1.1 设计 支架制备、表征和细胞学实验,单因素方差分析。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2017年3月至2018年2月在广州中医药大学完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 支架材料 聚羟基丁酸戊酸共聚酯(Y1000P,宁波天安生物材料有限公司,中国);半水硫酸钙(实验室自制);壳聚糖(脱乙酰度:75%-85%;分子质量:50-190 kD;黏度:20–300 cP,Sigma公司,美国)。
1.3.2 主要仪器和试剂 3D打印机(Prusa i3,广东机电职业技术学院,中国);双螺杆挤出机(SHJ-30,南京杰思特机电公司,中国);微型注射机(SZS-15,武汉瑞鸣塑料机械制造公司,中国);电热恒温鼓风干燥箱(DHG-9146A,上海精宏实验设备有限公司,中国);超净工作台(JSM-IT300,苏州安泰空气技术有限公司,中国);超净工作台(细菌实验用) (SW-CJ-1F,苏州安泰空气技术有限公司,中国);倒置相差显微镜(CKX31,Olympus公司,日本);CO2恒温培养箱(Forma-3111,Thermo Scientific公司,美国);台式离心机(4200,KUBOTA公司,日本);多动能酶标仪(Multiskan GO,Thermo Scientific公司,美国);生化培养箱(LRH-150B,广东省医疗器械厂,中国);回旋式气浴恒温振荡器(ZD-85A,科析仪器公司,中国);低温制冷微生物BOD种发芽箱(SPX-70BE,广东省医疗器械厂,中国);高分辨扫描电子显微镜(JSM-IT300,尼康公司,日本);CCK-8试剂盒(同仁公司,日本);LB培养基(广东环凯生物科技有限公司,中国);营养琼脂(广东环凯生物科技有限公司,中国);成骨诱导液(赛业生物科技有限公司,美国)。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 制备聚羟基丁酸戊酸共聚酯/半水硫酸钙复合材料 根据实验室前期制备方法[19],通过水热-盐溶液法制备半水硫酸钙,随后将聚羟基丁酸戊酸共聚酯颗粒在真空炉中干燥,并与所制备的半水硫酸钙混合(其中半水硫酸钙用量分别为聚羟基丁酸戊酸共聚酯用量的0%和20%)。熔融共混后,形成标准的聚羟基丁酸戊酸共聚酯/半水硫酸钙复合材料,利用双螺杆挤出机制备成标准直径为1.75 mm的3D打印丝。
1.4.2 制备聚羟基丁酸戊酸共聚酯/半水硫酸钙和PHBV/CSH/CS支架 通过熔融沉积成型技术制备聚羟基丁酸戊酸共聚酯/半水硫酸钙多孔支架,所用3D打印机如图1A所示。首先使用SolidWorks(Dassault Systemes S.A)设计软件,设计一个直径为10 mm、高度为5 mm、3D打印丝的直径为400 μm且丝间距为400 μm的三维圆柱体支架,如图1B所示,3D打印聚羟基丁酸戊酸共聚酯/半水硫酸钙支架参数设置:喷追尺寸0.4 mm,层高0.32 mm,填充率50%,填充图案为直线,外圈圈数为3,打印速度30 mm/s,首层打印速度25 mm/s,喷头温度200 ℃及热床温度50 ℃,根据预设参数对聚羟基丁酸戊酸共聚酯/半水硫酸钙支架进行3D打印直至支架实体成型,如图1C所示。
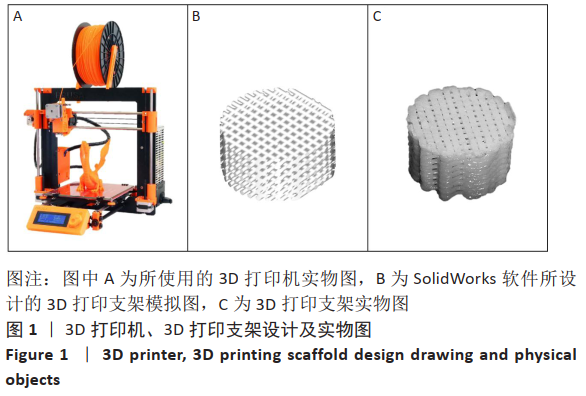
为了制造PHBV/CSH/CS支架,将已制备成型的聚羟基丁酸戊酸共聚酯/半水硫酸钙支架泡在壳聚糖溶液中(壳聚糖浓度3%,乙酸浓度1.5%)1 h,随后将支架放入烘箱37 ℃烘干,使得壳聚糖充分涂覆在支架上。随后将支架放入超纯水中,此时壳聚糖水凝胶形成并复合在支架上,制备得PHBV/CSH/CS支架。然后将该支架浸入5% NaOH溶液中30 min,以中和乙酸酸性,并使用超纯水反复冲洗支架3次以备用。
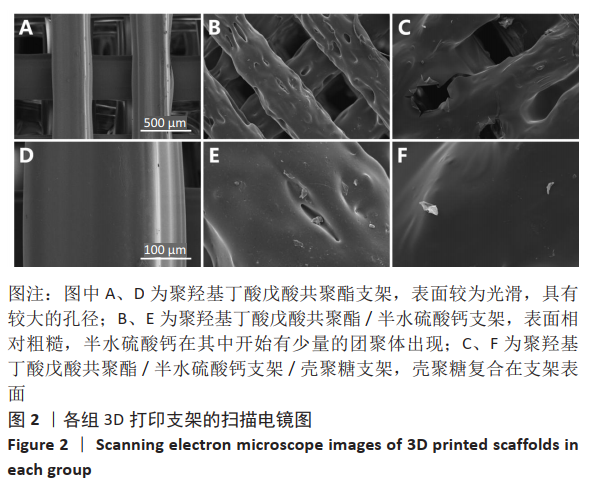
1.4.3 支架表面形貌与多孔结构 各组支架在真空下干燥、喷金后,利用用扫描电镜评估支架的表面形态和孔径。同时利用Micro CT对支架进行观察和评估。
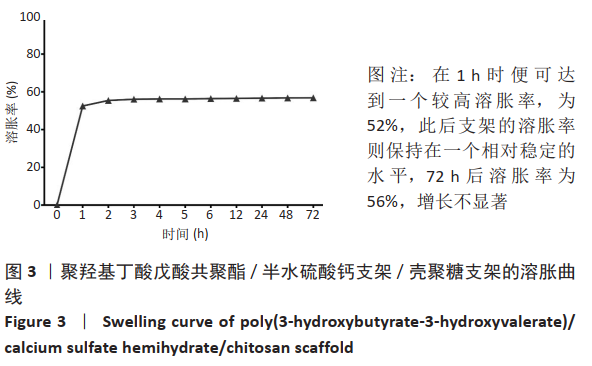
1.4.4 PHBV/CSH/CS支架的溶胀行为检测 将PHBV/CSH/CS支架浸入PBS中,分别于1,2,3,4,5,6, 12,24,72 h将支架取出,用干燥滤纸吸干PHBV/CSH/CS支架表面水分,然后称取其质量,直至PHBV/CSH/CS支架质量不再变化,共设置3个平行样。然后利用公式(1)计算溶胀率:
溶胀率(SR)= (mt-ms)/ms × 100% (1)
