中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (3): 371-375.doi: 10.12307/2022.061
• 数字化骨科 digital orthopedics • 上一篇 下一篇
3D打印可控式张力带的张力与皮肤缺损模型鼠皮肤再生
买合木提•亚库甫,孙琴琴,陈洪涛,刘 旭,伊力亚尔•阿不都斯木,阿布都萨拉木•阿布都克力木,刘建疆
- 新疆医科大学第六附属医院运动医学科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830002
Tension of 3D printed controllable tension band and skin regeneration of skin defect model rats
Maihemuti•Yakufu, Sun Qinqin, Chen Hongtao, Liu Xu, Yiliyaer•Abudusimu, Abudushalamu•Abudukelimu, Liu Jianjiang
- Department of Sports Medicine, Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
皮肤缺损:为创伤、烧伤、肿瘤等原因导致皮肤组织的缺失,目前临床上常用的治疗方法包括皮肤移植、皮瓣移植等。
绑鞋带技术:是皮肤缺损创面的一种治疗方法,类似于鞋带一样,缝线或硅胶线从创面两侧来回相互交叉穿过,能够将缝线的张力均匀分散到皮肤缺损创面边缘,有效刺激皮肤边缘增殖,从而治疗皮肤缺损。
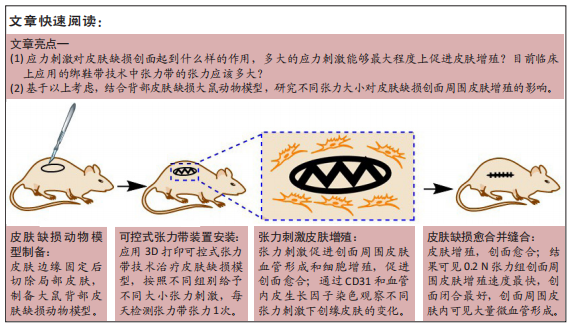
背景:虽然张力带技术能够刺激皮肤再生修复皮肤缺损,被成功应用于临床取得了满意的效果,但最适宜皮肤再生的张力大小尚无定论。
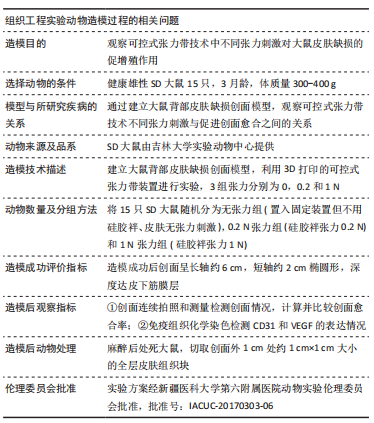
目的:探讨不同张力刺激对皮肤缺损模型大鼠皮肤再生的影响。
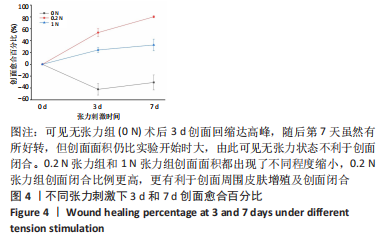
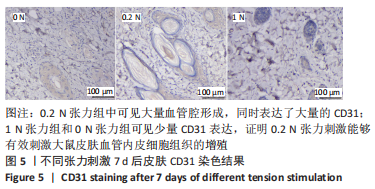
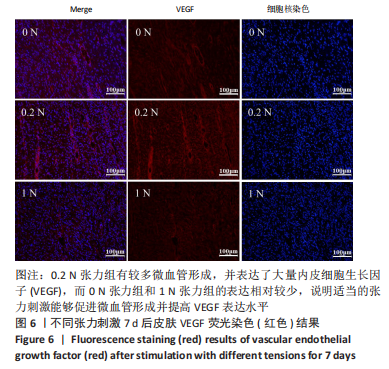
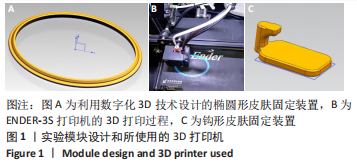
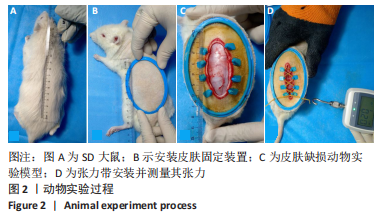
方法:选用雄性3月龄SD大鼠作为实验动物,通过3D打印的椭圆形皮肤固定装置固定SD大鼠背部皮肤,建立大鼠背部皮肤缺损创面模型,3D打印张力带装置固定在皮肤边缘,绑鞋带原理安装硅胶袢,并通过拉力检测器调整硅胶袢的不同张力参数(0,0.2,1 N)。造模术后当天、3 d和7 d观察测量皮肤缺损面积的变化;造模术后7 d取创面边缘皮肤组织学切片进行CD31和血管内皮生长因子免疫组织化学染色,观察不同张力刺激对皮肤再生的影响。
结果与结论:①适当大小的张力刺激能够有效刺激皮肤增殖愈合;无张力刺激的皮肤缺损创面会随着皮肤边缘的挛缩,创面进一步扩大,增加皮肤缺损面积,不利于皮肤缺损的治疗;②张力刺激不是越大越好,在同样时间点0.2 N张力组创面缩小速度比1 N张力组快,1 N张力组可见创面边缘皮肤硬化、弹性降低,考虑可能因为较大张力导致皮肤缺血所导致;③0.2 N张力组微血管数量明显增多,血管内皮生长因子表达量明显高于0 N张力组和1 N张力组,说明张力刺激能够促进微血管形成,能够提高血管内皮生长因子表达量,但是高张力刺激(此次研究中1 N)不利于皮肤缺损周围皮肤微血管形成,不利于创面愈合;④提示适当的张力刺激能够引起局部皮肤中广泛细胞外基质的重建;可通过诱导血管再生、改善局部细胞代谢所需营养物质的供应,促进细胞骨架重组,此过程对张力的大小有严格要求。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9853-1923 (买合木提•亚库甫)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: