapy of breast cancer patients--a long-term follow-up.Acta Oncol. 2000;39:373-82.
[27] 薛兵,卢宏.放射性神经系统损伤2例分析并文献回顾[J].神经损伤与功能重建,2019,14(2):72-75.
[28] VAN LUIJK P, PRINGLE S, DEASY JO, et al. Sparing the region of the salivary gland containing stem cells preserves saliva production after radiotherapy for head and neck cancer.Sci Transl Med. 2015;7(305):305ra147.
[29] YOO C, VINES JB, ALEXANDER G, et al. Adult stem cells and tissue engineering strategies for salivary gland regeneration: a review. Biomater Res.2014;18:9.
[30] OGAWA M, TSUJI T. Functional salivary gland regeneration as the next generation of organ replacement regenerative therapy. Odontology. 2015;103(3):248-257.
[31] NEZU A, MORITA T, NAGAI T, et al. Simultaneous monitoring of Ca2+ responses and salivary secretion in live animals reveals a threshold intracellular Ca2+ concentration for salivation.Exp Physiol. 2019;104(1):61-69.
[32] TANAKA ISOMURA E, YOSHITOMI K, HAMAGUCHI M, et al.Transplantation of vascularized submandibular gland in dogs.J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2006;64: 1561-1565.
[33] SHIP JA.Diagnosing, managing, and preventing salivary gland disorders.Oral Dis. 2002;8:77-89.
[34] NEUMANN Y, DAVID R, STIUBEA-COHEN R, et al. Long-term cryopreservation model of rat salivary gland stem cells for future therapy in irradiated head and neck cancer patients.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2012;18(9):710-718.
[35] SU X, LIU Y, BAKKAR M, et al. Labial Stem Cell Extract Mitigates Injury to Irradiated Salivary Glands.J Dent Res. 2020;99:293-301.
[36] VISSINK A, VAN LUIJK P, LANGENDIJK JA, et al. Current ideas to reduce or salvage radiation damage to salivary glands. Oral Dis. 2015;21(1):e1-10.
[37] LOMBAERT I, MOVAHEDNIA MM, ADINE C, et al. Concise Review: Salivary Gland Regeneration: Therapeutic Approaches from Stem Cells to Tissue Organoids.Stem Cells. 2017;35(1):97-105.
[38] 王英鑫. 低氧预处理人羊膜间充质干细胞修复放射性涎腺损伤功能的研究[D].遵义:遵义医学院,2018.
[39] 王涛,强艳丽.脂肪干细胞对小鼠放射性唾液腺损伤的治疗作用[J].山东医药,2017,57(33):32-34.
[40] ANDREADIS D, BAKOPOULOU A, LEYHAUSEN G, et al. Minor salivary glands of the lips: a novel, easily accessible source of potential stem/progenitor cells.Clin Oral Investig.2014;18: 847-856.
[41] NANDURI LS, BAANSTRA M, FABER H, et al.Purification and ex vivo expansion of fully functional salivary gland stem cells.Stem Cell Reports. 2014;3(6):957-964.
[42] SUI Y, ZHANG S, LI Y, et al. Generation of functional salivary gland tissue from human submandibular gland stem/progenitor cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020; 11(1):127.
[43] ZHANG C, LI Y, ZHANG XY, et al. Therapeutic potential of human minor salivary gland epithelial progenitor cells in liver regeneration.Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):12707.
[44] PRINGLE S, MAIMETS M, VAN DER ZWAAG M, et al. Human Salivary Gland Stem Cells Functionally Restore Radiation Damaged Salivary Glands.Stem Cells. 2016;34(3):640-652.
[45] ZHANG NN, HUANG GL, HAN QB, et al. Functional regeneration of irradiated salivary glands with human amniotic epithelial cells transplantation.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013;6(10):2039-2047.
[46] LANCASTER MA,KNOBLISH JA. Organogenesis in a dish: modeling development and disease using organoid technologies. Science.2014;345(6194):1247125.
[47] MORITANI Y, USUI M, SANO K, et al. Spheroid culture enhances osteogenic potential of periodontal ligament mesenchymal stem cells. J Periodont Res. 2018; 53:870-882.
[48] TANAKA J, MISHIMA K. In vitro three-dimensional culture systems of salivary glands. Pathol Int. 2020;70(8):493-501.
[49] 吴婷,李朝晖,崔占峰,等.应用多种水凝胶支架材料构建三维神经干细胞培养模型[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2015,37(1):66-73.
[50] GASTON J, THIBEAULT SL. Hyaluronic acid hydrogels for vocal fold wound healing.Biomatter.2013;3(1):e23799.
[51] 董娇,张霓霓,姚礼,等.HP-HA-肝ECM水凝胶制备及细胞相容性研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2019,35(6):779-784.
[52] Shin HS, Hong HJ, Koh WG, et al. Organotypic 3D Culture in Nanoscaffold Microwells Supports Salivary Gland Stem-Cell-Based Organization.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018;4(12):4311-4320.
[53] JEE JH, LEE DH, KO J, et al. Development of Collagen-Based 3D Matrix for Gastrointestinal Tract-Derived Organoid Culture.Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019: 8472712.
[54] SHIN K, KOO KH, JEONG J, et al. Three-Dimensional Culture of Salivary Gland Stem Cell in Orthotropic Decellularized Extracellular Matrix Hydrogels. Tissue Eng Part A. 2019;25(19-20):1396-1403.
[55] 刘磊. 生物工程化人唾液腺类器官构建的实验研究[D].北京:北京协和医学院,2017.
[56] KHALILI S, LIU Y, KORNETE M, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells improve salivary function and reduce lymphocytic infiltrates in mice with Sjögren’s-like disease.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38615.
[57] EMMERSON E, KNOX SM. Salivary gland stem cells: A review of development, regeneration and cancer.Genesis. 2018;56(5):e23211.
|