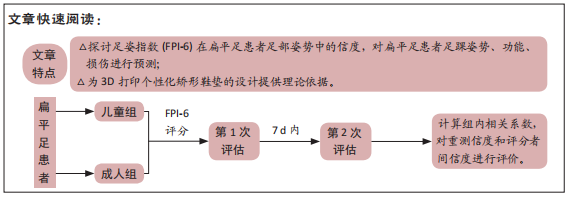
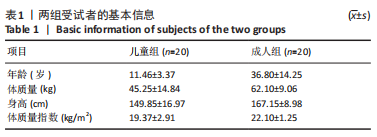
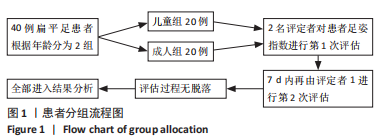
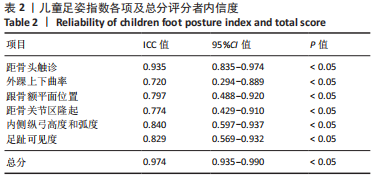
[1] CHEN KC, CHEN YC, YEH CJ, et al. The effect of insoles on symptomatic flatfoot in preschool-aged children: A prospective 1-year follow-up study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(36):e17074.
[2] RASENBERG N, RIEL H, RATHLEFF MS, et al. Efficacy of foot orthoses for the treatment of plantar heel pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Br J Sports Med. 2018;52(16):1040-1046.
[3] LIGON SC, LISKA R, STAMPFL J, et al. Polymers for 3D Printing and Customized Additive Manufacturing. Chem Rev. 2017;117(15): 10212-10290.
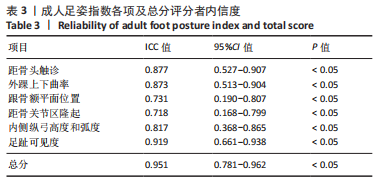
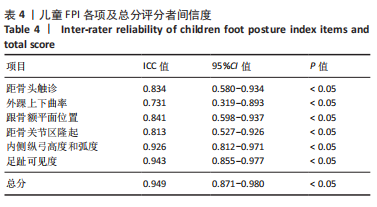
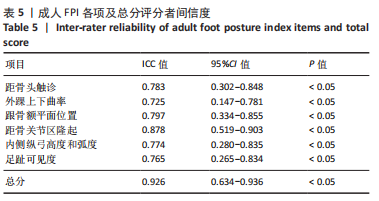
[4] REDMOND AC, CROSBIE AC, OUVRIER RA. Development and validation of a novel rating system for scoring standing foot posture: The Foot Posture Index. Clin Biomech. 2006;21:89-98.
[5] DARS S, UDEN H, BANWELL HA, et al. The effectiveness of non-surgicalintervention (Foot Orthoses) for paediatric flexible pes planus: A systematic review: Update. PLoS One. 2018;13(2):e0193060.
[6] TERADA M, WITTWER AM, GRIBBLE PA. Intra-rater and inter-rater reliability of the five image-based criteria of the foot posture index-6.Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2014;9(2):187-194.
[7] EVANS AM, ROME K, PEET L. The foot posture index, ankle lunge test, Beighton scale and the lower limb assessment score in healthy children: a reliability study. J Foot Ankle Res. 2012;5(1):1.
[8] CORNWALL MW, MCPOIL TG, LEBEC M, et al. Reliability of the modified Foot Posture Index. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2008;98(1):7-13.
[9] AQUINO MRC, AVELAR BS, SILVA PL, et al. Reliability of Foot Posture Index individual and total scores for adults and older adults. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2018;36:92-95.
[10] 陈泽华,叶翔凌,陈伟健,等.足姿指数评价足部位置的信效度研究[J].中国康复理论与实践,2020,26(10):1193-1197.
[11] 张新语,霍洪峰.足姿指数(FPI):足部姿势及足踝功能的定量表达[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(13):1194-1199.
[12] CHEN G, WU J, CHEN G, et al. Reliability of a portable device for quantifying tone and stiffness of quadriceps femoris and patellar tendon at different knee flexion angles. PLoS One. 2019;14(7):e0220521.
[13] 宋雅伟,陈爱军,喻菊,等.基于压电效应原理的一种扁平足测量仪的研究开发[J].实验室研究与探索,2008,27(6):54-57.
[14] KOTHARI A, DIXON PC, STEBBINS J, et al. Are flexible flat feet associated with proximal joint problems in children? Gait & Posture. 2016;45:204-210.
[15] KOTHARI A, DIXON PC, STEBBINS J, et al. The relationship between quality of life and foot function in children with flexible flatfeet. Gait Posture. 2015;41:786-790.
[16] LIN CJ, LAI KA, KUAN TS, et al. Correlating factors and clinical significance of flexible flatfoot in preschool children. J Pediatr Orthop 2001;21:378-382.
[17] SHIBUYA N, JUPITER D, CILIBERTI L, et al. Characteristics of adult flatfoot in the United States. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2010;49(4):363-368 .
[18] ABOELNASR EA, HEGAZY FA, ZAGHLOUL AA,et al. Validation of normalized truncated navicular height as a clinical assessment measure of static foot posture to determine flatfoot in children and adolescents: A cross sectional study.Foot (Edinb). 2018;37:85-90.
[19] ZUIL-ESCOBAR JC, MARTÍNEZ-CEPA CB, MARTÍN-URRIALDE JA,et al. Evaluating the Medial Longitudinal Arch of the Foot: Correlations, Reliability, and Accuracy in People With a Low Arch. Phys Ther. 2019; 99(3):364-372.
[20] GIJON-NOGUERON G, MARCHENA-RODRIGUEZ A, MONTES-ALGUACIL J, et al. Evaluation of the paediatric foot using footprints and foot posture index: A cross‐sectional study. J Paediatr Child Health. 2020; 56(2):201‐206.
[21] HEGAZY FA, ABOELNASR EA, SALEM Y, et al. Validity and diagnostic accuracy of foot posture Index-6 using radiographic findings as the gold standard to determine paediatric flexible flatfoot between ages of 6-18 years: A cross-sectional study. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2020;46:102107.
[22] TOYOOKA S, SHIMAZAKI N, YASUI Y, et al. Validity of a simple footprint assessment board for diagnosing the severity of flatfoot: a prospective cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):285.
[23] MARTINEZ BR, OLIVEIRA JC, VIEIRA KVSG, et al. Translation, cross-cultural adaptation, and reliability of the Foot Posture Index (FPI-6) - Brazilian version. Physiother Theory Pract. 2021;37(1):218-223.
[24] KIRMIZI M, CAKIROGLU MA, ELVAN A, et al. Reliability ofDifferent Clinical Techniques for Assessing Foot Posture. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2020;43(9):901-908.
[25] 陈泽华,叶翔凌,陈伟健,等.基于足姿指数评分评价旋前足姿对本体感觉和姿势稳定性的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(9): 1324-1328.
[26] CRANAGE S, BANWELL H, WILLIAMS CM. Gait and Lower Limb Observation of Paediatrics (GALLOP): development of a consensus based paediatric podiatry and physiotherapy standardised recording proforma. J Foot Ankle Res. 2016;9:8.
[27] ŽUKAUSKAS S, BARAUSKAS V, ČEKANAUSKAS E. Comparison of multiple flatfoot indicators in 5-8-year-old children. Open Med (Wars). 2021;16(1):246-256.
[28] MOTANTASUT P, HUNSAWONG T, MATO L, et al. Reliability of novice and experienced physiotherapists using the normalized navicular height truncated and the foot posture index-6 for classifying static foot posture in adults. J Phys Ther Sci. 2019;31(4):392-397.
[29] Ventola CL. Medical Applications for 3D Printing: Current and Projected Uses. P T. 2014;39(10):704-711.
[30] AL-RIMAWI A, EZELDEEN M, SCHNEIDER D, et al. 3D Printed Temporary Veneer Restoring Autotransplanted Teeth in Children: Design and Concept Validation Ex Vivo. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(3): 496.
[31] SPENCER SR, KAY WATTS L. Three-Dimensional Printing in Medical and Allied Health Practice: A Literature Review.J Med Imaging Radiat Sci. 2020;51(3):489-500.
[32] LIU Z, ZHANG P, YAN M, et al. Additive manufacturing of specific ankle-foot orthoses for persons after stroke: A preliminary study based on gait analysis data. Math Biosci Eng.2019;16(6):8134-8143.
[33] MANNISI M, DELL’ISOLA A, ANDERSEN MS, et al. Effect of lateral wedged insoles on the knee internal contact forces in medial knee osteoarthritis. Gait Posture. 2019;68:443-448.
[34] TARRADE T, DOUCET F, SAINT-LÔ N, et al. Are custom-made foot orthoses of any interest on the treatment of foot pain for prolonged standing workers?.Appl Ergon. 2019;80:130-135.
[35] CHOO YJ, BOUDIER-REVÉRET M, CHANG MC. 3D printing technology applied to orthosis manufacturing: narrative review. Ann Palliat Med. 2020;9(6):4262-4270.
[36] 黄楚红,黄文华,黄国志.3D打印技术在康复医学中的应用与研究进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2020,35(1):95-99.
[37] XU R, WANG Z, REN Z, et al. Comparative Study of the Effects of Customized 3D printed insole and Prefabricated Insole on Plantar Pressure and Comfort in Patients with Symptomatic Flatfoot. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:3510-3519.
[38] LEE KKW, LING SKK, YUNG PSH. Controlled trial to compare the Achilles tendon load during running in flatfeet participants using a customized arch support orthoses vs an orthotic heel lift. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):535.
[39] SU S, MO Z, GUO J, et al. The Effect of Arch Height and Material Hardness of Personalized Insole on Correction and Tissues of Flatfoot. J Healthc Eng. 2017;2017:8614341.
[40] EVANS AM, KARIMI L. The relationship between paediatric foot posture and body mass index: do heavier children really have flatter feet? J Foot Ankle Res. 2015;8:46.
[41] Gijon-Nogueron G, Martinez-Nova A, Alfageme-Garcia P, et al.International normative data for paediatric foot posture assessment: a cross-sectional investigation. BMJ Open. 2019;9(4):e023341.
[42] KHAN FR, CHEVIDIKUNNAN MF, MAZI AF, et al. Factors affecting foot posture in young adults: a cross sectional study. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2020;20(2):216-222.
[43] 李辉,宗心南,季成叶,等.中国2~18岁儿童青少年超重和肥胖筛查体重指数界值点的研究[J].中华流行病学杂志,2010,31(6): 616-620.
|