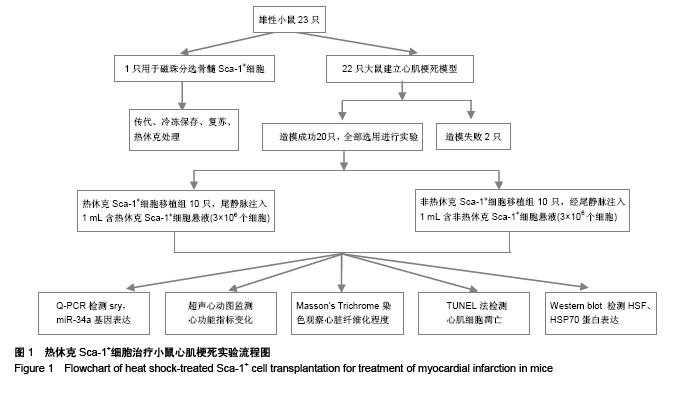
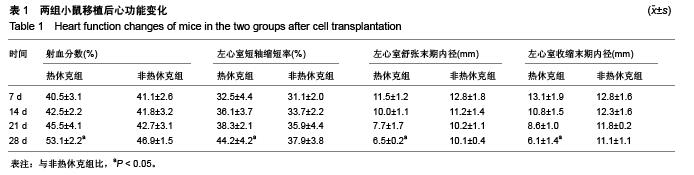
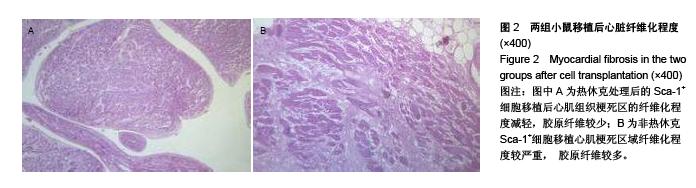
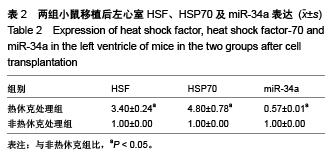
| [1] 包玉梅,赵燕平,周丽华.骨髓干细胞移植与心肌再生的研究进展[J].中国误诊学杂志,2010,10(11):2537-2538.[2] Bhaskar B, Mekala NK, Baadhe RR,et al. Role of signaling pathways in mesenchymal stem cell differentiation.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;9(6):508-512.[3] Tian H, Chen GH, Xu Y,et al. Biological characteristics of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and JAK2 mutation in myeloproliferative neoplasms.Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2012;33(9):701-704.[4] Zhu X, Du J, Liu G. The comparison of multilineage differentiation of bone marrow and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Clin Lab. 2012;58(9-10):897-903.[5] Wang B, Wu SM, Wang T, et al. Pre-treatment with bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibits systemic intravascular coagulation and attenuates organ dysfunction in lipopolysaccharide-induced disseminated intravascular coagulation rat model. Chin Med J (Engl). 2012;125(10): 1753-1759.[6] Wu Y, Zhao RC. The role of chemokines in mesenchymal stem cell homing to myocardium. Stem Cell Rev. 2012;8(1): 243-250.[7] Tong J, Ding J, Shen X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation enhancement in myocardial infarction rat model under ultrasound combined with nitric oxide microbubbles. PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e80186.[8] Won YW, Patel AN, Bull DA. Cell surface engineering to enhance mesenchymal stem cell migration toward an SDF-1 gradient. Biomaterials. 2014;35(21):5627-5635.[9] 何庚戌,要彤,张浩,等.骨髓间充质干细胞经静脉移植到心肌梗死大鼠体内后的分布[J].心脏杂志,2009,21(2):201-205.[10] Rodrigo SF, van Ramshorst J, Hoogslag GE, et al. Intramyocardial injection of autologous bone marrow-derived ex vivo expanded mesenchymal stem cells in acute myocardial infarction patients is feasible and safe up to 5 years of follow-up. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2013;6(5):816-825.[11] Narita T, Shintani Y, Ikebe C, et al. The use of scaffold-free cell sheet technique to refine mesenchymal stromal cell-based therapy for heart failure. Mol Ther. 2013;21(4):860-867.[12] Tano N, Narita T, Kaneko M, et al. Epicardial placement of mesenchymal stromal cell-sheets for the treatment of ischemic cardiomyopathy; in vivo proof-of-concept study. Mol Ther. 2014;22(10):1864-1871.[13] Chen Y, Teng X, Chen W, et al. Timing of transplantation of autologous bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells for treating myocardial infarction. Sci China Life Sci. 2014;57(2): 195-200.[14] Chullikana A, Majumdar AS, Gottipamula S, et al. Randomized, double-blind, phase I/II study of intravenous allogeneic mesenchymal stromal cells in acute myocardial infarction. Cytotherapy. 2015;17(3):250-261. [15] Qu Z, Xu H, Tian Y, et al. Atorvastatin improves microenvironment to enhance the beneficial effects of BMSCs therapy in a rabbit model of acute myocardial infarction. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;32(2):380-389.