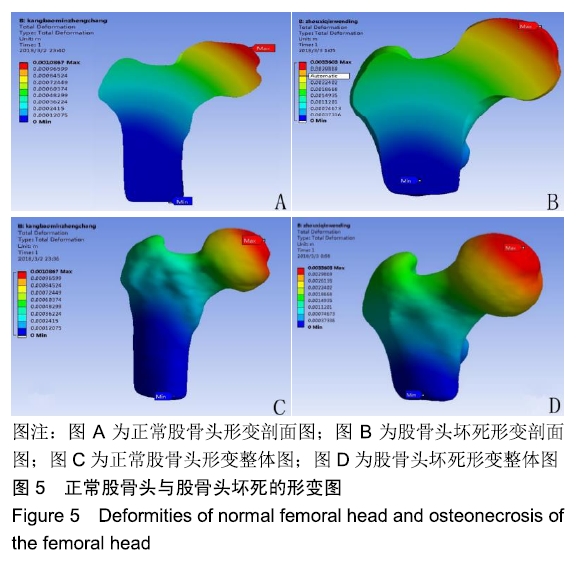
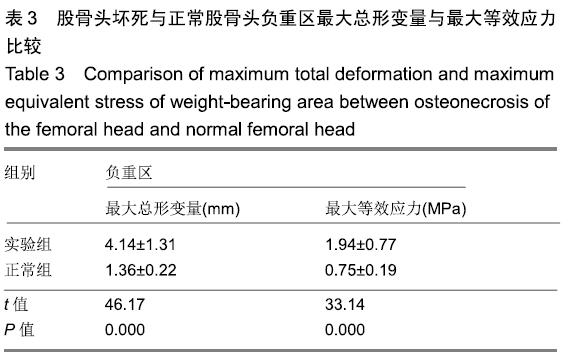
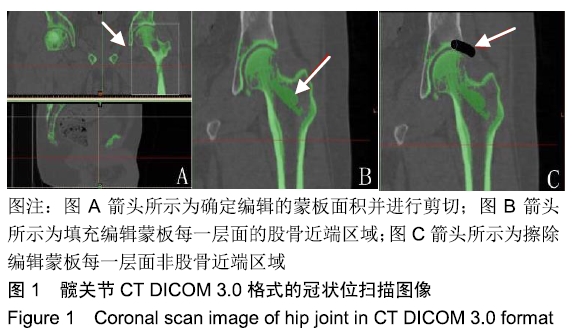
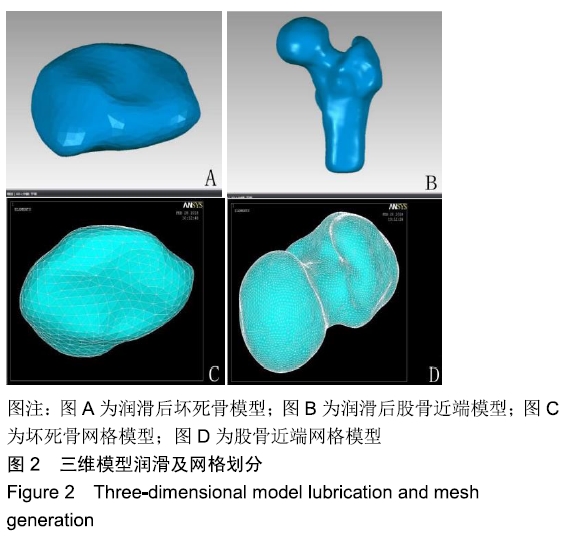
[1] LESPASIO MJ, SODHI N, MONT MA. steonecrosis of the Hip: A Primer.Perm J. 2019;23. pii: 18-100.
[2] 李子荣.股骨头坏死:早期诊断与个体化治疗[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(19):1909-1911.
[3] 叶奕亨,陈凯,金可可,等.塌陷前期股骨头坏死的保头手术治疗的进展[J].中国骨伤,2017,30(3): 287-292.
[4] 中国医师协会骨科医师分会显微修复工作委员会,中国修复重建外科专业委员会骨缺损及骨坏死学组,中华医学会骨科分会显微修复学组.成人股骨头坏死临床诊疗指南(2016)[J].中华骨科杂志,2016, 36(15):945-954.
[5] MOTOMURA G, YAMAMOTO T, YAMAGUCHI R, et al. Morphological analysis of collapsed regions in osteonecrosis of the femoral head.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2011;93-B(2):184-187.
[6] KARASUYAMA K, YAMAMOTO T, MOTOMURA G, et al. The role of sclerotic changes in the starting mechanisms of collapse: a histomorphometric and FEM study on the femoral head of osteonecrosis. Bone.2015;81:644-648.
[7] BROWN TD, PEDERSEN DR, BAKER KJ, et al. Mechanical consequences of core drilling and bone-grafting on osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1993;75(9):1358.
[8] 何海军,陈卫衡,鲁超,等.基于CT图像建立可供动态力学模拟分析的股骨头坏死有限元模型[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2016, 24(9):5-10.
[9] 谢亮文.不同属性建模方法对股骨近端有限元分析影响的研究[D].福州:福建医科大学,2015. .
[10] 杨宾宾,刘耀升,刘蜀彬,等.多种髓芯减压术治疗股骨头坏死的有限元研究[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2017,12(1):39-45.
[11] MONT MA, HUNGERFORD DS. Non-tranmatie avascular necrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg(Am).1995; 77:459.
