[1] FURIN J, COX H, PAI M. Tuberculosis. Lancet. 2019;(10181):1642-1656.
[2] PIGRAU-SERRALLACH C, RODRGUEZ-PARDO D. Bone and joint tuberculosis. Eur Spine J. 2013(Suppl 4):556-566.
[3] ALI A, MUSBAHI O, WHITE VLC, et al. Spinal Tuberculosis: A Literature Review. JBJS Rev. 2019;7(1):e9.
[4] 周朝玺.脊柱结核的诊疗进展[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017, 32(9):1006-1008.
[5] DUNN RN, HUSIEN MB. Spinal tuberculosis: review of current management. Bone Joint J. 2018;100-B(4):425-431.
[6] 秦壁松,唐建东.自体骨移植在颈前路椎间盘切除椎间植骨融合术中的应用现状[J].医学综述,2020:1-59 http://210.42.38.36/rwt/CNKI/https/NNYHGLUDN3WXTLUPMW4A/kcms/detail/11.3553.R.20200710.1501.080.html
[7] UENO M, IMURA T, INOUE G, et al. Posterior corrective fusion using a double-trajectory technique (cortical bone trajectory combined with traditional trajectory) for degenerative lumbar scoliosis with osteoporosis: Technical note(Article). J Neurosurg Spine. 2013;19(5): 600-607.
[8] LI M, DU J, MENG H, et al. One-stage surgical management for thoracic tuberculosis by anterior debridement, decompression and autogenous rib grafts, and instrumentation. Spine J. 2011;11(8):726-733.
[9] ALAM S, PHAN K, KARIM R, et al. Surgery for Spinal Tuberculosis: A Multi-Center Experience of 582 Case. J Spine Surg. 2015;1(1):65-71.
[10] GONG K, WANG Z, LUO Z. Single-stage posterior debridement and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with autogenous bone grafting and posterior instrumentation in the surgical management of lumbar tuberculosis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(2):217-223.
[11] CHA J, HWANG I, KWON S, et al. Autogenous Bone Grafts versue Metal Cage with Allogenic Bone Grafts for Post-Corpectomy Anterior Column Reconstruction in Patients with Infectious Spondylitis. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2020;63(2):218-227.
[12] 王健.人重组骨形态发生蛋白-2在脊柱融合中的作用[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2016,13(5):62-66.
[13] TABATABAEI FS, MOTAMEDIAN SR, GHOLIPOUR F, et al. Craniomaxillofacial Bone Engineering by Scaffolds Loaded with Stem Cells: A Systematic Review. J Dent Educ. 2012;30(2):115-131.
[14] MOTAMEDIAN SR, IRANPARVAR P, NAHVI G, et al. Bone Tissue Engineering: A Literature Review. Triple R. 2016;(3):103-120.
[15] HOSSEINPOUR S, GHAZIZADEH AHSAIE M, REZAI RAD M, et al. Application of selected scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: a systematic review. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;21(2):109-129.
[16] 王鹏波,盛伟斌,王丙超,等.结构性同种异体冻干骨植入治疗腰椎结核[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(34):5439-5444.
[17] ABULIZI Y, LIANG W, MAIMAITI M. Smith-Petersen osteotomy combined with anterior debridement and allografting for active thoracic and lumbar spinal tuberculosis with kyphotic deformity in young children A prospective study and literature review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017; 96(32):e7614.
[18] 王锡阳,罗承科,邓强,等.同种异体骨与自体骨植骨治疗胸腰段结核的研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(9):782-785.
[19] 邓晓楠.同种异体髂骨块与自体髂骨块移植治疗颈椎结核的临床疗效对比[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2020.
[20] 印飞,孙振中,殷渠东,等.短节段椎弓根钉固定联合重组人BMP-2和同种异体骨植骨治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2017,31(9):1080-1085.
[21] JAIN AK, JAIN S. Instrumented stabilization in spinal tuberculosis. Int Orthop. 2012;36(2):285-292.
[22] LU DC, WANG V, CHOU D. The use of allograft or autograft and expandable titanium cages for the treatment of vertebral osteomyelitis. Neurosurgery. 2009;64(1):122-129.
[23] ROBINSON Y, TSCHOEKE SK, KAYSER R, et al. Reconstruction of large defects in vertebral osteomyelitis with expandable titanium cages. Int Orthop. 2009;33(3):745-749.
[24] WANG YX, ZHANG H, LI M, et al. Debridement, interbody graft using titanium mesh cages, posterior instrumentation and fusion in the surgical treatment of multilevel noncontiguous spinal tuberculosis in elderly patients via a posterior-only. Injury. 2017;48(2):378-383.
[25] ZHANG H, GUO Q, WANG Y, et al. The efficiency of the posterior-only approach using shaped titanium mesh cage for the surgical treatment of spine tuberculosis in children: A preliminary study(Article). J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2018;26(3):1-7.
[26] ZHANG HQ, LI M, WANG YX, et al. Minimum 5-Year Follow-Up Outcomes for Comparison Between Titanium Mesh Cage and Allogeneic Bone Graft to Reconstruct Anterior Column Through Posterior Approach for the Surgical treatment of Thoracolumbar Spinal Tuberculosis with Kyphosis. World Neurosurg. 2019;127:E407-E415.
[27] WANG B, HUA W, KE W, et al. The efficacy of allograft bone using titanium mesh in the posterior-only surgical treatment of thoracic and thoracolumbar spinal tuberculosis. BMC Surg. 2020;20(1):133.
[28] HUR JW, RYU KS, AHN S, et al. Comparative Analysis of 2 Different Types of Titanium Mesh Cage for Single-level Anterior Cervical Corpectomy and Fusion in Terms of Postoperative Subsidence and Sagittal Alignment. Clin Spine Surg. 2020;33(1):E8-E13.
[29] JI C, YU S, YAN N, et al. Risk factors for subsidence of titanium mesh cage following single-level anterior cervical corpectomy and fusion. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):32.
[30] 范时洋,曾忠友.椎体间融合术中植骨材料的研究进展[J].脊柱外科杂志,2018,16(1):57-61.
[31] 王强,罗为民,许宇霞,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66椎体支撑体在儿童脊柱结核前柱重建手术中的应用[J].中国现代手术学杂志, 2017,21(4):279-282.
[32] 吴鹏,刘晓印,范凤龙,等.载异烟肼、利福平纳米羟基磷灰石-半水硫酸钙人工骨局部治疗兔脊柱结核的研究[J].宁夏医科大学学报, 2020,42(3):223-229.
[33] 曹烨,宋言峥,刘保池,等.Bi-OsteticTM人工骨粒在脊柱结核病灶清除手术中的临床应用[G].第二届骨关节结核临床诊断与治疗进展及其规范化专题研讨会资料汇编,大连,2014:133-134.
[34] 杨明明,汪焰恩,魏生民,等.三维打印羟基磷灰石/磷酸三钙骨支架工艺中粉体材料组分比及黏结剂对骨支架性能的影响[J].生物加工过程,2018,16(5):85-91.
[35] 张海鸽,索海瑞,王玲,等.基于3D打印的双相磷酸钙胶原改性支架[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(30):4780-4786.
[36] 杨明明,汪焰恩,魏生民,等.三维打印羟基磷灰石/磷酸三钙骨支架工艺中粉体材料组分比及黏结剂对骨支架性能的影响[J].生物加工过程,2018,16(5):85-91.
[37] 刘俭涛,张峰,高正超,等.人工椎体的发展与应用[J].中国骨伤, 2017,30(12):1157-1164.
[38] 毛克亚,刘建恒,崔翔.骨组织工程材料在大段骨缺损修复中的应用进展[J].武警医学,2020(4):277-280.
[39] IGNATIUS AA, BETZ O, AUGAT P, et al. In vivo investigations on composites made of resorbable ceramics and poly(lactide) used as bone graft substitutes. J Biomed Mater Res. 2001;58(6):701-709.
[40] 韩莹松.PLGA的生物相容性与动物椎间融合实验研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2009.
[41] 何进文 , 岳学锋 , 施建党 , 等 . 载 HRZ 乙酰乙酸涂层的自体髂骨修复兔脊柱结核骨缺损的病理学观察 [J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志 ,2018, 28(6):552-561.
[42] KALIARAJ R, GANDHI S, SUNDARAMURTHI D, et al. A biomimetic mesoporous silica-polymer composite scaffold for bone tissue engineering. J Porous Mat. 2018;(2):397-406.
[43] TAO Z, WU X, ZHOU W, et al. Local administration of aspirin with β-tricalcium phosphate/poly-lactic-co-glycolic acid (β-TCP/PLGA) could enhance osteoporotic bone regeneration J Bone Miner Metab. 2019;37(6):1026-1035.
[44] KAČAREVIĆ ŽP, RIDER P, ALKILDANI S, et al. An introduction to bone tissue engineering. Int J Artif Organs. 2020;43(2):69-86.
[45] SHAW KA, GRIFFITH MS, SHAW VM, et al. Harvesting Autogenous Cancellous Bone Graft from the Anterior Iliac Crest JBJS Essent Surg Tech. 2018;8(3):e20.
[46] JUNIOR EA, de LIMA VN, MOMESSO GAC, et al. Potential of autogenous or fresh-frozen allogeneic bone block grafts for bone remodelling: a histological, histometrical, and immunohistochemical analysis in rabbits. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;55(6):589-593.
[47] 王庆男,董大明.钛网笼在颈前路手术后沉降的原因及改进策略[J].医学综述,2020,26(17):3456-3460.
[48] WANG C, YU B, FAN Y, et al. Incorporation of multi-walled carbon nanotubes to PMMA bone cement improves cytocompatibility and osseointegration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;103:109823.
[49] NAVARRO M, MICHIARDI A, CASTAÑO O, et al. Biomaterials in orthopaedics(Review). J R Soc Interface. 2008;5(27):1137-1158.