[16] Wang F, Zhou H, Du Z, et al. Cytoprotective effect of melatonin against hypoxia/serum deprivation-induced cell death of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;748:157-65.[17] Liu XB, Wang JA, Ji XY, et al. Preconditioning of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by prolyl hydroxylase inhibition enhances cell survival and angiogenesis in vitro and after transplantation into the ischemic heart of rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(5):111.[18] 温倜,戚勋.生长因子可促进自体骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗急性心肌梗死[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(19):3017-3022.[19] Tang Y, Gan X, Cheheltani R, et al. Targeted delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor improves stem cell therapy in a rat myocardial infarction model. Nanomedicine. 2014; 10(8):1711-1718.[20] 周卢琨,曹文彬,姚剑峰,等.过表达Akt1 对小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞生物学功能的影响[J].生物医学工程与临床,2014,12(4): 380-385.[21] Chen XQ, Chen LL, Fan L, et al. Stem cells with FGF4-bFGF fused gene enhances the expression of bFGF and improves myocardial repair in rats Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;447(1):145-151.[22] Mao J, Lv Z, Zhuang Y. MicroRNA-23a is involved in tumor necrosis factor-α induced apoptosis in mesenchymal stem cells and myocardial infarction. Exp Mol Pathol. 2014;97(1):23-30.[23] Deng JH, Deng P, Lin SL, et al. Gene silencing in vitro and in vivo using intronic microRNAs. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1218: 321-340.[24] Starega-Roslan J, Koscianska E, Kozlowski P, et al. The role of the precursor structure in the biogenesis of microRNA. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011;68(17):2859-2871.[25] Kroh EM, Parkin RK, Mitchell PS, et al. Analysis of circulating microRNA biomarkers in plasma and serum using quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR). Methods. 2010;50(4): 298-301.[26] Fichtlscherer S, De Rosa S, Fox H, et al. Circulating microRNAs in patients with coronary artery disease. Circ Res. 2010;107(5):677-684.[27] Wang R, Li N, Zhang Y, et al. Circulating microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers of acute myocardial infarction. Intern Med. 2011;50(17):1789-1795.[28] Olivieri F, Antonicelli R, Lorenzi M, et al. Diagnostic potential of circulating miR-499-5p in elderly patients with acute non ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 2013;167(2): 531-536.[29] Meder B, Keller A, Vogel B, et al. MicroRNA signatures in total peripheral blood as novel biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction. Basic Res Cardiol. 2011;106(1):13-23.[30] Gidlöf O, Andersson P, van der Pals J, et al. Cardiospecific microRNA plasma levels correlate with troponin and cardiac function in patients with ST elevation myocardial infarction, are selectively dependent on renal elimination, and can be detected in urine samples. Cardiology. 2011;118(4):217-226.[31] Matsumoto S, Sakata Y, Nakatani D, et al. A subset of circulating microRNAs are predictive for cardiac death after discharge for acute myocardial infarction Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;427(2):280-284. |