| [1] Ku KC, Lee MW, Kuo SM, et al. Preparation and evaluation of collagen I/ gellan gum/beta-TCP microspheres as bone graft substitute materials. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2013; 2013:6667-6770.[2] Temple JP, Hutton DL, Hung BP,et al. Engineering anatomically shaped vascularized bone grafts with hASCs and 3D-printed PCL scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A.2014; 102(12):4317-4325.[3] 王雪莹. 3D打印技术与产业的发展及前景分析[J].中国高新技术企业,2012,26:3-5.[4] Leong KF, Cheah CM, Chua CK. Solid freeform fabrication of three-dimensional scaffolds for engineering replacement tissues and organs. Biomaterials.2003;24(13):2363-2378.[5] 王镓垠.人体器官3D打印的最新进展[J]. 机械工程学报,2014, 50(23):119-127.[6] Cox SC, Thornby JA, Gibbons GJ, et al. 3D printing of porous hydroxyapatite scaffolds intended for use in bone tissue engineering applications. Mater Sci Eng:C,2015;47: 237-247.[7] Seol YJ, Kang TY, Cho DW.Solid freeform fabrication technology applied to tissue engineering with various biomaterials. Soft Matter.2012;8(6):1730-1735.[8] 田冶,曾庆慧,胡相华,等. 3D打印技术及在组织工程领域的研究进展[J].中国医疗器械信息,2015,21(8):7-12.[9] Jansen J, Melchels FP, Grijpma DW, et al. Fumaric acid monoethyl ester-functionalized poly(D,L-lactide)/N-vinyl-2 -pyrrolidone resins for the preparation of tissue engineering scaffolds by stereolithography. Biomacromolecules.2009;10(2):214-220.[10] Matsuo A,Chiba H,Takahashi H,et al.Clinical application of a custom-made bioresorbable raw particulate hydroxyapatite/poly-L-lactide mesh tray for mandibular reconstruction. Odontology. 2010;98(1):85-88.[11] 王宁,李杰,王晓龙,等. 应用3D打印熔融沉积技术制作个性化种植修复体的精确度研究[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2015,33(5): 509-512.[12] Hoy MB. 3D printing: making things at the library.Med Ref Serv Q.2013,32(1): 94-99.[13] Tarafder S, Balla VK, Davies NM, et al. Microwave-sintered 3D printed tricalcium phosphate scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2013;7(8):631-641.[14] Cui X, Boland T, D'Lima DD, et al. Thermal inkjet printing in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul.2012;6(2):149-155.[15] Yao Q, Wei B, Guo Y, et al.Design, construction and mechanical testing of digital 3D anatomical data-based PCL-HA bone tissue engineering scaffold. J Mater Sci Mater Med.2015;26(1):5360.[16] Hollister SJ.Scaffold Design and Manufacturing: From Concept to Clinic.Adv Mater.2009;21(32-33):3330-3342.[17] Yang S, Leong KF, Du Z, et al.The design of scaffolds for use in tissue engineering. Part I. Traditional factors.Tissue Eng. 2001;7(6):679-689. [18] Guarino V, Ambrosio L.Temperature-driven processing techniques for manufacturing fully interconnected porous scaffolds in bone tissue engineering. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2010;224(12):1389-1400.[19] Jang JH, Castano O, Kim HW. Electrospun materials as potential platforms for bone tissue engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2009;61(12):1065-1083.[20] 廖南,邓金杨,陈殷曹.复合喷射低温沉积快速成形工艺制备包芯骨组织工程仿生复合支架[J].新疆医科大学学报,2012,35(6):755-761.[21] Gomez S, Vlad MD, Lopez J, et al. Design and properties of 3D scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomaterialia. 2016;42:341-350.[22] Luo Y, Zhai D, Huan Z, et al.Three-Dimensional Printing of Hollow-Struts-Packed Bioceramic Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(43): 24377-24383.[23] Butscher A, Bohner M, Hofmann S, et al.Structural and material approaches to bone tissue engineering in powder-based three-dimensional printing. Acta biomateri. 2011;7(3):907-920.[24] Farzadi A, Solati-Hashjin M, Asadi-Eydivand M, et al. Effect of layer thickness and printing orientation on mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy of 3D printed porous samples for bone tissue engineering. PloS one.2014;9(9): e108252.[25] Khalyfa A, Vogt S, Weisser J, et al. Development of a new calcium phosphate powder-binder system for the 3D printing of patient specific implants. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2007; 18(5):909-916.[26] Lee SJ, Lee D, Yoon TR, et al. Surface modification of 3D-printed porous scaffolds via mussel-inspired polydopamine and effective immobilization of rhBMP-2 to promote osteogenic differentiation for bone tissue engineering.Acta biomater. 2016;40:182-191.[27] Kim SS, Sun Park M, Jeon O, et al. Poly(lactide-co-glycolide)/ hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials.2006;27(8):1399-409.[28] Cavo M, Scaglione S. Scaffold microstructure effects on functional and mechanical performance: Integration of theoretical and experimental approaches for bone tissue engineering applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;68:872-879.[29] 张帆. 新型纳米金刚石-PLGA可吸收复合材料3D打印制备颈椎间融合器的研究[D]. 第二军医大学,2015.[30] Wang X, Schroder HC, Feng Q, et al. The deep-sea natural products, biogenic polyphosphate (Bio-PolyP) and biogenic silica (Bio-Silica), as biomimetic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: fabrication of a morphogenetically-active polymer. Marine drugs.2013;11(3):718-46.[31] 林山,黄晓梅,芮钢,等.数字化珊瑚羟基磷灰石人工骨支架的体外降解性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(3):330-5.[32] 张海峰,杜子婧,毛曦媛,等. 3D打印PLA-HA复合材料构建组织工程骨的实验研究[J].国际骨科学杂志,2016,37(1):57-63.[33] 赖毓霄,李龙,李烨,等.基于新型3D打印技术的复合活性多孔骨修复支架的研发[C]. 2015年全国高分子学术论文报告会,苏州: 2015.[34] 邓伟,金格勒,杨毅,等.复合喷射低温沉积快速成形工艺制备包芯骨组织工程仿生复合支架[J].新疆医科大学学报,2012,35(6): 755-761.[35] Barabaschi GD, Manoharan V, Li Q, et al. Engineering Pre-vascularized Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration.Adv Exp Med Biol.2015;881:79-94.[36] Bose S, Tarafder S, Bandyopadhyay A. Effect of Chemistry on Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis Towards Bone Tissue Engineering Using 3D Printed Scaffolds. Ann Biomed Eng. 2017;45(1):261-272. |
.jpg)
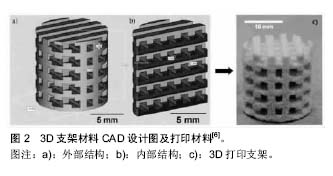
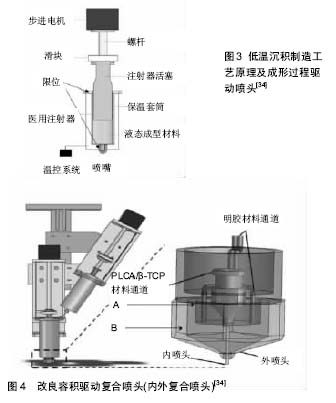

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)