[50] GUILLAUME MA, GARRAFFO RB, BENSALEM MA, et al. Pharmacokinetic and dynamic study of levofloxacin and rifampicin in bone and joint infections(Article). Med Mal Infect. 2012;42(9):414-420.
[51] VAN INGEN J, AARNOUTSE RE, DONALD PR, et al. Why do we use 600 mg of rifampicin in tuberculosis treatment? Clin Infect Dis. 2011; 52(9):e194-e199.
[52] 段海波.三维打印多孔生物陶瓷支架组装药物控释微球及细胞相容性研究[D].广州:华南理工大学,2016.
|
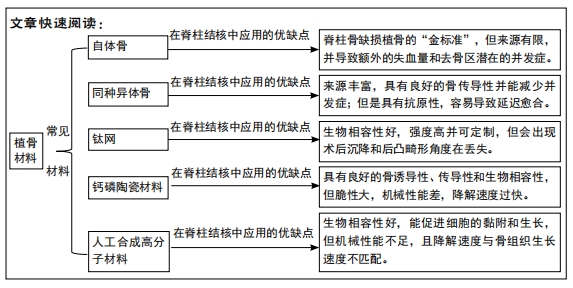

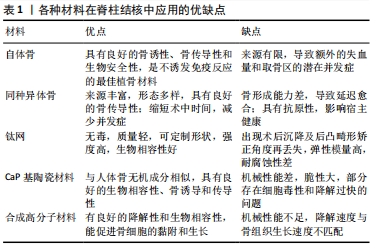 自体骨骨量有限,自体骨移植会引起供区出血和供骨区潜在的并发症[45];同种异体骨会导致延迟愈合和感染等并发症[46];钛网存在术后沉降及后凸畸形矫正角度再丢失的问题[47];以聚乳酸、聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯等为代表的有机高分子材料包埋药物体系又缺乏骨诱导性能[48];钙磷基陶瓷材料虽可作为抗结核药物的载体材料,但其生物力学性能常不能完全满足临床需要[49]。脊柱结核目前的治疗包括药物治疗和外科手术。药物治疗主要是采用口服、肌注或静脉途径应用抗结核药物,通过血液循环使药物到达病灶,从而达到杀灭结核菌的目的,但治疗脊柱结核需要长期全身给予抗结核药物,其会使药物在各脏器聚积,从而导致严重的肝肾损害、周围神经病变及胃肠道反应等一系列毒副作用[50];此外,这种全身给药的治疗方式难以保证在不引起药物对其他脏器毒副作用的同时,使得病灶区的药物分布达到有效作用浓度[51]。药物传输传输系统的出现为解决上述问题提供了一个新方法。药物传输系统主要依靠物理吸附或化学结合方法将药物装载到生物相容性良好的载体上,使药物在预定病患部位,按照某一释药速度对特定组织或器官进行作用,并保持药物在较长时间内持续有效释放,以达到有效治疗的目的[52]。因此,目前制备具有长效缓释药物的植骨材料在脊柱结核的外科手术治疗中至关重要,也是目前研究的热点,但是药物通过何种方式搭载在植骨材料上能确保不破坏药物的生物活性的同时提高载药量和包封率,这些都需要进一步研究;此外,如何调控植入体的降解速度,使其内搭载药物达到长时间缓释的抗结核作用也是一个需要解决的问题。
自体骨骨量有限,自体骨移植会引起供区出血和供骨区潜在的并发症[45];同种异体骨会导致延迟愈合和感染等并发症[46];钛网存在术后沉降及后凸畸形矫正角度再丢失的问题[47];以聚乳酸、聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯等为代表的有机高分子材料包埋药物体系又缺乏骨诱导性能[48];钙磷基陶瓷材料虽可作为抗结核药物的载体材料,但其生物力学性能常不能完全满足临床需要[49]。脊柱结核目前的治疗包括药物治疗和外科手术。药物治疗主要是采用口服、肌注或静脉途径应用抗结核药物,通过血液循环使药物到达病灶,从而达到杀灭结核菌的目的,但治疗脊柱结核需要长期全身给予抗结核药物,其会使药物在各脏器聚积,从而导致严重的肝肾损害、周围神经病变及胃肠道反应等一系列毒副作用[50];此外,这种全身给药的治疗方式难以保证在不引起药物对其他脏器毒副作用的同时,使得病灶区的药物分布达到有效作用浓度[51]。药物传输传输系统的出现为解决上述问题提供了一个新方法。药物传输系统主要依靠物理吸附或化学结合方法将药物装载到生物相容性良好的载体上,使药物在预定病患部位,按照某一释药速度对特定组织或器官进行作用,并保持药物在较长时间内持续有效释放,以达到有效治疗的目的[52]。因此,目前制备具有长效缓释药物的植骨材料在脊柱结核的外科手术治疗中至关重要,也是目前研究的热点,但是药物通过何种方式搭载在植骨材料上能确保不破坏药物的生物活性的同时提高载药量和包封率,这些都需要进一步研究;此外,如何调控植入体的降解速度,使其内搭载药物达到长时间缓释的抗结核作用也是一个需要解决的问题。