| [1]Minguell JJ,Erices A,Conget P. Mesenchymal stem cells.Exp Biol Med. 2001;226(6):507-520.[2]费腾,阎作勤.激素性股骨头坏死发病机制的研究进展[J].中华关节外科杂志,2011,5(4):504-508.[3]中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30.[4]Polisetti N,Chaitanya VG,Babu PP,et al. Isolation, characterization and differentiation potential of rat bone marrow stromal cells. Neurol India. 2010;58(2):201-208.[5]李晓峰,赵劲民,苏伟,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的培养与鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,6(10):990-994.[6]童培建,肖鲁伟,季卫锋,等.脂质代谢及破骨细胞活性在激素性股骨头坏死塌陷发生过程中的作用研究[J].中国骨伤,2009,22(2): 110-113.[7]Murata M, Kumagai K, Miyata N, et al.Osteonecrosis in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats:effect of glucocorticoid.Orthop Sci. 2007;12(3):289-295.[8]肖春生,林娜,林诗富,等.不同糖皮质激素诱导鸡股骨头坏死的实验研究[J].中国骨伤,2010,23(3):184-187.[9]Gori F, Thomas T, Hicok KC, et al. Differentition of human marrow stromal precursor cells bone morphogenetic protein-2 increases OSF2/CBFAI,enhances osteoblasts commitment and inhibits late adipocyte maturation. Bone Miner Res. 1999; 14(9):1522-1535.[10]Ahdjoudj S, Lasmoles F, Oyajobi BO, et al.Reciprocal control of osteoblast chondroblast and osteoblast adipocyte differentiation of multipotential clonal human marrow stromal F/STRO-1(+)cells. J Cell Biochem. 2001;81(1):23.[11]Kentaro I,Yutaka O,Yasunoro K,et al. Effect of simvastatin on steroid-induced osteonecrosis evidenced by the serum lipid level and hepatic cytochrome P4503A in a rabbit model. J OrthopSci.2008;13:463-468. [12]Pritchett JW.Statin therapy decreases the risk of osteonecrosis in patients receiving steroids.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;38(6):173-178. [13]吴学建,尹万乐,李月白,等.乙醇对人骨髓间充质干细胞成脂转录因子γ和骨钙素mRNA表达的影响[J].郑州大学学报: 医学版,2006,41(6)1098-1100. [14]Herman MA,Wu M.Non canonical Wnt signaling pathways in Celegans converge on POP-1 / TCF and control cell polarity. Front Biosci. 2004;9:1530-1539.[15]Veeman MT,Axelrod JD,Moon RT.Functions and mechanisms of beta-catenin independent Wnt signaling. Dev Cell. 2003; 5(3):367-377.[16]Yang Y.Wnts and wing:Wnt signaling in vertebrate limb development and musculoskeletal morphogenesis. Birth Defects Res Part C EmbryoToday. 2003;69(4):305-317.[17]Cong F, Zhang J, Pao W, et al. A protein knockdown strategy to study the function of beta-catenin in tumorigenesis. BMC Mol Biol. 2003;4:10.[18]Kang S,Bennett CN,Gerin I,et al.Wnt signaling stimulates osteoblastogenesis of mesenchymal precursors by suppressing CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteinαand peroxisome rroliferator-activated receptorγ.J Biol Chem. 2007;282(19):14515-14524.