| [1]Erices A,Conget P,Minguell JJ.Mesenchymal progenitor cell in human umbilical cord blood.Br J Haematol.2000;109(1): 235-242.[2]Bassett CA, Pilla AA, Pawluk RJ.A non-operative salvage of surgically-resisitant pseudarthroses and non-unions by pulsing electromagnetic fields. A preliminary report Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1977;(124):128-143.[3]Basset CA, pawlik RJ, Pilla AA.Augmentation of bone repair by inductively coupled electromagnetic fields. Science. 1974; 184(4136):575-577.[4]Gulotta LV, Kovacevic D, Packer JD, et al. Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Transduced With Scleraxis Improve Rotator Cuff Healing in a Rat Model. Am J Sports Med. 2011 Feb 18.[5]Javazon EH, Colter DC, Schwarz EJ, et al. Rat marrow stromal cells are more sensitive to plating density and expand more rapidly from single-cell-derived colonies than human marrow stromal cells. Stem Cells. 2001;19(3):219-225.[6]Minguell JJ,Erices A,Congetp.Mesenchymal stem Cell.Exp Biol Med.2001;226(6):507-526.[7]Trivedi HL,Vanilar AV,Thakker U,et al.Human Adipose Tissue-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Combined with Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplation Synthesize Insulin. Transplat Proc.2008;40(4):1135-1139.[8]Yagi K,Kojima M,Oyagi S,et al.Application of Mesenchmal Stem Cell to Liver Regenerative Medicine. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2008;128(1):3-9. [9]Sato K,Ozaki K,OH I,et,al.Nitric Oxide Plays a Critical Role in Suppression of T-cell Proliferation by Mesenchymal Stem Cell. Blood. 2007;109(1):228-234.[10]Blazra BR,Taylor PA.Regulatiory T cells.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant.2005;11(2Sup12):46-49.[11]Tang J, Wang J, Guo L,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells modified with stromal cell-derived factor 1 alpha improve cardiac remodeling via paracrine activation of hepatocyte growth factor in a rat model of myocardial infarction.Mol Cells.2010;29(1):9-19.[12]Jeong WK, Park SW, Im GI. Growth factors reduce the suppression of proliferation and osteogenic ifferentiation by titanium particles on MSCs.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008; 86(4):1137-1144.[13]Ebra S,Nadayama K. Mechanism for the action of bone morphogenetic proteins and regulation of their activity. Spine.2002;27(16 suppl 1): 10-15.[14]Bhatia M,Shokui S.Inflammatory Mediators in Acute Pancreatitis.Pathol.J Pathol.2000;190(2):117-125. [15]刘震,程若川,方向,等. PAAF与ASPAAF诱导的肠损伤比较的实验研究[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2008,15(8):555-559.[16]Boer HH, Schot LP, Veenstra JA, et al. Immunocytochemical identification of neural elements in the central nervous systems of a snail, some insects, a fish, and a mammal with an antiserum to the molluscan cardio-excitatory tetrapeptide FMRF-amide. Cell Tissue Res.1980;213(1): 21-27.[17]Bock J,Liebisch G,Schweimer J,et al.Exogenous Sphingo2 Myelinase Causes Impaired Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function. World Gastroenterol.2007;13(39):5217-5225.[18]Zhang XP,Chen L,Hu QF,et al.Effects of Large Dose of Dexamethasone on Inflammatory Mediators and Pancreatic Cell Apoptosis of Rats with Severe Acute Pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13(41):5506-5511[19]Tsutsui K, Bentley GE, Kriegsfeld LJ,et al. Vaudry Discovery and evolutionary history of gonadotrophin-inhibitory hormone and kisspeptin: new key neuropeptides controlling reproduction. J Neuroendocrinol. 2010;22(7):716-727.[20]Chartrel N, Dujardin C, Leprince J,et al. Isolation, characterization, and distribution of a novel neuropeptide, Rana RFamide (R-RFa), in the brain of the European green frog Rana esculenta. J Comp Neurol. 2002;448(2):111-127. [21]Takayasu S, Sakurai T, Teranishi H ,et al.A neuropeptide ligand of the G protein-coupled receptor GPR103 regulates feeding,behavior arousal,and blood pressure in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(19):7438-7443.[22]Linacre A, Kellett E, Saunders S, et al. Burke Cardioactive neuropeptide Phe-Met-Arg-Phe-NH2 (FMRFamide) and novel related peptides are encoded in multiple copies by a single gene in the snail Lymnaea stagnalis.J Neurosci. 