[12] GARDENIERS JWM.The ARCO perspective for reaching one uniform staging system of osteonecrosis//Bone circulation and vascularization in normal and pathological conditions. Springer,Boston,MA,1993:375-380.
[13] TANG Q, HE HJ, CHEN WH, et al. Mechanical evaluation of osteonecrosis of femoral head preand post-medical treatment: patient-specific computations.Neuroscience and Biomedical Engineering.2017;5(2):94-100.
[14] YUE Y, YANG H, LI Y, et al. Combining ultrasonic and computed tomography scanning to characterize mechanical properties of cancellous bone in necrotic human femoral heads. Med Eng Phys.2019;66:12-17.
[15] PENG L, BAI J, ZENG X, et al. Comparison of isotropic and orthotropic material property assignments on femoral finite element models under two loading conditions. Med Eng Phys. 2006;28(3):227-233.
[16] RHO JY, HOBATHO MC, ASHMAN RB. Relations of mechanical properties to density and CT numbers in human bone. Med Eng Phys.1995;17(5):347-355.
[17] BROWN TD, WAY ME, FERGUSON AB JR. Mechanical characteristics of bone in femoral capital aseptic necrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1981;(156):240-247.
[18] LI B, HU R, SUN L, et al. A CARE-compliant article: Biomechanics of treating early-stage femoral-head osteonecrosis by using a β-tricalcium phosphate bioceramic rod system: a 3-dimensional finite-element analysis. Medicine (Baltimore).2018;97(25):e10808.
[19] READ L, NIGG BM. An analysis of hip joint loading during walking, running, and skiing. Med Sci Sports Exerc.1999; 31(1):131-142.
[20] 李子荣.晚期股骨头坏死人工关节置换术的选择[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版)[J].2008.2(1):51-52.
[21] ÜNAL MB, CANSU E, PARMAKSIZOĞLU F, et al. Treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head with free vascularized fibular grafting: results of 7.6-year follow-up. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2016;50(5):501-506.
[22] KIM YM, LEE SH, LEE FY, et al. Morphologic and biomechanical study of avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Orthopedics.1991;14(10):1111-1116.
[23] BROWN TD, BAKER KJ, BRAND RA. Structural consequences of subchondral bone involvement in segmental osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Orthop Res.1992;10(1): 79-87.
[24] SHI J, CHEN J, WU J, et al. Evaluation of the 3D finite element method using a tantalum rod for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Med Sci Monit.2014;20:2556-2564.
[25] 庞智晖,魏秋实,周广全,等.个体股骨头坏死三维有限元模型的建立与应用[J].生物医学工程学杂志. 2012(2):251-255.
[26] 张海峰,宋翠荣,庞胤,等.基于CT数据建立髋关节三维有限元模型的研究[J].中国临床医学影像杂志, 2015,26(9):667-670.
[27] 彭军,胡冬发,邓立柳,等.股骨头坏死钽棒支撑植入术模拟及有限元模型的建立[J].中国数字医学,2014,9(4):66-68.
[28] TAYLOR WR, ROLAND E, PLOEG H, et al. Determination of orthotropic bone elastic constants using FEA and modal analysis. J Biomech.2002;35(6):767-773.
[29] 杨立峰,肖东民,彭春雷,等.自制股骨头内撑器治疗早期股骨头坏死的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(7):1096-1101.
[30] 李孝林,吕志鹏,刘迎军.股骨头坏死有限元模型的建立[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(30): 5522-5525.
[31] CHEN L, HONG G, FANG B, et al. Predicting the collapse of the femoral head due to osteonecrosis: From basic methods to application prospects. J Orthop Translat.2017;11:62-72.
[32] KNAPIK JJ, REYNOLDS K, HOEDEBECKE KL. Stress Fractures: Etiology, Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention. J Spec Oper Med. Summer.2017;17(2):120-130.
[33] MALEKIPOUR F, OETOMO D, LEE PV. Equine subchondral bone failure threshold under impact compression applied through articular cartilage. J Biomech. 2016;49(10): 2053-2059.
[34] ESCUDIER JC, OLLIVIER M, DONNEZ M, et al. Superimposition of maximal stress and necrosis areas at the top of the femoral head in hip aseptic osteonecrosis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2018;104(3):353-358.
[35] MEDIOUNI M, SCHLATTERER DR, KHOURY A, et al. Optimal parameters to avoid thermal necrosis during bone drilling: A finite element analysis. J Orthop Res.2017;35(11): 2386-2391.
[36] 史风雷,张美超.建立股骨头坏死有限元模型的方法[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(30):5890-5891.
[37] BAE JY, KWAK DS, PARK KS, et al. Finite element analysis of the multiple drilling technique for early osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Ann Biomed Eng. 2013;41(12):2528-2537.
[38] 袁高翔,张伟滨.有限元分析在骨骼肌肉系统模型材料特性研究中的应用[J].国际骨科学杂志,2011, 32(6):352-355+366.
[39] 冀勇,胡永成,张春秋,等.股骨近端骨干组配式假体在下蹲步态下的三维有限元分析[J].天津理工大学学报,2018,34(3):12-16.
[40] 刘欣伟,闫寒,刘中洋,等.包含肌肉、韧带组织的骨盆、髋臼3D有限元模型的构建[J].临床军医杂志, 2014,42(4):331-335.
[41] 李泰贤. 健脾活骨方治疗非创伤性股骨头坏死生物力学机理与塌陷危险因素分析[D].北京:中国中医科学院,2018.
|