[19]Jennifer AK, MacDougald OA. Wnt Signaling InhibitsAdipogenesis through β-Catenin dependent and independent Mechanisms. Biol Chemstry. 2005;280(25): 24004-24010.[20]Kanazawa A,Tsukada S, Kamiyama M, et al. Wnt5b partially inhibits canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and promotes adipogenesis in 3T3-LI preadipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;330(2):505-510.[21]Wright WS,Longo KA,Dolinsky VW,et al.Wntl0b inhibits obesity in ob/ob and agouti mice. Diabetes. 2007;56 (2): 295-303.[22]Christodoulides C,Laudes M,Cawthorn WP,et al.The Wnt antagonist Dickkopf-1 and its receptors are coordinately regulated during early human adipogenesis.Cell Sci. 2006; 119(12):2613-2620.[23]Barker N, Clevers H. Catenins, Wnt signaling and cancer. Bioessays. 2000;22 (11):961-965.[24]Kitagawa M, Hatakeyama S, Shirane M, et al. An F-box protein, FWD1, mediates ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis of beta-catenin. Embo J. 1999;18(9):2401-2410.[25]Zheng P,Ji G,Ma Z,et al. Therapeutic effect of puerarin on non-alcoholic rat fatty liver by improving leptin signal transduction throughJAK2/STAT3 pathways.Am J Chin Med. 2009;37(1):69-83.[26]Pan ZY,Bao ZS,Wu ZM,et al. The myocardial protective effects of puerarin on STZ-induced diabetic rats.Fen Zi Xi Bao Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2009;42(2):137-44.[27]Ajar M,Gilani AH,Mustafa MR.Effects of flavonoids onvascular smooth muscle of the isolated rat thoracic aorta.Life Sci. 2005; 74(5) :603-612. [28]Liu Q, Zhan LF, Li Z, et al. Effect of puerarin on thesmooth muscles of the vessels in rats and guineapigs. J Chin Med Univ. 2005;31(6):401-403.[29]王久亮,郑忠志,李灵芝,等.葛根素对大鼠成骨细胞增殖和分化的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(36):7138- 7141.[30]殷晓雪,陈仲强,党耕町.葛根素和淫羊藿甙对成骨细胞生物学作用的比较研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2007,22(3):210-212.[31]李灵芝,刘启斌,姜孟臣,等.葛根素对体外破骨细胞性骨吸收的影响[J].第三军医大学学报,2004,26(20):1830-1834.[32]董必晟,孙玉明,詹秀琴.蛋白免疫印迹杂交法研究葛根素对于促进成骨细胞OPG/RANKL蛋白表达的影响[J].吉林中医药,2012, 32(2):181-184.[33]高培国,强辉.葛根素对骨髓基质干细胞氧化损伤的保护作用[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2011,5(4):1141-1144.[34]齐振熙,张占勇,万甜,等.葛根素对激素诱导骨髓间充质干细胞PPARγmRNA和CEBPαmRNA表达的影响[J].福建中医药大学学报, 2013,23(2):21-24. [35]杨妍,于雅丽,杨春喜,等.葛根素抑制酒精导致人骨髓间充质干细胞的成脂分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009,13(32): 6388-6392. |
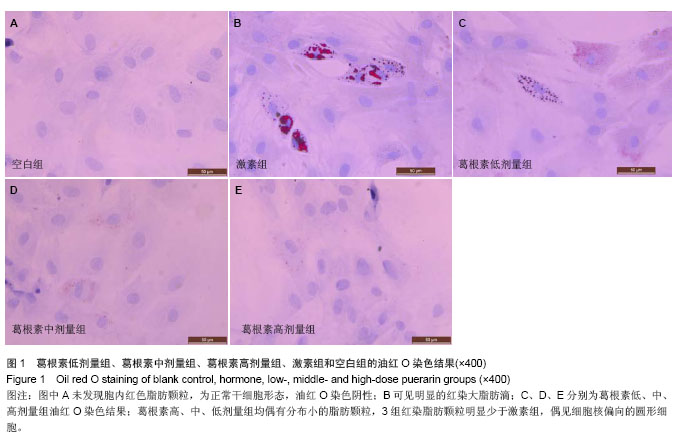
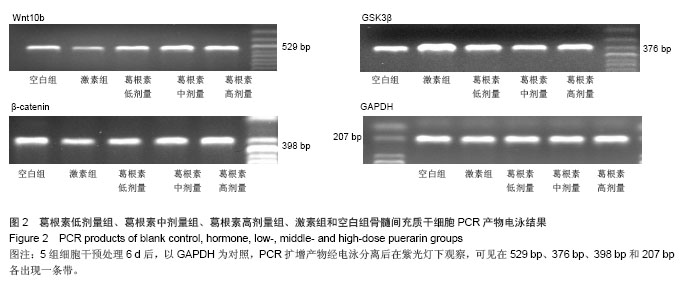
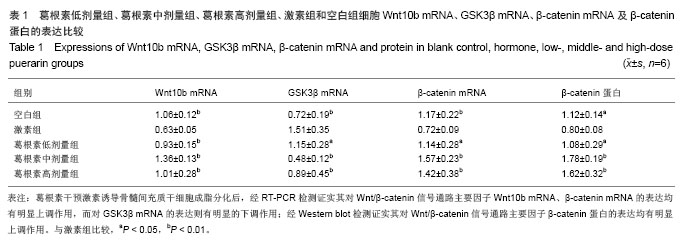
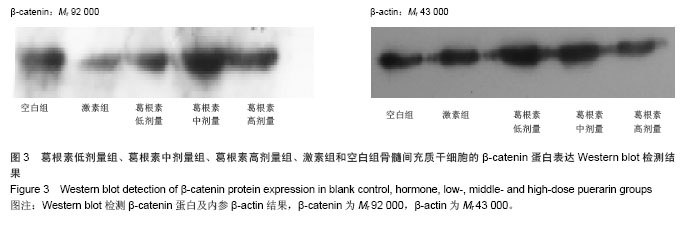
.jpg)