1990;10(2): 412-419.[23]Fukusumi S, Yoshida H, Fujii R, et al. A new peptidic ligand and its receptor regulating adremal fuction in rats. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(47):46387-46395. [24]Tobari Y, Iijima N, Tsunekawa K, et al.Identification, localisation and functional implication of 26RFa orthologue peptide in the brain of zebra finch (Taeniopygia guttata). J Neuroendocrinol. 2011;23(9):791-803.[25]Liu Y, Zhang Y, Li S, et al. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of the first non-mammalian 26RFa/QRFP orthologue in Goldfish, Carassius auratus. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2009;303(1-2):82-90. [26]Yang HY, Tang J, Iadarola M, et al. Are Phe-Met-Arg-Phe-NH2 immunoreactive peptides endacoids modulating opiate antinociception? Prog Clin Biol Res. 1985; 192:313-322. [27]Fukusumi S, Habata Y, Yoshida H,et al. Characteristics and distribution of endogenous RFamide-related peptide-1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001;1540(3):221-232. [28]Chartrel N, Alonzeau J, Alexandre D, et al. Llorens-Cortes The RFamide neuropeptide 26RFa and its role in the control of neuroendocrine functions Front. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2011;32(4):387-397.[29]Baribault H, Danao J, Gupte J, et al.The G-protein-coupled receptor GPR103 regulates bone formation. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26(2):709-717.[30]Ohtaki T, Shintani Y, Honda S,et al. Metastasis suppressor gene KiSS-1 encodes peptide ligand of a G-protein-coupled receptor.Nature.2001;411(6837): 613-617.[31]Bruzzone F, Lectez B, Alexandre D,et al. Distribution of 26RFa binding sites and GPR103 mRNA in the central nervous system of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 2007;503(4): 573-591. [32]Zhang Q, Qiu P, Arreaza MG, et al. P518/Qrfp sequence polymorphisms in SAMP6 osteopenic mouse. Genomics. 2007; 90(5):629-35[33]王琳琳,董为人,朱衍菲,等.脂肪源性干细胞向心肌细胞分化及其移植治疗心血管疾病[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(14):2648-2652.[34]Nakamichi I, Toivola DM, Strnad P, et al. Keratin 8 overexpression promotes mouse Mallory body formation. J Cell Biol. 2005;171(6):931-937.[35]Ukena K, Tachibana T, Iwakoshi-Ukena E,et al. Identification, localization, and function of a novel avian hypothalamic neuropeptide, 26RFa, and its cognate receptor, G protein-coupled receptor-103. Endocrinology. 2010;151(5): 2255-2264.[36]Casado-Díaz A, Santiago-Mora R, Jiménez R,et al. Cryopreserved human bone marrow mononuclear cells as a source of mesenchymal stromal cells: application in osteoporosis research. Cytotherapy. 2008;10(5):460-468.[37]Matsumoto T,Kuroda R,Mifune Y,et al.Circulating endothelial/skeletal progenitor cells for bone regeneration and healing. Bone.2008;43(3):434-439.[38]Lippens E, Cornelissen M.Slow Cooling Cryopreservation of Cell-Microcarrier Constructs. Cells Tissues Organs. 2010. [Epub ahead of print] [39]Zajac JM, Mollereau C.RFamide peptides.Introduction. Peptides. 2006; 27(5):941-942.[40]Bechtold DA, Luckman SM. The role of RFamide peptides in feeding. J Endocrinol. 2007;192(1):3-15.[41]Jiang Y, Luo L, Gustafson EL, et al.Identification and characterization of a novel RF-amide pepfide ligand for orphan G-protein-coupled receptor SP9155. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(30):27652-27657.[42]Mulumba M, Jossart C, Granata R, et al. GPR103b functions in the peripheral regulation of adipogenesis. Mol Endocrinol. 2010 ;24(8):1615-1625. [43]Chartrel N, Dujardin C, Anouar Y,et al. Identification of 26RFa, a hypothalamic neuropeptide of the RFamide peptide family with orexigenic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2003; 100(25): 15247-15252.[44]Bruzzone F, Lectez B, Tollemer H,et al.Anatomical distribution and biochemical characterization of the novel RFamide peptide 26RFa in the human hypothalamus and spinal cord.J Neurochem. 2006;99(2):616-627. |
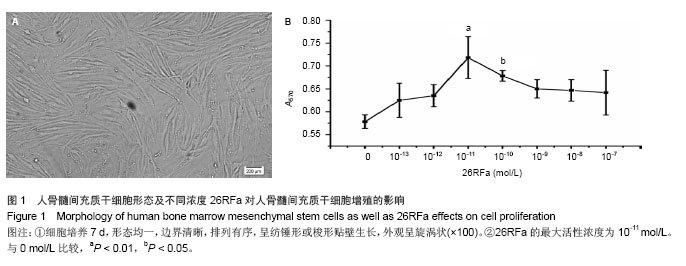
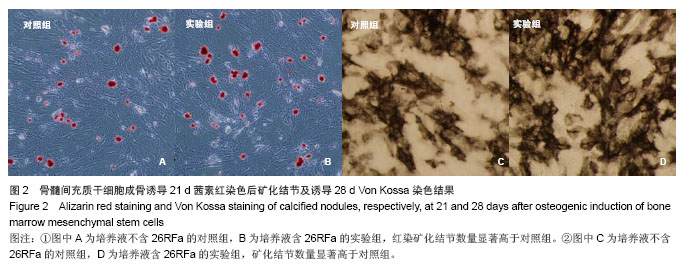
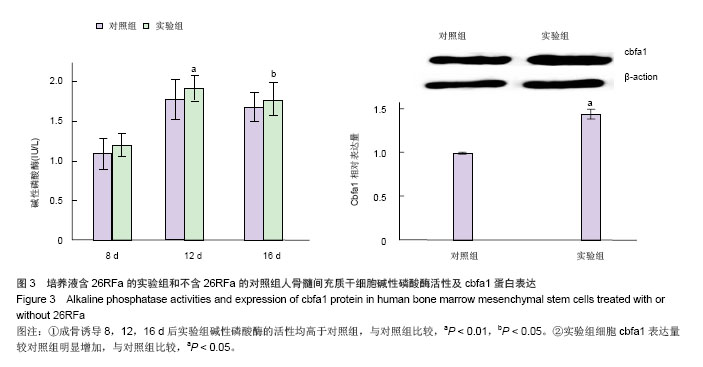
.jpg)