公式(1)中,SR为平衡溶胀率,ms为干燥时PHBV/CSH/CS支架的质量,mt为溶胀时PHBV/CSH/CS支架的质量。
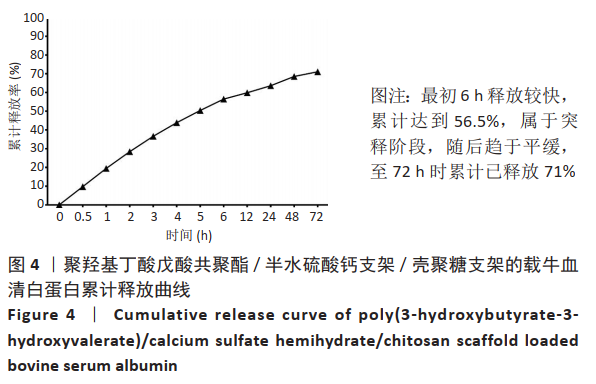
1.4.5 PHBV/CSH/CS支架的载药及释放性能
标准曲线绘制:使用牛血清白蛋白作为模拟载药药物,配置质量浓度为 1 g/L的牛血清白蛋白溶液,取梯度稀释后的牛血清白蛋白溶液50 µL加入96孔板,再加入 200 µL的蛋白定量分析牛血清白蛋白液,随后放入细胞培养箱孵育30 min,并于酶标仪 562 nm处测吸光度值,计算出标准曲线方程Y=1.694 9X+0.244 8,其中 R²=0.995 5,线性关系良好。
载药率的测定:将PHBV/CSH/CS支架放入24孔板中,并质量浓度为 1 g/L的1 mL牛血清白蛋白液滴入,1 h后将支架取出,并将孔板内剩余的牛血清白蛋白移至1.5 mL离心管,并用PBS补足至1 mL。随后将吸取50 µL补足后的溶液,加入200 µL的蛋白定量分析 BCA 液孵育30 min,酶标仪562 nm处测吸光度值。将所得吸光度值带入标准曲线计算出液体的载药量,根据公式(2)可得出支架的载药率:
支架载药率(%)= (1–支架溶胀后剩余液体吸光度值)/总蛋白量吸光度值× 100% (2)
释放性能的测试:将PHBV/CSH/CS支架放入24孔板中,将质量浓度为50 g/L的1 mL牛血清白蛋白液滴入,浸润支架1 h后取出,随后放入PBS中,于0.5,1,2,3,4,5,6,12,24,48,72 h不同时间点吸取50 µL的溶液,加入200 µL的BCA液孵育30 min,酶标仪562 nm处测吸光度值。将所得吸光度值带入标准曲线,计算出牛血清白蛋白的累积释放率。
1.4.6 支架细胞相容性评估
细胞培养:将SD大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞(RASMX-01001,赛业生物科技有限公司,中国)常规复苏、离心,将离心管内的骨髓间充质干细胞悬液接种至25 cm²细胞培养瓶,细胞浓度为1×107 L-1,并加入低糖培养基(含体积分数10%胎牛血清、1%青霉素及链霉素),随后放入细胞培养箱(体积分数5%CO2,37 ℃)中培养,隔天更换培养基。
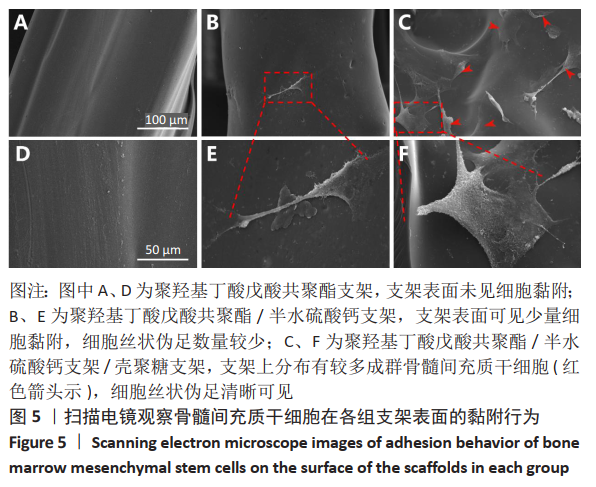
细胞黏附实验:每次使用前将各组支架放入体积分数75%乙醇中灭菌2 h,将消毒后的聚羟基丁酸戊酸共聚酯、聚羟基丁酸戊酸共聚酯/半水硫酸钙、PHBV/CSH/CS支架置入24孔细胞培养板中。将细胞浓度为2×107 L-1的骨髓间充质干细胞悬液接种至上述支架材料,每孔接种500 μL,置于细胞培养箱中(37 ℃,体积分数5%CO2)培养24 h。然后在4 ℃下用2.5%戊二醛固定4 h,并使用不同浓度的乙醇梯度脱水,并在叔丁醇中干燥。将支架在真空下干燥,喷金,通过扫描电镜观察附着在支架表面的骨髓间充质干细胞形态特征。
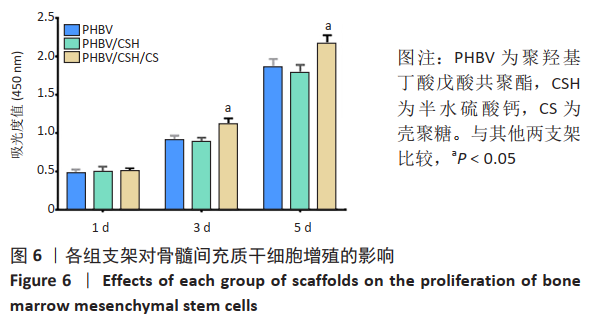
细胞增殖实验:将消毒后的聚羟基丁酸戊酸共聚酯、聚羟基丁酸戊酸共聚酯/半水硫酸钙、PHBV/CSH/CS支架置入24孔细胞培养板中,每组3个平行孔。将细胞浓度为2×107 L-1的骨髓间充质干细胞悬液接种至上述含支架材料的细胞培养板中,每孔600 μL。1,3,5 d后每组取3个孔,加入60 μL(培养基与CCK-8试剂比为10∶1)的CCK-8试剂,细胞培养箱孵育2 h,待孵育时间结束取出细胞培养板,用移液枪吸取每孔200 μL溶液至96孔板。然后设置酶标仪波长为450 nm测其吸光度值,每孔重复测量3次,取平均值作为最终结果。
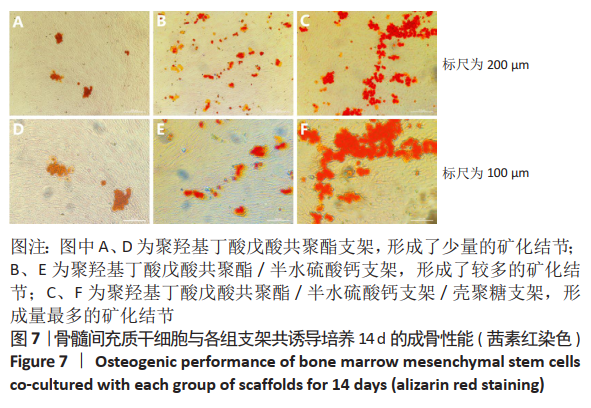
1.4.7 支架材料成骨性能评估 将消毒后的聚羟基丁酸戊酸共聚酯、聚羟基丁酸戊酸共聚酯/半水硫酸钙、PHBV/CSH/CS支架置入24孔细胞培养板中。将细胞浓度为1×107 L-1的骨髓间充质干细胞悬液接种至上述支架材料,每孔500 μL。培养 24 h待细胞贴壁后,更换含有成骨诱导成分的细胞培养液进行成骨诱导培养, 隔天换液。待培养至14 d后终止培养。将24孔内的支架取出,PBS洗2遍后,每孔加入500 μL的40 g/L多聚甲醛固定20 min,弃固定液ddH2O洗3遍,每孔加入200 μL茜素红S染色液染色30 min,弃染料并用ddH2O洗3遍,置于倒置显微镜下观察拍照。
1.4.8 支架材料抗菌性能评估
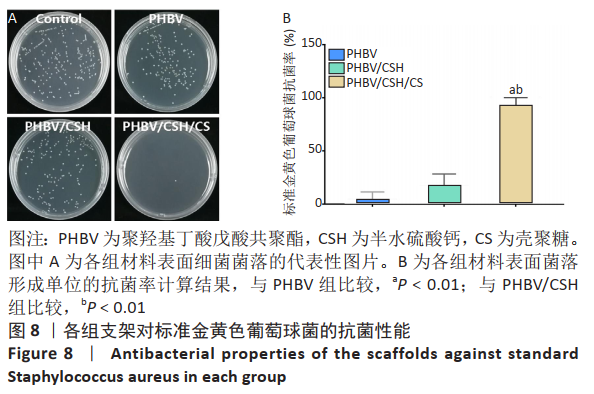
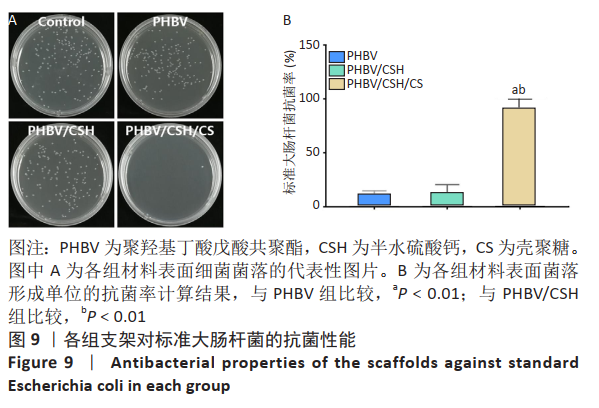
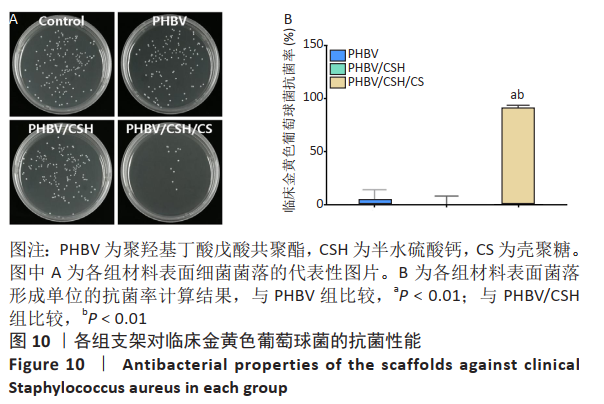
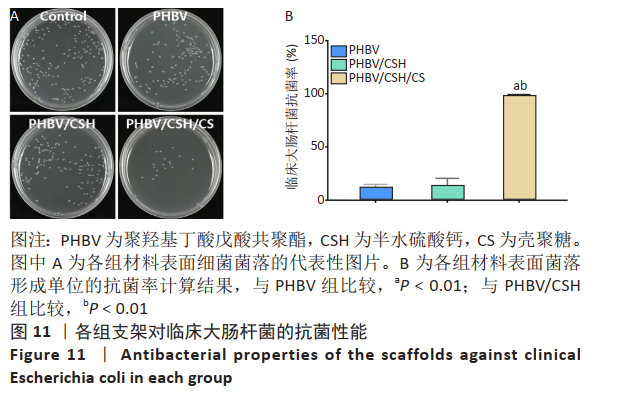
细菌培养:分别取冻存在广州中医药大学第五临床医学院检验科-80 ℃冰箱里的标准金黄色葡萄球菌、标准大肠肝菌、临床金黄色葡萄球菌及临床大肠杆菌放入无菌台,使用接种环在无菌操作下挑取少量菌液,然后按照四区接种法将细菌按4个不同面积的区域接种到血平板上;将划线后的血平板倒置放入37 ℃生化培养箱培养24 h。24 h后,从血平板中分离单克隆纯种细菌;向分离至试管内的细菌加入5 mL LB培养基,并将其放至摇床(150 r/min,37 ℃)培养6 h。随后取50 µL菌液加入至5 mL LB培养基中(按1∶100比例),放至摇床(150 r/min,37 ℃)培养24 h,隔天得到传代后的细菌;将传代后的细菌用麦氏比浊法稀释成浓度为1×108 CFU/mL的实验用菌液。
涂布平板法涂板:将4种菌液的浓度稀释至1×105 CFU/mL,然后将消毒后的3种支架放入24孔板中,并在每个孔板中分别加入1 mL浓度为1×105 CFU/mL的各种菌液,每组设置3个平行样,同时设置3个完全空白孔作为对照组。将各组放入温度为37 ℃的生化培养箱内培养12 h;12 h后,将孔板内的各组培养液梯度稀释500倍用于涂布平板。先用无菌吸管吸取稀释好的0.1 mL菌液对号接种于营养琼脂平板上,并将菌液在平板上涂布均匀,然后置于的恒温箱中培养24 h,根据公式(3)计算各组营养琼脂平板上的菌落数:
抗菌率(%)=(N对照–N支架)/N对照× 100% (3)
公式(3)中,N对照是对照样品中的平均细菌数量(CFU/样本),N支架是抗菌实验样品中的平均细菌数量(CFU/样品)。
1.5 主要观察指标 各组支架的表面形貌、孔径、孔隙率及溶胀率,细胞体外相容性与抗菌性。
1.6 统计学分析 所得实验数据以x±s表示,样本量以n表示,数据使用SPSS 25.0进行数据分析。若方差齐,采用单因素方差分析(one way ANOVA test);若方差不齐,则采用多重比较法(Dunnett´s T3)进行分析。假设检验为双重检验,检验水平为P=0.05,当P > 0.05表示差异无显著性意义,P < 0.05表示差异有显著性意义,P < 0.01表示差异有非常显著性意义。
 文题释义:
文题释义: