中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (19): 2976-2981.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3532
• 脂肪干细胞 adipose-derived stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
人髌下脂肪垫干细胞的鉴定及成软骨分化
李聪聪1,2,姚 楠1,2,3,黄丹娥1,2,3,宋 敏1,2,彭 莎1,2,3,李安安1,2,卢 超2,刘文刚1,2
- 1广州中医药大学第五临床医学院,广东省广州市 510095;2广东省第二中医院(广东省中医药工程技术研究院),广东省广州市 510095;3广东省中医药研究开发重点实验室,广东省广州市 510095
Identification and chondrogenic differentiation of human infrapatellar fat pad derived stem cells
Li Congcong1, 2, Yao Nan1, 2, 3, Huang Dane1, 2, 3, Song Min1, 2, Peng Sha1, 2, 3, Li Anan1, 2, Lu Chao2, Liu Wengang1, 2
- 1The Fifth Clinical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510095, Guangdong Province, China; 2Guangdong Second Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital (Guangdong Province Engineering Technology Research Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine), Guangzhou 510095, Guangdong Province, China; 3Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Research and Development in Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510095, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
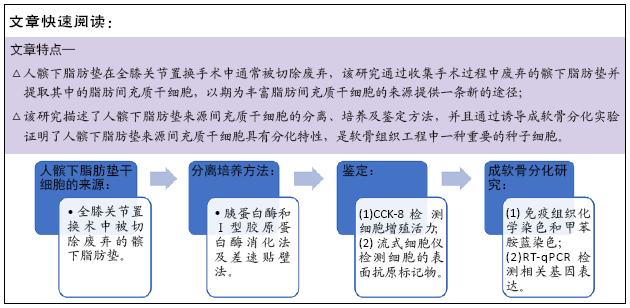
髌下脂肪垫干细胞:髌下脂肪垫干细胞具有向软骨细胞、成骨细胞、脂肪细胞、肌细胞及内皮细胞等细胞定向分化的能力,且其增殖能力、分化能力强和免疫应答能力弱,是很有临床运用前景的种子细胞,必将在软骨组织工程等多个领域发挥重要作用。
软骨:软骨细胞是关节软骨中唯一的细胞形式,关节软骨主要由软骨细胞(约占软骨组织的5%)和软骨细胞外基质(约占软骨组织的95%)组成,软骨细胞分泌的物质往往具有合成或分解软骨细胞外基质的功能。骨关节炎的主要病理改变是关节软骨的退变和损伤,由于缺乏神经分布和血管供应,软骨一旦损伤将很难自我修复。
背景:人髌下脂肪垫是在全膝关节置换手术中经常被切除的废弃物,如果充分加以利用可以作为间充质干细胞的主要来源用于软骨组织工程。
目的:探索人髌下脂肪垫干细胞体外分离、培养及鉴定方法,并在特定条件下诱导其成软骨分化,探讨其作为软骨组织工程种子细胞的可行性。
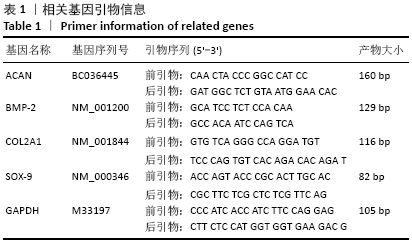
方法:获取8例人工膝关节置换术患者废弃的髌下脂肪垫,综合运用胰蛋白酶和Ⅰ型胶原蛋白酶消化法及差速贴壁法分离培养人髌下脂肪垫干细胞,体外培养至第3代后进行细胞形态学观察、细胞生长曲线以及细胞表面抗原分析,然后进行成软骨诱导分化,通过免疫组化和甲苯胺蓝染色以及RT-qPCR方法对人髌下脂肪垫干细胞成软骨分化能力进行鉴定。
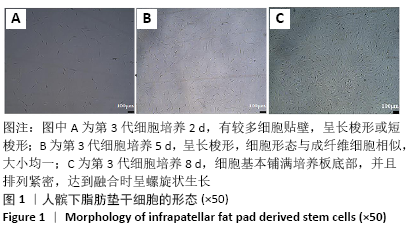
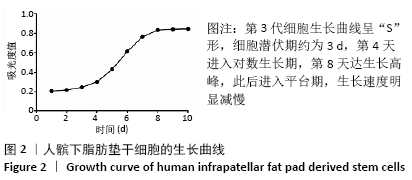
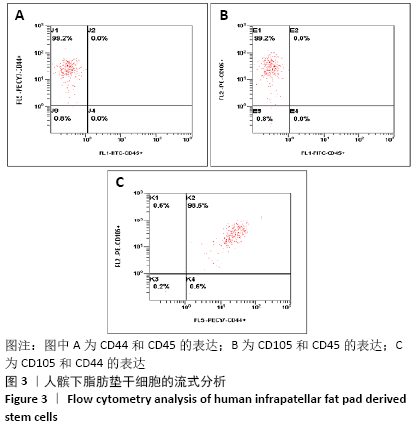
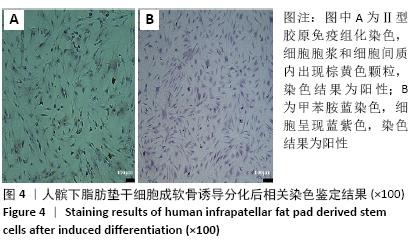
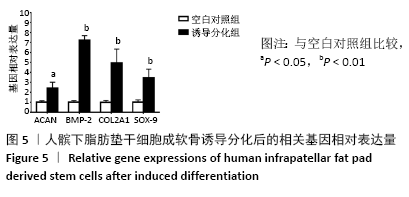
结果与结论:①分离纯化及培养出的人髌下脂肪垫干细胞呈梭形贴壁生长,第3代细胞生长曲线呈“S”形,CD44、CD105呈阳性表达,而CD45呈阴性表达;②成软骨诱导14 d后,诱导分化组免疫组织化学染色和甲苯胺蓝染色均呈阳性,并且ACAN、BMP-2、COL2A1和SOX-9的基因相对表达量明显高于空白对照组;③该研究证实了从髌下脂肪垫中可分离出具有分化潜能的间充质干细胞,其具有较强的体外增殖能力以及成软骨分化能力,有望成为软骨组织工程理想的种子细胞。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9678-1440(李聪聪);https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8887-8429(刘文刚)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: